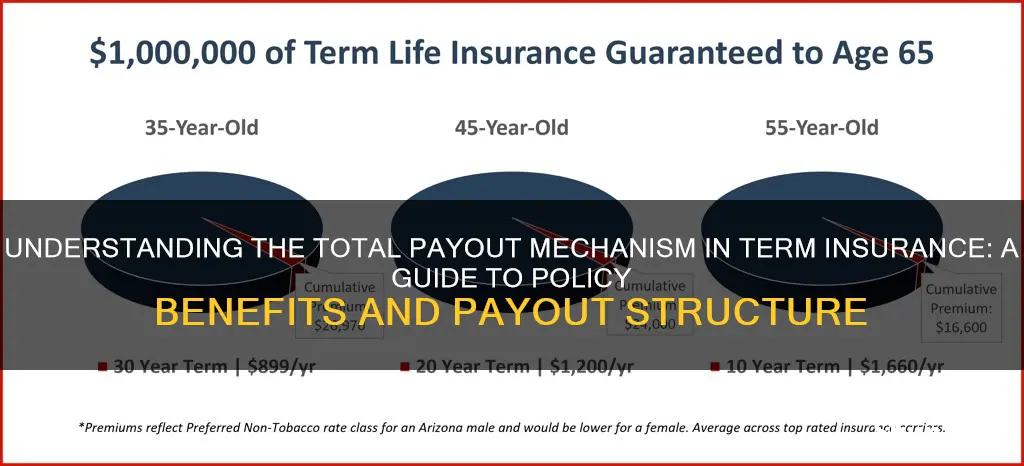
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder for a specified period. The total payout in term insurance refers to the sum of money that is paid out to the beneficiaries when the insured person dies during the term of the policy. This payout is often a large sum of money that is intended to provide financial support to the dependents of the deceased.
There are several options for how the total payout is distributed to the beneficiaries, including a lump-sum payment, annuity, or retained asset account. The choice of payout option depends on the preferences of the beneficiaries and the specific offerings of the insurance company.
The total payout in term insurance ensures that the dependents of the deceased have financial support to help them meet their monetary needs, such as funeral costs, consumer debt, mortgage debt, and other expenses.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is term insurance? | A type of life insurance that provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder for a specified period of time. |
| Who is it for? | Young people with children, people with growing families, older surviving spouses |
| How does it work? | The policyholder pays premiums for an extended period, and if they die within the policy term, the insurer pays the policy's face value to the beneficiaries. |
| How much does it cost? | The cost of term life insurance depends on a person's age, health, and life expectancy. It is usually the least costly type of life insurance available. |
| What are the different types of term life insurance? | Level-premium policy, yearly renewable term policy, decreasing term policy |
| What are the payout options? | Lump sum, life insurance annuity, retained asset account, monthly income payout, part sum assured plus monthly income |
What You'll Learn
- Term life insurance payouts are simple and only occur if the policyholder dies during the policy's term
- Permanent life insurance payouts are more complicated and include a savings component called cash value
- Lump sum payments are the most common payout type and are given to the beneficiary once the amount has been approved
- Installments are another payout option, usually in the form of an annuity
- A third option is for the insurer to function like a bank account, holding on to the death benefit until it's needed

Term life insurance payouts are simple and only occur if the policyholder dies during the policy's term
Term life insurance is a type of insurance that provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder for a specified period of time. It guarantees payment of a stated death benefit to the insured's beneficiaries if the insured person dies during the specified term. These policies do not accumulate cash value and do not have a savings component like permanent life insurance products. Instead, term life insurance policies have a fixed duration, such as 10, 20, or 30 years, and offer a simple payout structure.
The payout process for term life insurance is straightforward. If the policyholder passes away during the policy's term, the beneficiaries can claim the death benefit by filing a claim with the insurance company. They will need to submit a certified copy of the death certificate and complete any additional paperwork required by the insurer. The death benefit is typically paid out as a lump sum, providing the beneficiaries with the entire death benefit amount at once. This lump sum payout is tax-free and gives the beneficiaries the most flexibility in using the funds as they see fit.
In addition to the lump sum payout, some insurance companies offer alternative payout options for term life insurance policies. One option is a monthly income payout, where the beneficiaries receive a portion of the insured amount each month over an extended period, such as 15 to 20 years. This option is useful for families who may not be savvy with investments and need periodic financial support. Another option is a combination of a partial sum assured and monthly income, where a certain percentage of the sum assured is paid immediately, and the rest is paid in monthly installments. This can help meet the family's regular financial requirements.
It is important to note that term life insurance policies only provide a payout if the policyholder dies during the policy's term. If the policy expires before the policyholder's death or if they outlive the policy term, there is no payout. However, policyholders do have the option to renew their term policy at expiration, although the premiums may increase due to their advanced age.
Understanding the Criteria: Unlocking Short-Term Insurance Eligibility
You may want to see also

