Life insurance and mutual funds are two distinct financial products that serve different purposes. Life insurance is a contract between an individual and an insurance company, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a lump sum amount upon the insured's death. This coverage provides financial security to the policyholder's family or beneficiaries, ensuring they receive financial support during challenging times. On the other hand, mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. Investors buy shares in the mutual fund, and the fund manager invests the pooled money, aiming to grow the value of the investment over time. The key difference lies in their primary functions: life insurance offers financial protection and security, while mutual funds focus on wealth accumulation and investment growth.
What You'll Learn
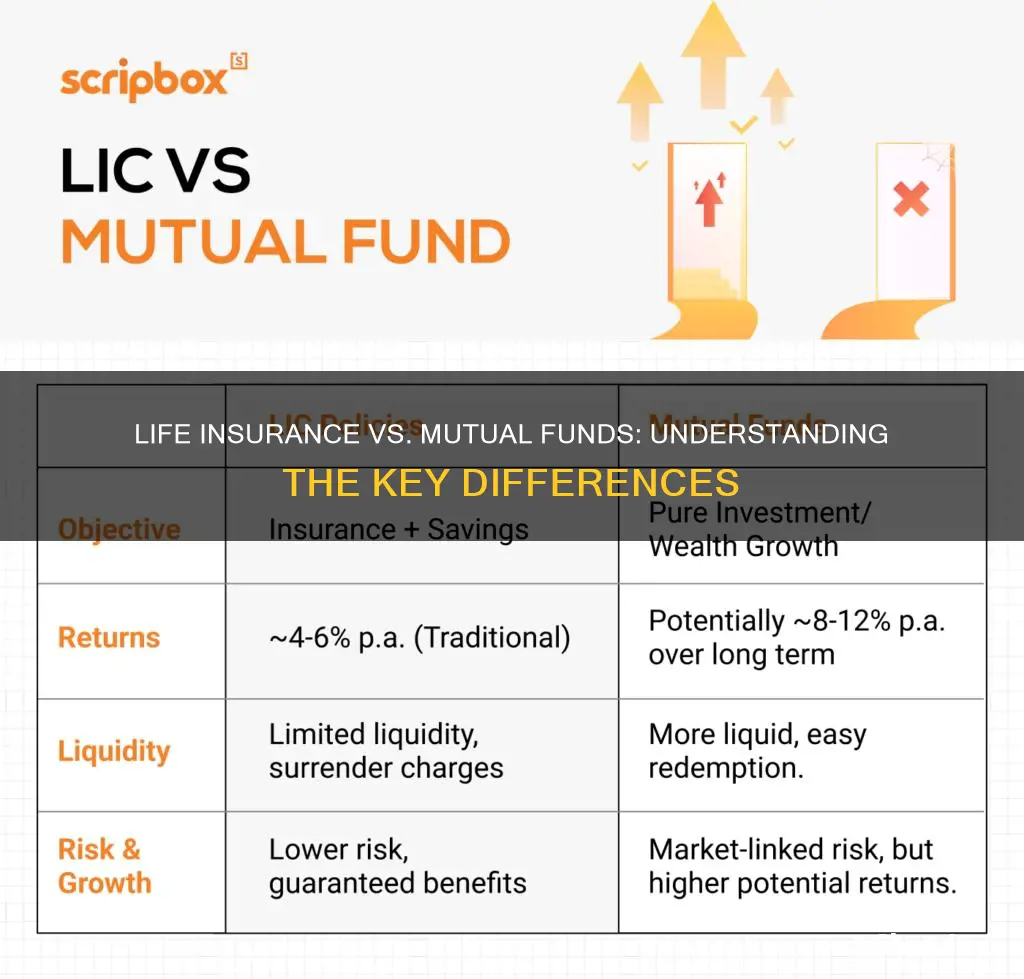
- Insurance vs. Investment: Life insurance provides financial security, while mutual funds offer long-term wealth growth
- Risk and Return: Life insurance offers guaranteed returns, whereas mutual funds carry market risk with variable returns
- Liquidity: Mutual funds are more liquid, allowing easy conversion to cash, unlike life insurance's long surrender periods
- Tax Benefits: Both offer tax advantages, but life insurance's tax-free withdrawals differ from mutual fund capital gains
- Long-Term Goals: Life insurance supports financial security, while mutual funds are ideal for retirement and investment goals

Insurance vs. Investment: Life insurance provides financial security, while mutual funds offer long-term wealth growth
Life insurance and mutual funds are two distinct financial instruments that serve different purposes in the realm of personal finance. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for individuals seeking to secure their financial future and make informed decisions about their investments.
