When you get into a car accident, you'll have to pay a deductible before your insurance company covers the remaining cost of repairing or replacing your vehicle. However, when it comes to liability insurance, which covers damage or injuries to others when you're at fault, there is no deductible. This means that your insurance company will pay the full cost of any claims made against you, and you won't have to pay anything out of pocket. This is because liability insurance covers the other party in an accident, not the policyholder's vehicle, so there is no deductible to be paid by the policyholder.
What You'll Learn
- Liability insurance covers damage to another person or their property
- There are no deductibles for liability insurance
- Liability insurance does not cover damage to your own property
- Collision coverage pays for damage to your own property
- Comprehensive coverage pays for non-collision damage to your own property

Liability insurance covers damage to another person or their property
Liability insurance is an insurance product that provides protection against claims resulting from injuries and damage to other people or their property. It covers legal costs and payouts for which the insured party would be found liable. Liability insurance is often required for automotive insurance policies, product manufacturers, and anyone who practices medicine or law.
In the context of auto insurance, liability insurance covers injuries you cause to someone else while driving, damage you cause to other vehicles while driving, and damage you cause to someone else's property, such as a mailbox or street sign. It also covers legal expenses for accident-related lawsuits. For example, if you back into someone's car, your auto policy's liability coverage could pay for the damage to their vehicle.
Liability insurance does not cover intentional or criminal acts, even if the insured party is found legally responsible. It also does not cover contractual liabilities or damage to the policyholder's own property or injuries.
When it comes to auto insurance deductibles, the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance covers the rest, liability insurance does not typically have any deductible attached. This means that in the event of an accident, you will not have to pay anything out of pocket for damages or injuries you cause to another person or their property, up to your policy's limits.
U.S. Auto Association: Exploring the USAA App for Auto Insurance
You may want to see also

There are no deductibles for liability insurance
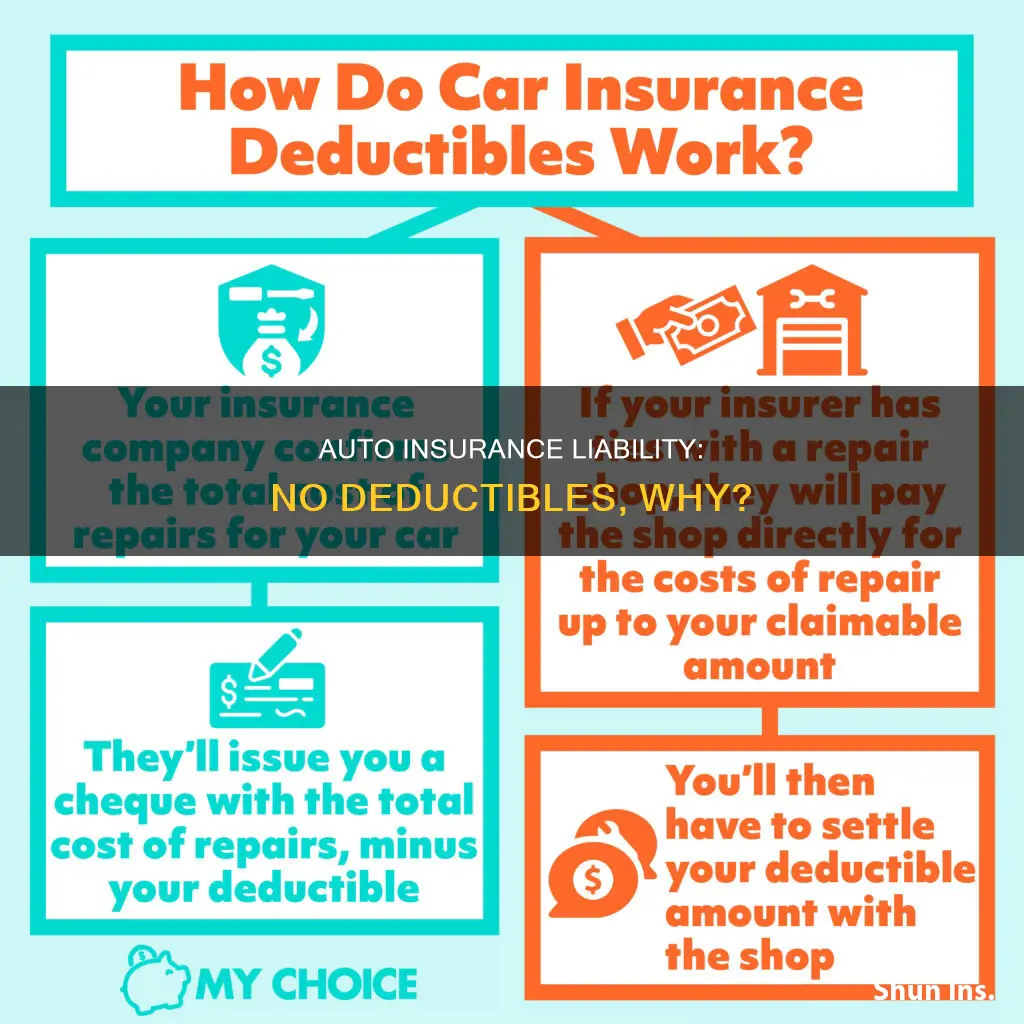
When it comes to auto insurance, a deductible is the amount of money that the policyholder must pay out of pocket towards an insured loss before their insurance coverage pays the remaining costs. Typically, deductibles are applied to collision coverage and comprehensive coverage. Collision coverage helps pay for damage to your vehicle when you are in a crash with another vehicle or any stationary object. Comprehensive coverage pays for damage to your vehicle in instances other than a collision, such as weather damage or theft.
However, there are no deductibles for liability insurance. Liability insurance covers damages that you cause to another person or their property in an accident. This means that if you are responsible for an accident, your insurance company will pay the other party directly, and you will not have to pay any deductible. For example, if you rear-end someone else's vehicle, they can make a claim against your liability insurance, and your insurance company will pay for the damages without you having to pay any deductible.
The absence of deductibles for liability insurance is an important feature of auto insurance policies. It ensures that individuals who cause accidents can rely on their insurance company to cover the costs of any damages without having to worry about paying a deductible out of pocket. This can be especially important in situations where the damages caused are significant and the policyholder may not have the financial means to pay a deductible.
It is worth noting that while there are no deductibles for liability insurance, policyholders may still experience a rate increase at renewal time due to the accident. Additionally, the specific terms and conditions of auto insurance policies, including deductible amounts, can vary from state to state, and it is important to review your own policy to understand the specific coverage and deductibles that apply.
Understanding Auto Insurance Claims: Timely Reimbursement Explained
You may want to see also