Permanent life insurance payouts are more complicated and include a savings component called cash value
Permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life insurance, are designed to be active throughout a policyholder's life as long as premiums are paid. Permanent life insurance payouts are more complicated than term life insurance payouts because they include a savings component called cash value that the policyholder can draw from during their life.
The cash value of a permanent life insurance policy is the portion of the policy that earns interest and may be available for the policyholder to withdraw or borrow against in case of an emergency. A portion of each premium paid goes towards insuring the policyholder's life, while the other portion contributes to building up the cash value. The cash value portion of the policy accrues tax-deferred interest, and the money can earn interest in different ways depending on the type of permanent life insurance policy.
While the cash value of a permanent life insurance policy will not be available to the beneficiary, it is important to note that any money borrowed from the cash value and not repaid will be subtracted from the death benefit. For example, if it is a $500,000 whole life policy and $10,000 was borrowed to start a business, the beneficiary would only receive $490,000 unless the $10,000 is repaid before the policyholder dies.
E-Health Short-Term Insurance: Exploring the Digital Revolution in Healthcare Coverage
You may want to see also

Lump sum payments are the most common payout type and are given to the beneficiary once the amount has been approved
Lump sum payments are the most common type of payout in term insurance. This is when the beneficiary receives the entire sum assured amount in one go. For example, if the sum assured is Rs. 1 Crore, the beneficiary will receive the full amount at once. This is in contrast to staggered payouts, where the beneficiary receives a certain percentage of the sum assured as a lump sum, followed by monthly instalments over the next 15-20 years.
Lump sum payments give the beneficiary complete freedom to use the death benefit as they see fit. They can be used to cover large expenses, such as a child's education or marriage costs, or to settle any large debts. The beneficiary could also invest a portion of the lump sum to make use of the power of compounding and receive higher returns.
However, receiving a large amount of money all at once can be overwhelming for the beneficiary. They will need to be financially savvy to make the most of the payout and ensure that it lasts. If the beneficiary is not good with finances, there is a risk that they will spend the money too quickly and end up with less financial security. In this case, staggered payouts may be a better option.
When choosing between a lump sum and staggered payouts, it is important to consider the financial literacy and needs of the beneficiary. Lump sum payouts offer more flexibility, while staggered payouts provide a steady income stream and may be better suited to covering short-term financial needs.
The Hidden Dangers of Physical Hazards: Uncovering the Insurance Perspective
You may want to see also

Installments are another payout option, usually in the form of an annuity
When it comes to term insurance, beneficiaries can often choose to receive their payout in the form of an annuity, or regular payments over a set period of time. This is in contrast to a lump sum payout, where the beneficiary receives the entire death benefit at once.
Annuities are a good option for those who are worried about spending a large sum of money too quickly. They can also provide a steady income for those who are dependent on the policyholder, such as family members. This is especially true for families with limited financial knowledge, who may not know how to best invest a large sum of money.
There are several types of annuity or instalment options available. With a fixed monthly payout, the beneficiary will first receive a percentage of the total coverage as a lump sum, and then receive a fixed monthly payment for a predetermined duration. A staggered payout sees the beneficiary paid in monthly instalments over 10-15 years, or a term agreed upon at the time of purchase. With an increasing monthly payout, the beneficiary will receive a gradually increasing monthly payment over time to account for inflation.
There are some potential drawbacks to annuity payments. The younger the beneficiary, the smaller the payout amounts will be, as they will have to be distributed over a longer period of time. There may also be fees associated with this option, as well as a surrender charge if the beneficiary wishes to withdraw all of the cash at once. Additionally, if the beneficiary dies before receiving the full benefit amount, the remaining money will be kept by the insurance company.
Understanding the Role of Short-Term Insurance in Meeting FRS Requirements
You may want to see also

A third option is for the insurer to function like a bank account, holding on to the death benefit until it's needed
When it comes to term insurance, the payout options available to the beneficiary are crucial. While a lump sum payout is the most common option, providing the beneficiary with full control over a large sum of money, it can be overwhelming for those without financial knowledge to manage this amount effectively. This is where the staggered or monthly payout options offered by insurance companies come into play.
One key advantage of this approach is that it eliminates the concern of FDIC insurance limits. When receiving a large death benefit payout, individuals might need to spread it across multiple accounts to stay within the FDIC deposit insurance limit of $250,000 per depositor per FDIC-insured bank. By keeping the payout in a retained asset account with the insurer, the entire amount is protected.
However, it's important to consider the potential downside of lower interest rates compared to what could be achieved with a high-yield savings account or investment. Additionally, any interest earned on the account will be subject to taxation.
When deciding on the best term insurance plan, it's crucial to select one that offers high returns while keeping premiums reasonable. This option of holding the payout with the insurer strikes a balance between providing immediate access to funds and allowing for periodic withdrawals, ensuring the beneficiary's financial needs are met during a challenging time.
Understanding Term Insurance Compatibility with Islamic Principles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides a death benefit to the beneficiaries of the policyholder for a specified period of time.
Term insurance lasts for a specific term of time, whereas whole life insurance lasts for the entire life of the policyholder. Term insurance is also simpler and more affordable, but whole life insurance offers additional benefits such as a savings component that allows you to borrow from your policy.
The beneficiary of the policy needs to file a claim with the insurance company and submit a certified copy of the death certificate. The insurance company will then process the claim and pay the beneficiary.
Yes, there are typically three ways that a term insurance payout can be distributed: as a lump sum, through a life insurance annuity, or via a retained asset account.
A lump sum payout gives the beneficiary full control over the money and the most flexibility in terms of usage. However, receiving a large amount of money at once can be overwhelming, and there may be issues with deposit insurance limits if the payout is very large.







