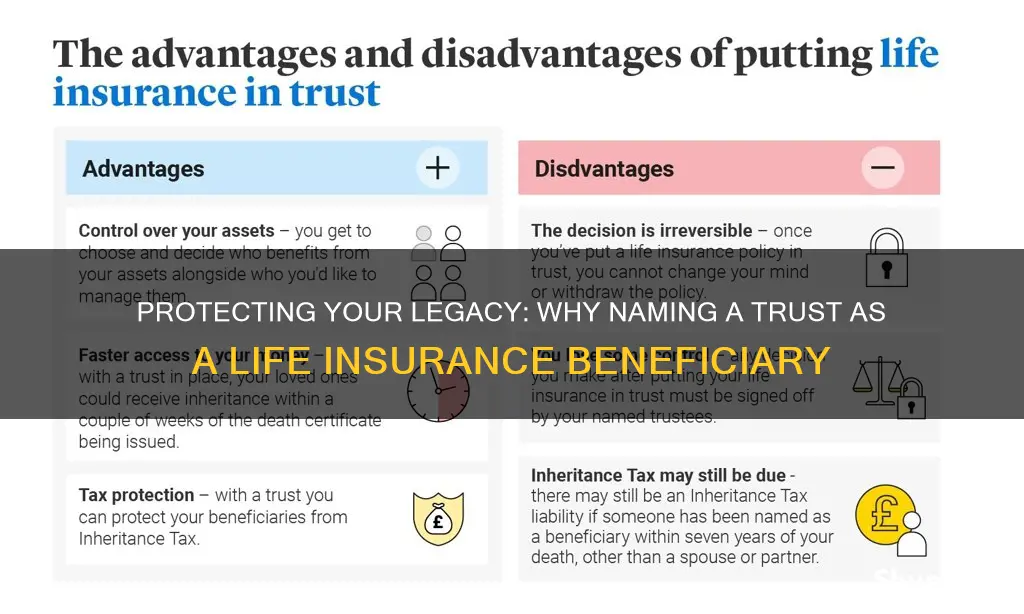
Naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary can be a strategic financial move for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that the proceeds from the insurance policy are distributed according to the trust's terms, providing a structured and efficient way to manage assets. This can be particularly useful for avoiding probate, reducing estate taxes, and maintaining privacy. Additionally, a trust can provide a layer of protection for the insurance payout, safeguarding it from potential creditors or divorce settlements. By utilizing a trust, individuals can create a more secure and controlled distribution of their insurance benefits, aligning with their long-term financial goals and wishes.
What You'll Learn
- Tax Benefits: Trusts can help avoid probate fees and provide tax advantages for the trust's beneficiaries
- Control and Flexibility: You can specify how and when the trust's assets are distributed
- Asset Protection: Trusts can shield assets from creditors and protect them from divorce or bankruptcy
- Privacy: Trust distributions are private, unlike public wills, which can be scrutinized by anyone
- Long-Term Management: Trusts can ensure consistent management and distribution of assets over time

Tax Benefits: Trusts can help avoid probate fees and provide tax advantages for the trust's beneficiaries
Naming a trust as a beneficiary of your life insurance policy can offer significant tax benefits and help you avoid probate fees, which can be substantial and costly. When you pass away, the proceeds from your life insurance policy are typically subject to probate, a legal process that determines the distribution of your assets. During probate, the court evaluates the validity of the will and ensures the distribution of assets according to the legal procedures. This process can be lengthy and expensive, often incurring fees that are a percentage of the total estate value.
By naming a trust as the beneficiary, you can bypass the probate process entirely. Trusts are legal entities that hold assets on behalf of beneficiaries. When you name a trust as the beneficiary, the insurance company pays the trust directly, and the assets are distributed according to the trust's terms without the need for court intervention. This not only saves time but also eliminates the potential for disputes among beneficiaries, as the trust's terms provide a clear and predetermined distribution plan.
One of the key tax advantages of using a trust is the ability to take advantage of tax-efficient distributions. When you name a trust as the beneficiary, you can structure the trust to make tax-efficient payouts to the beneficiaries. This is particularly beneficial if the trust is well-crafted and tailored to the specific needs of the beneficiaries. For example, you can set up the trust to make annual payments to the beneficiaries, ensuring a steady income stream for them while also minimizing the tax impact on the trust's assets.
Additionally, trusts can provide tax advantages by allowing for the utilization of various tax deductions and credits. For instance, charitable trusts can offer significant tax benefits by allowing donors to claim charitable contributions, which can reduce their taxable income. Similarly, certain types of trusts, such as qualified personal residence trusts, can provide tax advantages by allowing the transfer of a primary residence to a trust while still allowing the grantor to reside in it tax-free for a specified period.