Liability insurance does not cover damage to your own property
Liability insurance is an insurance product that provides protection against claims resulting from injuries and damage to other people or property. It covers legal costs and payouts for which the insured party would be found liable. However, it does not cover damage to the insured party's own property.
Liability insurance is often required for automotive insurance policies and is mandatory in most states. It is also called third-party insurance because it pays third parties, and not policyholders. In the context of auto insurance, liability insurance covers the costs of the other driver's property and bodily injuries if the policyholder is found at fault in an accident.
There are two primary types of liability coverage in auto insurance: bodily injury liability and property damage liability. Bodily injury liability covers medical expenses, pain and suffering, and loss of income for the other party if the policyholder is found at fault in the accident. Property damage liability covers the costs associated with damage caused by the policyholder to someone else's property, including other vehicles, buildings, utility poles, and fences.
While liability insurance is essential for drivers, it is important to note that it does not cover damage to the policyholder's own property. For that, separate collision and comprehensive coverage is needed. Collision coverage pays for damage to the insured's vehicle when involved in a crash with another vehicle or stationary object, while comprehensive coverage pays for damage to the insured's vehicle in instances other than a crash, such as hail or falling tree limbs.
U.S. Auto Insurance: Payment Methods and Options
You may want to see also

Collision coverage pays for damage to your own property
Collision coverage is an optional add-on to your auto insurance policy that pays for damage to your own vehicle. It covers the cost of repairs or replacement for your car, regardless of who was at fault for the accident. This includes collisions with other vehicles, stationary objects, and roll-overs. It may also cover damage caused by uninsured or underinsured drivers, as well as damage from potholes or hitting a curb.
The cost of collision coverage varies depending on the company and the specifics of your policy. It is typically offered with a range of deductible amounts, such as $250, $500, $1,000, and $2,000. The deductible is the amount you will have to pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. For example, if you have a $1,000 deductible and your car requires $5,000 worth of repairs, you will have to pay the first $1,000, and your insurance will cover the remaining $4,000.
When purchasing collision coverage, it's important to consider the value of your car. Collision coverage becomes less valuable over time because it will never pay out more than the car's market value. If the cost of collision coverage and the deductible combined is higher than the current market value of your car, it may not be worth purchasing.
Additionally, some lenders may require you to have collision coverage if you are financing or leasing your vehicle. In these cases, you may be required to maintain collision coverage until the contract ends or the loan is paid off.
It's worth noting that collision coverage has certain limitations. It does not cover damage to personal belongings inside your car, normal wear and tear, or medical costs from injuries to you or your passengers. Furthermore, collision coverage will not pay for car damage resulting from non-traffic events, such as animal collisions, extreme weather, or theft. For protection against these types of incidents, you may consider adding comprehensive coverage to your policy.
Infiniti Lease: Gap Insurance Included?
You may want to see also

Comprehensive coverage pays for non-collision damage to your own property
Comprehensive coverage is an optional form of auto insurance that helps cover the cost of damage to your own vehicle in instances other than a collision. It is sometimes referred to as "other than collision" coverage. Comprehensive coverage does not cover damage caused by hitting another vehicle or object, which is covered under collision insurance. It also does not cover normal wear and tear on your vehicle.
Comprehensive coverage can include damage to your vehicle caused by natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, and volcanic eruptions. It can also cover theft of the vehicle, or parts of the vehicle, as well as damage caused by fallen objects, such as trees, branches, or ice. In some cases, it can also cover damage caused by contact with animals, such as hitting a deer.
Comprehensive coverage is subject to a deductible, which is the amount you agree to pay before the insurance company starts paying for damages. Typically, the higher the deductible, the lower your insurance cost will be, and vice versa. For example, if you have a $100 deductible and your vehicle sustains $1000 in damage, you will pay the first $100, and your insurance company will pay the remaining $900.
Comprehensive coverage is separate from liability insurance, which covers damage you cause to another person or their property in an accident. Liability insurance does not have a deductible, meaning there is no out-of-pocket cost for the insured person in the event of an accident.
Get Licensed to Sell Auto Insurance in New Jersey
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Liability insurance covers the cost of damage to another person or their property in an accident caused by the insured. It does not cover the cost of damage to the insured's own property. Therefore, there are no deductibles for liability insurance.
An auto insurance deductible is the amount of money you are responsible for paying before your insurance company covers the rest.
The most common auto insurance deductible is $500. However, deductibles can range from $250 to $2,000 or more.
If you have a $500 deductible and $3,000 in damage from a covered accident, your insurer will pay $2,500, and you will be responsible for the remaining $500.
A low deductible means a higher insurance rate, whereas a high deductible means a lower insurance rate.







