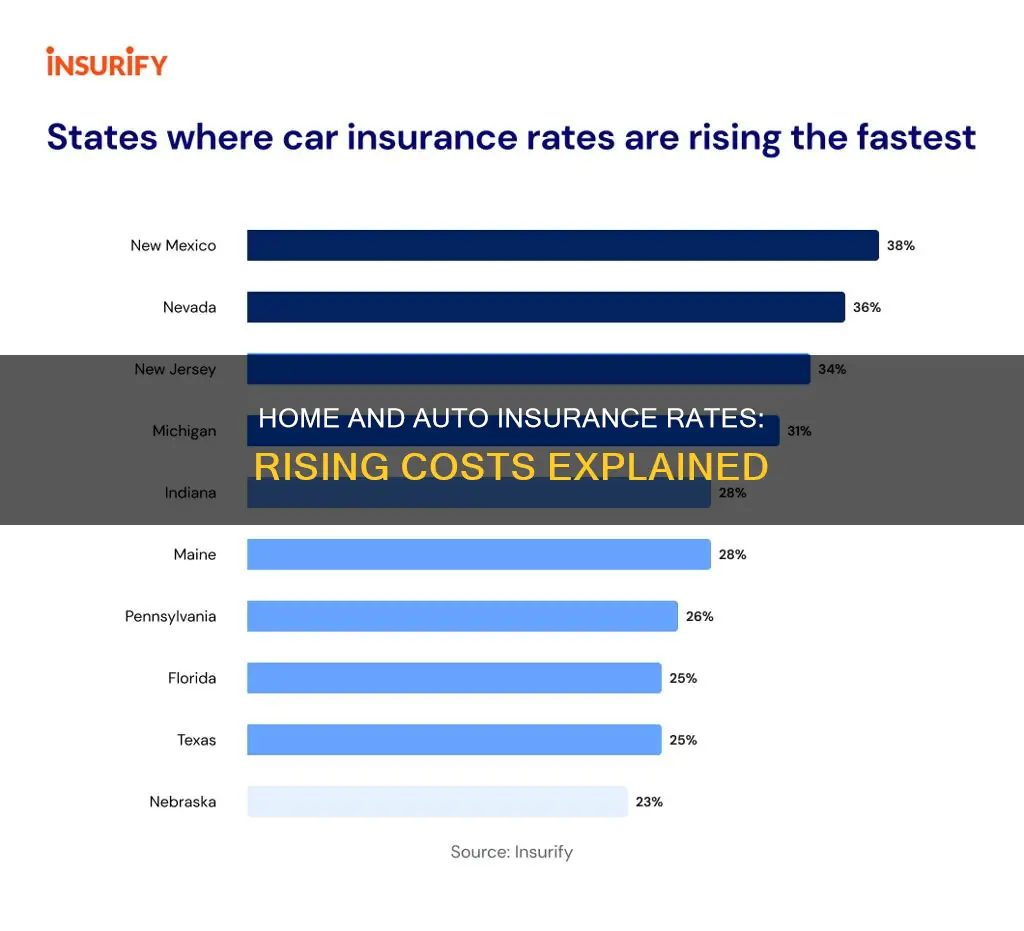
Home and auto insurance rates are going up due to a variety of factors, including inflation, an increase in natural disasters, and rising costs of repairs and replacements. Inflation has contributed to the rising prices of goods, including cars, which are now more expensive to purchase, repair, and replace. This has led to higher insurance rates as insurers need to cover the increased costs of claims. Additionally, there has been an increase in natural disasters such as wildfires, hurricanes, and floods, which have resulted in record-setting claim payouts and financial losses for insurance companies, causing them to increase rates to compensate. The rising costs of repairs and replacements are also due to supply chain issues, labor shortages, and the integration of new technology in vehicles. These factors have collectively driven up the cost of home and auto insurance, impacting consumers and contributing to overall inflation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Inflation | Inflation has been at a 15-year high, affecting the prices of goods including cars, groceries, gas, and housing. |
| Natural disasters | A growing number of natural disasters, such as wildfires, hurricanes, and floods, have caused record-setting claim payouts and financial losses in the insurance industry. |
| Inflation | Inflation has increased the cost of fixing or replacing damaged homes and cars due to rising labor and material prices. |
| Supply chain issues | Supply chain issues and inflation have increased the cost of building materials, leading to higher home insurance rates. |
| Claims | An increase in the number of claims in certain areas has contributed to rising insurance rates. |
| Repair costs | The cost of repairing vehicles has increased due to supply chain disruptions, labor issues, and the use of new technology. |
| Electric vehicles | The increased popularity of electric vehicles has contributed to rising insurance rates as they are more expensive to repair and replace. |
| Distracted driving | Increased accidents due to distracted driving, such as texting or watching videos while driving, have led to higher insurance rates. |
What You'll Learn