Life insurance is a safety net designed to provide financial security to individuals and their families in the event of unforeseen circumstances. It offers a payout or benefit upon the insured individual's death, ensuring that loved ones are financially protected. This type of insurance is particularly valuable for those with dependents, as it provides a steady income to cover essential expenses, such as mortgage payments, education costs, or daily living expenses. The primary purpose of life insurance is to offer peace of mind and financial stability during challenging times. It is a long-term commitment, often taken out for a specific period, and can be tailored to individual needs through various policy types, including term life, whole life, and universal life insurance.
On the other hand, mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. Mutual funds offer a way to invest in a wide range of assets without the need for individual stock picking. They provide an opportunity for long-term wealth growth, as the value of the fund's assets can appreciate over time. Investors can choose from various mutual fund types, including equity funds, bond funds, and balanced funds, each with different risk and return profiles. Mutual funds are typically considered a long-term investment strategy, allowing investors to benefit from the power of compounding and the potential for significant returns over extended periods.
The key difference lies in their objectives and outcomes. Life insurance is primarily about financial security and protection, ensuring that your loved ones are taken care of in your absence. It provides a guaranteed payout, which can be a critical source of income for those who rely on it. Mutual funds, on the other hand, focus on wealth accumulation and growth. They offer the potential for higher returns over the long term but also come with a higher level of risk. Mutual funds are suitable for investors who are willing to accept short-term market fluctuations in exchange for the possibility of substantial gains over time.
In summary, life insurance and mutual funds serve different financial needs. Life insurance provides a safety net and financial security, ensuring that your family is protected during challenging times. Mutual funds, however, are investment vehicles that offer the potential for long-term wealth growth, allowing investors to benefit from market trends and diversify their portfolios. Understanding these distinctions is essential for individuals to make informed choices when planning their financial future.
Universal Life Insurance: Variable Payments and Changing Premiums
You may want to see also

Risk and Return: Life insurance offers guaranteed returns, whereas mutual funds carry market risk with variable returns
Life insurance and mutual funds are two distinct financial instruments that serve different purposes and offer varying levels of risk and return. Understanding the differences between these two can help individuals make informed decisions about their financial planning and investments.
Life insurance is a contract between an individual and an insurance company. It provides financial protection to the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of the insured's death. The primary purpose of life insurance is to offer financial security to the family or dependents of the insured. One of the key features of life insurance is that it offers guaranteed returns. The insurance company promises to pay out a predetermined amount, known as the death benefit, to the designated beneficiaries upon the insured's passing. This guaranteed return is a significant advantage, especially for those seeking long-term financial security for their loved ones. For example, if an individual purchases a term life insurance policy for $500,000, the insurance company will pay out this amount to the beneficiaries if the insured dies during the policy term.
On the other hand, mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets. These assets can include stocks, bonds, or other securities. Mutual funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. One of the critical aspects of mutual funds is that they carry market risk with variable returns. The performance of a mutual fund depends on the overall market conditions and the specific investments made by the fund manager. If the market performs well, the mutual fund may generate substantial returns, but during market downturns, the returns can be negative. For instance, an investor might purchase shares of a mutual fund that primarily invests in technology stocks. If the technology sector experiences a decline, the mutual fund's value may drop, resulting in a loss for the investors.