In summary, naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary can be a powerful strategy to avoid probate fees and provide tax advantages for the trust's beneficiaries. By bypassing the probate process and utilizing tax-efficient distribution strategies, you can ensure a smoother transition of assets and potentially reduce the tax burden on your loved ones. It is essential to consult with legal and financial professionals to create a trust that aligns with your specific goals and provides the desired tax benefits.
Unum Supplemental Life Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Control and Flexibility: You can specify how and when the trust's assets are distributed
Naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary offers a level of control and flexibility that can be advantageous for estate planning. When you designate a trust as the recipient of your life insurance policy, you have the power to outline specific distribution guidelines. This means you can decide how and when the trust's assets are distributed, ensuring your wishes are followed precisely.
One of the key benefits is the ability to control the timing of asset distribution. You can structure the trust to release funds in a manner that aligns with your desired timeline. For instance, you might choose to have the trust's assets distributed in a series of payments over time, providing a steady income stream for beneficiaries or ensuring that certain expenses are covered first. This level of control allows you to adapt the distribution strategy to your specific needs and those of your loved ones.
Additionally, trusts offer flexibility in how assets are allocated. You can specify different distribution methods within the trust, such as lump sums, periodic payments, or a combination of both. This customization ensures that the trust's assets are distributed according to your preferences, whether it's providing immediate financial support to beneficiaries or a more gradual approach that aligns with their long-term financial goals.
The trust's flexibility also extends to the types of assets that can be included. You can include various assets, such as cash, real estate, investments, or even personal belongings, and define how and when they should be distributed. This comprehensive approach allows for a tailored distribution plan that considers all aspects of your estate.
By naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary, you gain the freedom to make decisions about asset distribution, ensuring that your estate plan reflects your unique circumstances and goals. This level of control and flexibility is a powerful tool in estate planning, providing peace of mind and the assurance that your wishes will be honored.
Term Life Insurance Lapse: What Happens and What to Do?
You may want to see also

Asset Protection: Trusts can shield assets from creditors and protect them from divorce or bankruptcy
Trusts are powerful legal instruments that can provide significant benefits when it comes to asset protection, especially in the context of life insurance beneficiaries. One of the primary advantages of naming a trust as a beneficiary is the ability to safeguard assets from potential creditors and legal claims. When you establish a trust and name it as the recipient of your life insurance policy, the assets within the trust become protected from the reach of creditors. This is particularly relevant for individuals who own valuable assets, such as real estate, businesses, or substantial financial investments, as it ensures that these assets remain secure and cannot be easily seized or claimed in the event of financial difficulties or legal judgments.
In the event of a divorce, trusts can also play a crucial role in preserving assets. During a divorce, marital assets are typically subject to division between the spouses. By placing assets into a trust, you can ensure that these assets remain separate and are not considered part of the marital estate. This protection can be especially valuable for high-net-worth individuals who want to maintain control over their assets and prevent them from being divided in a way that may not align with their wishes.
Furthermore, trusts offer a layer of protection against bankruptcy. If an individual files for bankruptcy, their assets are generally subject to liquidation to pay off debts. However, assets held in a trust may be exempt from this process, depending on the jurisdiction and the specific trust structure. By naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary, you create a legal entity that can hold and manage assets, providing a safeguard against the potential loss of valuable possessions during a bankruptcy proceeding.
The process of setting up a trust for asset protection involves careful consideration and legal expertise. It is essential to work with an experienced attorney who specializes in estate planning and trust law. They can guide you through the process, ensuring that the trust is structured correctly to meet your specific needs and goals. This may include selecting the appropriate trust type, such as a revocable living trust or an irrevocable trust, each offering different levels of control and protection.
In summary, naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary is a strategic move for asset protection. It provides a robust defense against creditors, safeguards assets during divorce proceedings, and offers potential protection against bankruptcy. By utilizing trusts, individuals can take control of their financial legacy and ensure that their assets are preserved for their intended beneficiaries, even in the face of legal or financial challenges. This approach demonstrates the importance of proactive estate planning and the significant role that trusts can play in securing one's financial future.
Understanding Life Health Insurance: A Comprehensive Lookup Guide
You may want to see also

Privacy: Trust distributions are private, unlike public wills, which can be scrutinized by anyone
When it comes to naming beneficiaries for life insurance, one of the key advantages of using a trust is the enhanced privacy it offers. Unlike wills, which are public documents that can be accessed by anyone, trust distributions are kept confidential and private. This means that the details of how your assets are allocated upon your passing remain hidden from the public eye.
In the case of a will, once it is filed with the court, it becomes a matter of public record. Anyone can access and examine the will, including family members, friends, and even strangers. This level of exposure can lead to potential disputes and conflicts, especially if the distribution of assets is not clearly outlined. However, with a trust, the distribution of your possessions is managed by a trustee, who is responsible for following the instructions set forth in the trust document. This process is typically carried out privately, ensuring that the details of your estate's allocation remain confidential.
