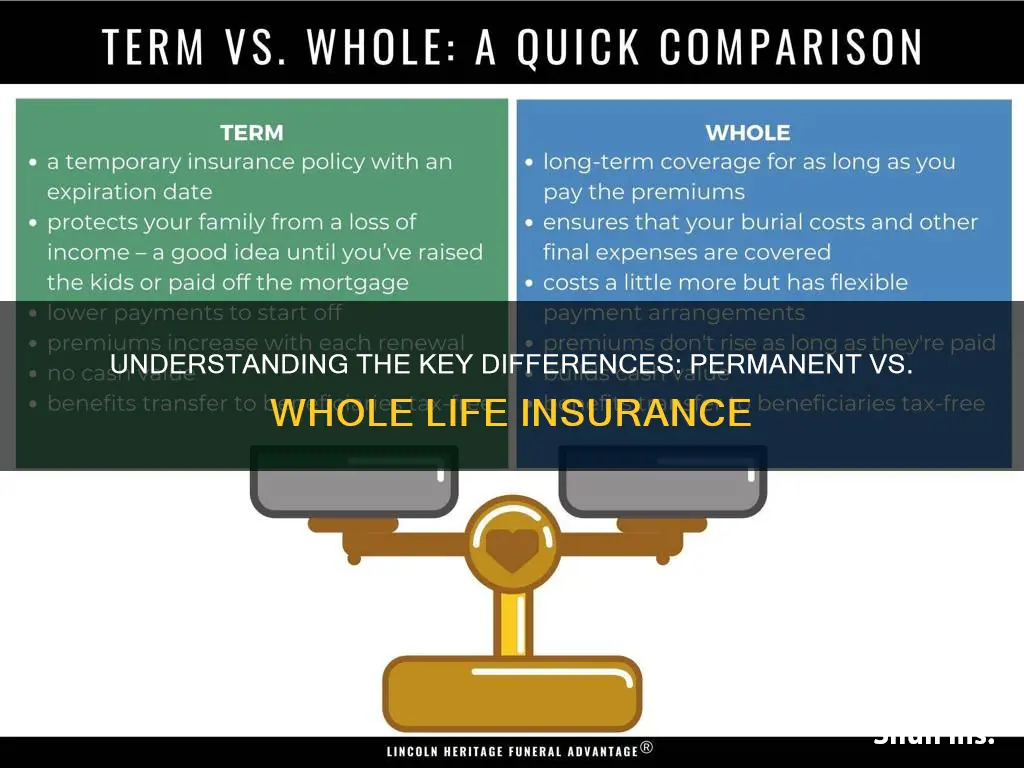
When it comes to insurance, understanding the nuances between different types of coverage is crucial. Two common types of life insurance are permanent and whole life insurance, each offering unique benefits and characteristics. Permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage, ensuring financial security for the insured's beneficiaries regardless of age or health status. It combines a death benefit with a savings component, allowing policyholders to build cash value over time. In contrast, whole life insurance offers a fixed death benefit and a guaranteed premium, providing coverage for the entire life of the insured. While both types of insurance offer long-term financial protection, they differ in their investment components, flexibility, and cost structures, making it essential to consider individual needs and financial goals when choosing between the two.
What You'll Learn
- Definition: Permanent insurance is a long-term policy, while whole life offers lifelong coverage
- Cost: Permanent plans have higher premiums, but whole life may be more affordable over time
- Flexibility: Permanent insurance allows for policy modifications, whereas whole life is fixed
- Tax Advantages: Both offer tax benefits, but permanent policies may provide more flexibility
- Death Benefit: Whole life guarantees a death benefit, while permanent insurance may have a cash value component

Definition: Permanent insurance is a long-term policy, while whole life offers lifelong coverage
When it comes to insurance, understanding the nuances between different types of policies is crucial. Two common types of insurance that often cause confusion are permanent insurance and whole life insurance. While both provide financial protection and coverage, they differ significantly in their structure, benefits, and long-term implications.
Permanent insurance, as the name suggests, is designed to provide coverage for an individual's entire lifetime. This type of policy is a long-term commitment, offering financial security that remains constant over the policyholder's life. One of the key advantages of permanent insurance is its ability to accumulate cash value over time. This means that a portion of the premium payments goes towards building a cash reserve, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn if needed. Permanent insurance policies typically include various riders and options, allowing policyholders to customize their coverage to suit their specific needs.
On the other hand, whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage, ensuring that the insured individual is protected throughout their entire life. This type of policy offers a guaranteed death benefit, which means the insurance company will pay out a specified amount upon the policyholder's death. One of the unique features of whole life insurance is its fixed premium structure. Once the initial premium is paid, the rate remains the same for the entire life of the policy, providing stability and predictability. Additionally, whole life insurance policies also accumulate cash value, similar to permanent insurance, but the growth rate is typically more consistent and predictable.
The primary distinction between permanent and whole life insurance lies in their flexibility and the level of control they offer. Permanent insurance provides more flexibility in terms of policy customization, allowing individuals to tailor their coverage to their specific needs and preferences. It offers a wide range of riders and options, such as increasing the death benefit, adding critical illness coverage, or participating in the investment aspects of the policy. In contrast, whole life insurance has a more straightforward structure, providing a fixed death benefit and a consistent cash value growth rate. While it offers lifelong coverage, the customization options are generally more limited compared to permanent insurance.
In summary, permanent insurance is characterized by its long-term nature and the ability to customize coverage, while whole life insurance provides lifelong protection with a fixed premium and consistent cash value growth. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals to make informed decisions when choosing the right insurance policy that aligns with their financial goals and needs.
Banner Life Insurance: Still in Business?
You may want to see also