The risk and return profile of life insurance and mutual funds differ significantly. Life insurance provides a guaranteed return in the form of the death benefit, ensuring financial security for the insured's dependents. In contrast, mutual funds offer the potential for higher returns but come with the risk of market fluctuations and variable performance. Investors should carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon when deciding between these two options. For long-term financial security, life insurance might be more suitable, while mutual funds can be a viable choice for those seeking potential capital appreciation and willing to accept market risks.
In summary, life insurance and mutual funds represent different approaches to financial planning and investment. Life insurance offers guaranteed returns, making it a reliable source of financial protection, while mutual funds carry market risk with variable returns, providing an opportunity for higher gains. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals to make informed choices that align with their specific financial needs and objectives.
Life Insurance Cancellation: Can You Get a Refund?
You may want to see also

Liquidity: Mutual funds are more liquid, allowing easy conversion to cash, unlike life insurance's long surrender periods
Mutual funds offer a level of liquidity that is often lacking in life insurance policies. When you invest in a mutual fund, you can typically buy or sell shares at the end of each trading day, meaning you can access your investment relatively quickly. This is particularly useful if you need to access your funds for unexpected expenses or if you want to take advantage of market opportunities. In contrast, life insurance policies, especially those with cash value, have long surrender periods. If you decide to surrender your policy early, you may face significant penalties and lose a portion of your premiums, making it a less liquid option compared to mutual funds.
The liquidity of mutual funds is a significant advantage for investors who require flexibility and the ability to access their money when needed. With life insurance, the process of surrendering a policy can be lengthy and may involve complex paperwork, making it a less convenient option for those seeking immediate access to their funds. This is especially important for individuals who have financial obligations or unexpected expenses that require prompt cash flow.
In the context of liquidity, mutual funds provide investors with a more dynamic and responsive investment vehicle. They can be easily converted into cash, providing a safety net for investors who may need to access their funds in a short period. Life insurance, on the other hand, is designed to provide long-term financial security and may not be suitable for those seeking immediate liquidity.
Understanding the liquidity aspect is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about their financial portfolios. Mutual funds offer a more accessible and flexible approach to investing, allowing individuals to manage their money according to their needs and preferences. This is in contrast to life insurance, which is more about long-term financial planning and may not provide the same level of liquidity as mutual funds.
Final Expense Life Insurance: Avoiding the Scam Trap
You may want to see also

Tax Benefits: Both offer tax advantages, but life insurance's tax-free withdrawals differ from mutual fund capital gains
When it comes to financial planning, understanding the tax benefits of different investment options is crucial. Both life insurance and mutual funds offer tax advantages, but there are distinct differences in how these benefits are structured.
Life insurance, particularly whole life insurance, provides tax-free withdrawals. This means that policyholders can take out funds from their life insurance policy without incurring any tax liabilities. The key advantage here is that the withdrawals are considered a loan against the policy's cash value, and as long as the policy is in force, these withdrawals are tax-free. This feature is especially beneficial for individuals who need immediate access to funds for various purposes, such as education expenses or unexpected medical bills.
On the other hand, mutual funds offer tax advantages through capital gains. When an investor sells mutual fund units, any capital gains realized are typically taxable. However, mutual funds often provide tax-efficient strategies to minimize these gains. For instance, investors can reinvest their distributions or take advantage of tax-efficient exchange plans, which allow them to swap units of one fund for another, potentially deferring taxes. This approach is particularly useful for long-term investors who aim to build a diversified portfolio over time.
The difference lies in the nature of the investments and the tax treatment of withdrawals or gains. Life insurance provides tax-free access to funds, making it an attractive option for those seeking immediate liquidity. In contrast, mutual funds offer tax advantages through capital gains, which can be optimized through strategic investing and reinvestment. Understanding these distinctions is essential for individuals to make informed decisions regarding their financial planning and tax efficiency.