The privacy afforded by trust distributions is particularly important for those who wish to keep their financial affairs discreet. It allows for a more personalized and tailored approach to asset allocation, as the trust can be customized to fit specific needs and wishes. For example, a trust can be structured to provide for different beneficiaries at different stages of their lives, ensuring that the distribution of assets aligns with your desired timeline and goals. This level of customization is not possible with a public will, which must adhere to legal requirements and may not reflect your personal preferences.
Furthermore, the privacy of trust distributions can provide a sense of security and peace of mind. Knowing that your affairs are being managed privately can reduce the risk of fraud or exploitation, as the details of your estate are not readily available to others. This is especially crucial when dealing with large sums of money or valuable assets, as it minimizes the potential for disputes or misunderstandings among beneficiaries.
In summary, naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary offers a significant advantage in terms of privacy. Trust distributions are private and confidential, ensuring that your personal wishes and asset allocation plans remain hidden from public scrutiny. This level of privacy provides a more secure and personalized approach to estate planning, allowing you to manage your affairs according to your specific needs and preferences.
Hepatitis C: Life Insurance Options and Availability
You may want to see also

Long-Term Management: Trusts can ensure consistent management and distribution of assets over time
Trusts are powerful legal instruments that can significantly enhance the long-term management and distribution of assets, especially when it comes to life insurance beneficiaries. One of the primary reasons to name a trust as a beneficiary is to ensure a consistent and controlled distribution of the insurance proceeds. When an individual is named as a direct beneficiary, the insurance company typically pays out the death benefit directly to the named person. However, this direct payment can lead to potential issues, especially if the beneficiary is not well-prepared to handle the financial responsibility.
By naming a trust as the beneficiary, the insurance proceeds are not paid out in a lump sum to an individual. Instead, the trust acts as a legal entity that can provide a structured and consistent approach to managing and distributing the assets. This is particularly beneficial for long-term financial planning and can help avoid potential pitfalls that may arise with direct beneficiaries. The trust can be designed to provide for the needs of the insured individual's family, spouse, or other dependents over an extended period.
The management of the trust can be tailored to the specific requirements of the family. For instance, the trust can be structured to provide regular payments for the support and maintenance of the family, ensuring that the beneficiaries have a steady income stream. This is especially useful for covering daily expenses, mortgage payments, or any other financial obligations that the family may have. Over time, the trust can also be used to accumulate and grow assets, providing a long-term financial safety net.
Furthermore, trusts offer a level of control and flexibility that direct beneficiaries may not have. The trustee, who is responsible for managing the trust, can make decisions regarding the distribution of funds based on the trust's terms and the best interests of the beneficiaries. This can include investing the assets, making regular payments, or providing for specific needs, all while ensuring the long-term stability of the trust. This level of control is crucial for maintaining the intended purpose of the insurance policy and can provide peace of mind to the insured individual and their beneficiaries.
In summary, naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary is a strategic approach to long-term asset management and distribution. It ensures that the insurance proceeds are managed consistently and controlled, providing for the financial needs of the beneficiaries over an extended period. With the ability to tailor the trust's management and distribution, individuals can create a robust financial plan that benefits their loved ones and provides a sense of security for the future.
Terminal Diagnosis: Life Insurance Options and Availability
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary can provide several benefits. Firstly, it allows for a more flexible distribution of the insurance proceeds, as the trust can be structured to benefit multiple individuals or entities. This can be especially useful for families with complex financial needs or those who want to ensure that the funds are managed according to specific instructions. Additionally, a trust can provide a layer of privacy, as the beneficiaries are not directly named on the policy, and the distribution of the proceeds can be managed by a trustee, who can make decisions based on the trust's terms.
Naming a trust as a life insurance beneficiary can have tax advantages. When a trust is the designated beneficiary, the insurance proceeds are typically paid out to the trust, not directly to an individual. This can help minimize the tax impact on the policyholder's estate, as the proceeds may be subject to lower tax rates or even tax-free status, depending on the trust's structure and the jurisdiction. Furthermore, the trust can be designed to distribute the proceeds in a tax-efficient manner, potentially reducing the overall tax liability for the beneficiaries.
Yes, a trust can remain a beneficiary even if the policyholder decides to change the beneficiaries. Once a trust is named as a beneficiary, it becomes a permanent part of the policy's ownership structure. The policyholder can update the policy to reflect new beneficiaries, but the trust's status as a beneficiary will persist unless explicitly removed. This flexibility allows individuals to adapt their insurance plans as their financial goals and relationships evolve over time.