Cost: Permanent plans have higher premiums, but whole life may be more affordable over time
When considering the financial implications of permanent and whole life insurance, the cost is a significant factor that distinguishes these two types of policies. One of the primary differences lies in the premium payments. Permanent life insurance, which includes various types such as whole life, universal life, and variable life, typically carries higher initial premiums compared to term life insurance. This is because permanent policies provide lifelong coverage, ensuring that the insured individual is protected for an extended period. The higher premiums are a result of the policy's long-term commitment, which includes building a cash value over time.
In contrast, whole life insurance, a type of permanent policy, offers a fixed premium that remains the same throughout the life of the policyholder. This predictability in costs can be advantageous for those seeking long-term financial planning. While the initial premium may seem higher, it provides a sense of stability and security, knowing that the insurance coverage will not increase over time. The higher cost of permanent plans is often justified by the comprehensive nature of the coverage, which includes both death benefit and investment components.
Over time, the cost-effectiveness of whole life insurance becomes more apparent. As the policy accumulates cash value, it can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing a source of funds that can be utilized for various financial needs. This flexibility allows policyholders to access the money they've paid in premiums without having to surrender the policy or take out a loan, which might be required in other types of insurance. The cash value growth in whole life insurance can also be a valuable asset, potentially outpacing the savings in other investment vehicles.
While permanent plans may have higher upfront costs, it's essential to consider the long-term benefits and the potential for long-term savings. Whole life insurance, in particular, offers a guaranteed death benefit and a consistent premium, making it a reliable choice for those seeking lifelong coverage. The higher premiums are an investment in a policy that provides financial security and a sense of peace of mind, knowing that the insured individual and their loved ones are protected.
In summary, the cost of permanent and whole life insurance is a critical aspect of decision-making. Permanent plans, especially whole life, may require higher initial investments, but they offer long-term financial benefits and a sense of security. Understanding the trade-offs between immediate costs and long-term savings is essential for individuals to make informed choices when selecting the right insurance policy for their needs.
Understanding Free Cover Limits in Group Life Insurance
You may want to see also

Flexibility: Permanent insurance allows for policy modifications, whereas whole life is fixed
When it comes to insurance, especially in the context of permanent and whole life policies, understanding the concept of flexibility is crucial. Permanent insurance, as the name suggests, offers a level of adaptability that sets it apart from its counterpart, whole life insurance. One of the key advantages of permanent insurance is its ability to allow policyholders to modify their coverage over time. This flexibility is a significant benefit, especially for those who may experience life changes that require adjustments to their insurance needs. For instance, a policyholder might start with a basic coverage amount but later decide to increase it to provide additional financial security for their family. This adaptability is particularly useful for individuals who want to ensure their insurance keeps pace with their evolving circumstances.
In contrast, whole life insurance operates on a fixed structure. Once the policy is in place, the terms and conditions are set, and any changes or modifications are limited. This fixed nature of whole life insurance means that the coverage amount, premiums, and other terms remain constant throughout the life of the policy. While this predictability can be appealing for those who prefer a stable and unchanging insurance plan, it also means that policyholders have less room to customize their coverage according to their specific needs.
The flexibility offered by permanent insurance is a powerful tool for individuals seeking to manage their insurance effectively. It allows for a more personalized approach, ensuring that the policy aligns with the policyholder's life stage and financial goals. For example, a young professional might opt for a lower coverage amount initially, but as they progress in their career and earn a higher income, they can easily increase the policy's value to match their new financial situation. This adaptability is especially valuable for those who want to maximize their insurance benefits without the burden of long-term commitments that may not be necessary at every life stage.
In summary, the difference in flexibility between permanent and whole life insurance is a critical aspect to consider when making an insurance decision. Permanent insurance provides the advantage of policy modifications, allowing individuals to adapt their coverage as their lives change. On the other hand, whole life insurance, with its fixed terms, offers a stable and predictable insurance plan but with limited customization options. Understanding this flexibility is essential for individuals to choose the insurance type that best suits their current and future needs.
Navigating Life's Twists: Insurance and Marketplace Filing
You may want to see also