Natural disasters and inflation
Natural disasters have a significant impact on insurance rates. The increase in expensive natural disasters, such as wildfires, hurricanes, tornadoes, flooding, earthquakes, and severe storms, has caused home insurance rates to skyrocket. In 2023, there were 28 separate billion-dollar disasters in the US, and this number is expected to grow in 2024. As a result, insurance companies are taking steps to mitigate their risk by increasing insurance rates and refusing to insure certain homes in high-risk areas.
The frequency and severity of these natural disasters have led to higher claim payouts for insurance companies. In addition, the cost of repairing or replacing damaged homes and cars has increased due to rising labor and material prices, further contributing to higher insurance rates.
Inflation is another factor contributing to the increase in insurance rates. The cost of replacing homes and vehicles has risen significantly due to inflation. This includes the increased cost of labor and construction materials due to supply chain issues. As a result, insurance companies have had to pay out more in claims, leading to higher insurance rates for consumers.
The combination of natural disasters and inflation has put pressure on insurance companies, who are passing on the increased costs to their customers in the form of higher insurance rates. These rates are expected to continue climbing, even as overall inflation cools.
Comprehensive Claims: Auto Insurance Rates Impact
You may want to see also

Repair costs and supply chain issues
The rising costs of repairs and the issues with the supply chain have had a significant impact on the surge in home and auto insurance rates. The pandemic has been a key factor in this development, causing component shortages, including semiconductor chips, which are essential for modern vehicles. This has resulted in a decrease in new car production and an increase in demand for used cars, which require more repairs and parts. Auto shops are facing inventory depletion due to distribution issues, longer shipping times, and unloading delays due to labour shortages.
The automotive industry is also experiencing a shortage of skilled mechanics, lengthening the time and increasing the cost of repairs. The use of advanced technology and new materials in vehicles, such as advanced safety systems and aluminium for fuel efficiency, has further driven up repair costs. The replacement parts for these advanced systems require trained technicians and special tools for installation and calibration. Additionally, some technological features have resulted in higher crash frequency and more severe vehicle damage, leading to costlier repairs.
The increase in repair costs is not limited to vehicles. Home insurance rates have also been affected by the rising cost of labour and construction materials due to supply chain issues and inflation. The cost of rebuilding homes has increased, leading to higher dwelling coverage limits in insurance policies. Inflation has contributed to higher prices for construction materials, such as lumber, wood products, asphalt roofing, and goods for new residential construction. Moreover, the labour shortage in the construction industry has resulted in higher wages, further adding to the overall cost of repairs and construction.
The combination of these factors has significantly contributed to the rise in home and auto insurance rates, as insurance companies adjust their premiums to account for the increased costs associated with repairs and construction.
Applying for New Jersey Manufacturer Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

Distracted driving
The consequences of distracted driving can be severe, ranging from moving violations to increased insurance rates and, in some cases, serious accidents. Most states have laws prohibiting the use of handheld phones while driving, and many consider texting while driving a primary offense, meaning a driver can be ticketed specifically for that action. However, the impact of distracted driving on insurance rates varies depending on state laws and insurance company policies.
In some states, a texting-while-driving ticket can lead to a significant increase in insurance rates, with an average rate increase of 28% across the country. These tickets are considered moving violations, which insurance companies view as an indicator of a higher risk of filing a claim. As a result, insurance companies may raise rates accordingly, similar to how they handle other minor moving violations.
However, it's important to note that some states, such as Idaho and North Carolina, have laws prohibiting insurance companies from raising rates based on texting violations. Additionally, certain insurance companies may have their own methods for adjusting rates after a moving violation, and the timeline for how long a distracted driving offense impacts rates can vary.
To avoid distracted driving, it is recommended to keep your phone out of reach, use apps that silence notifications while driving, model safe driving behaviour, pull over if you need to use your phone, use a cellphone mount, and take advantage of vehicle safety features that allow hands-free calls and text listening.
Vehicle Loan and No Insurance: What Now?
You may want to see also

Insurance company profits
The rise in insurance rates has been influenced by a range of factors, including inflation, an increase in natural disasters, and higher repair costs. Inflation has contributed to the rising cost of goods, including cars, which are now more expensive to purchase, repair, and replace. This has, in turn, impacted insurance rates.
In addition, there has been an increase in natural disasters, such as wildfires, hurricanes, and floods, which have resulted in higher claim payouts for insurance companies. As a result, insurance companies have increased rates to cover these losses and ensure they remain financially stable.
Another factor is the rise in car repair costs, which has been influenced by supply chain disruptions, labor issues, and the increasing use of advanced technology in vehicles. All of these factors have contributed to higher insurance rates and, ultimately, higher profits for insurance companies.
Understanding Auto Insurance: 02 Conviction Point Surcharge
You may want to see also

Policy changes
Changes in Coverage and Rates
Insurers may change the terms of coverage, including the scope, limits, and exclusions. This can lead to higher rates for policyholders as they seek to maintain adequate protection. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, some insurers may have offered reduced rates due to fewer cars on the road and lower accident risks. However, as the situation normalizes, insurers may revert to previous rates or even increase them to recoup losses.
Inflation and Repair Costs
Natural Disasters and Climate Change
The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, such as wildfires, hurricanes, and floods, contribute to rising insurance rates. Climate change is exacerbating these events, and insurers are adjusting their rates to account for the increased risk and payouts associated with climate-related disasters. This is particularly noticeable in areas that were previously considered low-risk but are now facing higher premiums due to changing weather patterns.
Underwriting Criteria and Risk Assessment
Insurers may change their underwriting criteria, becoming more stringent or selective in their policy offerings. This can lead to higher rates, especially in high-risk areas or for individuals with certain risk factors. For example, if an insurer experiences significant losses in a particular state due to natural disasters, they may decide to stop writing new policies or increase premiums for existing policyholders to mitigate future risks.
Discounts and Loyalty Programs
Gieco: Auto Insurance Adjustments
You may want to see also