Income Level: A Key Factor in Life Insurance Planning
You may want to see also

Long-Term Goals: Life insurance supports financial security, while mutual funds are ideal for retirement and investment goals
When considering long-term financial planning, it's essential to understand the distinct roles that life insurance and mutual funds play. Life insurance is a crucial tool for ensuring financial security for your loved ones in the event of your passing. It provides a financial safety net, offering a death benefit to your beneficiaries, which can help cover expenses such as mortgage payments, children's education, or daily living costs. This type of insurance is particularly valuable for those with dependents or financial obligations, as it provides peace of mind and financial stability during challenging times.
On the other hand, mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. They are well-suited for long-term goals, especially retirement planning. Mutual funds offer a way to grow your wealth over time through capital appreciation and regular income generation. By investing in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities, mutual funds provide an opportunity to benefit from the potential growth of the market while also managing risk through diversification.
For retirement, mutual funds can be a powerful tool to build a nest egg. They allow investors to take advantage of compound interest, where earnings are reinvested to generate even more returns over the long term. This strategy enables individuals to accumulate wealth steadily, ensuring a more secure and comfortable retirement. Additionally, mutual funds can provide regular income through dividends or interest payments, which can be particularly useful for retirees who rely on a steady stream of income.
Life insurance, while not an investment vehicle, is essential for financial security and peace of mind. It ensures that your loved ones are protected financially, even in your absence. This is especially important for those with long-term financial commitments or a family that relies on a steady income. The death benefit from life insurance can provide immediate financial support, allowing beneficiaries to cover essential expenses and maintain their standard of living.
In summary, for long-term goals, life insurance and mutual funds serve distinct purposes. Life insurance provides financial security and peace of mind, ensuring that your loved ones are protected in the event of your passing. Mutual funds, on the other hand, are ideal for retirement and investment goals, offering the potential for wealth growth and income generation over time. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed financial decisions and building a comprehensive long-term financial strategy.
Life Insurance: A Wealth-Building Tool for the Rich
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Life insurance is a financial product that provides a financial benefit to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon the insured individual's death. It offers a payout to cover expenses like funeral costs, outstanding debts, or provide financial security to loved ones. Mutual funds, on the other hand, are investment vehicles that pool money from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. The primary goal of mutual funds is to generate returns for investors through capital appreciation and/or income distribution.
Life insurance plays a crucial role in financial planning by providing a safety net for your loved ones. It ensures that your family is financially protected in the event of your untimely demise, helping them maintain their standard of living and covering essential expenses. Mutual funds, on the other hand, are a tool for long-term wealth creation. By investing in a mutual fund, individuals can benefit from the power of compounding, where their money grows over time through the collective efforts of professional fund managers. This can be particularly useful for retirement planning, education savings, or building a financial cushion.
Mutual funds offer investors an opportunity to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities without having to choose individual stocks or bonds. Fund managers make investment decisions on behalf of the investors, aiming to maximize returns while managing risk. Mutual funds can be categorized into different types, such as equity funds, debt funds, or hybrid funds, each with its own investment strategy. Investors can choose funds based on their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
Life insurance policies often provide tax advantages. For instance, in many countries, the cash value of a whole life insurance policy grows tax-deferred, allowing it to accumulate over time. Additionally, the death benefit paid out upon the insured's death is typically tax-free. Mutual funds, on the other hand, may offer tax benefits depending on the type of fund and the investor's tax jurisdiction. Capital gains realized by mutual funds are often taxed at a lower rate, and some funds may be eligible for tax-efficient distribution of dividends.
Life insurance is generally considered a low-risk investment. The primary risk is the possibility of the insured individual outliving the policy, which could result in lower returns for the policyholder. However, the guaranteed death benefit provides financial security. Mutual funds, on the other hand, offer a range of risk and return profiles. Equity-based funds may provide higher potential returns but also carry higher risks, while debt funds are generally more conservative. Investors can choose funds that align with their risk tolerance and financial goals.