Tax Advantages: Both offer tax benefits, but permanent policies may provide more flexibility
When it comes to insurance, understanding the tax advantages of different policies is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Both permanent and whole life insurance offer tax benefits, but there are some key differences in how these advantages are structured.
Permanent life insurance, also known as whole life insurance, provides a tax-advantaged way to build cash value over time. This cash value grows tax-deferred, meaning it accumulates without being subject to annual income taxes. As the policyholder, you can borrow against this cash value or withdraw funds, and these amounts are typically tax-free. This feature allows you to utilize the money for various purposes, such as funding education, starting a business, or supplementing retirement income, without incurring immediate tax liabilities.
On the other hand, whole life insurance also offers tax advantages, primarily in the form of tax-deductible premiums. The premiums paid for whole life insurance can be deducted from taxable income, providing an immediate tax benefit. This deduction can be particularly valuable for high-income earners who want to maximize their tax savings. Additionally, the cash value of whole life insurance grows tax-free, similar to permanent life insurance, allowing for tax-efficient accumulation of wealth.
The key difference lies in the flexibility of permanent life insurance. With permanent policies, you can access the cash value without facing significant tax consequences. This flexibility allows for more strategic use of the funds, especially during significant life events or financial milestones. For instance, you can use the cash value to pay for college tuition, cover medical expenses, or provide financial security for your loved ones. The ability to access and utilize the cash value tax-free can be a significant advantage, especially when compared to the more restricted access to cash value in whole life insurance.
In summary, both permanent and whole life insurance offer tax advantages, but permanent policies provide more flexibility in utilizing the tax-advantaged cash value. Understanding these differences can help individuals make informed choices when selecting insurance policies that align with their financial goals and needs. It is essential to consult with a financial advisor to determine the best insurance strategy based on individual circumstances.
Life Insurance Risk Factors: What Determines Your Premiums?
You may want to see also

Death Benefit: Whole life guarantees a death benefit, while permanent insurance may have a cash value component
When it comes to life insurance, understanding the differences between various types can be crucial in making an informed decision. One of the key distinctions lies in the death benefit, which is the amount paid out to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon their passing. Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a guaranteed death benefit. This means that regardless of the policyholder's age, health, or any changes in their circumstances, the insurance company will pay out a predetermined amount when the insured person dies. This guarantee provides peace of mind, knowing that your loved ones will receive financial support even if you are no longer around.
On the other hand, permanent insurance, which includes whole life and universal life, also provides a death benefit. However, the key difference here is that permanent insurance policies often come with an additional feature: a cash value component. This cash value is essentially a savings component built into the policy, allowing the policyholder to accumulate a reserve of money over time. It grows tax-deferred and can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing a financial safety net. While the death benefit is still guaranteed, the cash value in permanent insurance offers a unique advantage, allowing policyholders to build equity and potentially access funds during their lifetime.
The death benefit is a critical aspect of life insurance as it ensures financial security for your family or beneficiaries. With whole life insurance, the death benefit is locked in, providing a consistent and reliable source of income for those who depend on it. This is particularly important for covering expenses such as mortgage payments, children's education, or any other long-term financial commitments. In contrast, permanent insurance with a cash value component may offer more flexibility, allowing policyholders to adjust the death benefit or access the cash value for other financial needs.
It's important to note that while permanent insurance offers a guaranteed death benefit and a cash value component, the cost of these policies is typically higher compared to term life insurance. This is because the insurance company is committing to pay out a death benefit for the entire lifetime of the insured, and the cash value component adds an extra layer of complexity. However, for those seeking long-term financial security and the potential for tax-advantaged savings, permanent insurance can be a valuable investment.
In summary, when considering permanent and whole life insurance, the death benefit is a fundamental aspect to evaluate. Whole life insurance guarantees a death benefit, providing financial security for your loved ones. Permanent insurance, including whole life, also offers a guaranteed death benefit but with the added feature of a cash value component, allowing for potential financial flexibility and savings. Understanding these differences can help individuals choose the right type of insurance to meet their specific needs and provide peace of mind for the future.
Life Insurance Double Indemnity: Still a Viable Option?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main distinction lies in their coverage and flexibility. Permanent life insurance, also known as whole life or permanent insurance, offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows over time. This means the policy will remain in force as long as the premiums are paid, providing a guaranteed death benefit and a savings element. On the other hand, whole life insurance is a type of permanent insurance that also provides lifelong coverage, but it typically has a fixed premium and a guaranteed death benefit.
Permanent and whole life insurance policies generally have higher premiums compared to term life insurance. This is because they offer a combination of death benefit coverage and a savings or investment component. The premiums are usually level, meaning they remain the same throughout the policy's duration, providing long-term financial security. In contrast, term life insurance has lower premiums for a specified period, making it more affordable for shorter-term needs.
Yes, both permanent and whole life insurance policies include an investment component. The cash value of these policies accumulates over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn. This feature allows policyholders to build a savings or investment portfolio within their insurance policy. The investment aspect of whole life insurance is often more conservative, with a focus on long-term growth and stability. Permanent life insurance, especially those with higher cash values, may offer more investment options, allowing policyholders to customize their investment strategy.
Yes, there are tax benefits associated with permanent and whole life insurance. The cash value growth within these policies is typically tax-deferred, meaning it can grow without being taxed each year. Additionally, the death benefit paid out upon the insured's passing is generally tax-free. These policies can also be used as an estate planning tool, providing a tax-efficient way to pass on wealth to beneficiaries. It's important to note that tax laws may vary, so consulting a financial advisor is recommended for personalized advice.







