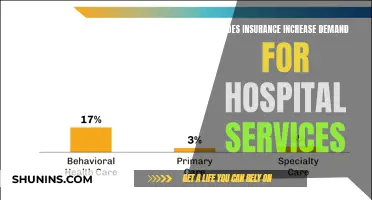
The date of service is a crucial aspect of medical billing, particularly when health insurance is involved. It refers to the specific time a patient receives medical treatment, and this date is recorded for billing and insurance purposes. Health insurers utilise the date of service, along with other factors, to determine reimbursement or payment amounts. After receiving treatment, the insured individual's insurance data is verified to ascertain whether the policy covers the treatment sought. Once confirmed, comprehensive treatment details, including the date of service, are forwarded to the insurer. The reimbursement or payment timing depends on the speed of data submission and the compatibility of the information with the insurer's system.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Date of service definition | The specific time at which a patient has been given medical treatment |
| Date of service purpose | Recorded for billing purposes, as an item in a patient's medical record, and for insurance reimbursement or payment |
| Who records the date of service | The patient's doctor or hospital |
| Date of service and billing | The date of service is not the same as the bill preparation date |
| Date of service and insurance | Health insurers base their reimbursement or payment on the date of service, along with other billing factors |
What You'll Learn

The date of service is when a patient receives medical treatment
The date of service is a specific time at which a patient receives medical treatment. It is a key date recorded for billing purposes and as an entry in a patient's medical record. The date of service is also important for insurance purposes, as health insurers use it as a basis for reimbursement or payment, along with other billing factors.
The date of service is recorded in a patient's medical record, which contains other important information such as diagnosis, treatment, and medication. This record is maintained by the patient's doctor or hospital and is used for reference and continuity of care. It is also used for billing and insurance purposes, as mentioned earlier.
When a patient receives medical treatment, the doctor's office or hospital submits a bill, also called a claim, to the patient's insurance company. This claim includes the date of service and a list of services provided by the doctor or hospital. The insurance company then uses this information to process the claim and reimburse or pay the doctor or hospital accordingly.
It is important to note that the date of service on the bill or claim should match the date recorded in the patient's medical record. This ensures accuracy in billing and helps to avoid any discrepancies or surprises in the patient's explanation of benefits (EOB). The EOB is a report sent by the insurance company to the patient, detailing what the insurance company paid for, what it didn't pay for, and why. It is not a bill but provides transparency and helps patients understand their financial responsibility.
In summary, the date of service is a critical piece of information in the medical billing and insurance process. It is recorded when a patient receives medical treatment and is used for billing, record-keeping, and insurance reimbursement purposes. Patients should always review their EOBs and ensure that the dates of service listed match their records to avoid any unexpected charges or discrepancies.

The date is recorded for billing and insurance purposes
The date of service is a specific time record of when a patient has been given medical treatment. It is a crucial piece of information that is recorded for billing and insurance purposes.
For billing, the date of service is essential as it allows for the creation of a bill or claim, which outlines the services provided to the patient on that date. This bill is then submitted to the patient's insurance company, which uses the information to reimburse or pay the healthcare provider accordingly. The date of service is also crucial for insurance purposes, as it helps insurance companies determine the reimbursement or payment amount based on the patient's policy coverage and other billing factors.
Additionally, the date of service is essential for maintaining accurate medical records for patients. It provides a timeline of when specific treatments or procedures were administered, which can be vital for ongoing care, monitoring, and future reference. The date of service also helps patients understand their medical bills and insurance coverage by providing a detailed breakdown of the services they received and the associated costs.
Moreover, the date of service plays a role in surprise medical billing protection. For instance, the No Surprises Act protects patients from surprise billing for emergency services and limits out-of-network cost-sharing. By recording the date of service, patients can identify when they received treatment and whether they are protected from unexpected charges.
In summary, the date of service is a critical piece of information that is recorded to facilitate billing, insurance reimbursement, and patient record-keeping. It ensures transparency in medical billing, helps patients understand their insurance coverage, and provides protection against surprise medical bills.
The Underwriting Craft: Unraveling the Art of Insurance Risk Assessment
You may want to see also

The patient's insurance data is verified before treatment
Verifying a patient's insurance coverage before providing treatment is a crucial step in the medical billing process. It ensures that healthcare providers know whether the services they are about to provide will be covered by the patient's insurance and to what extent. This process is beneficial for both patients and healthcare providers.
Benefits for Patients
- Patients can avoid unexpected bills and understand their financial obligations ahead of time.
- Patients won't face costly surprises and will have a better experience as they will understand their financial obligations.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
- Healthcare providers can be sure that they will receive payment for the services rendered, reducing the chances of denied claims, which can be costly and time-consuming to resolve.
- It ensures a steady cash flow as providers are more likely to receive timely payments from insurance companies.
- It reduces administrative burdens by minimising the need to address denied claims and chase payments after services have been rendered.
- It enables more efficient scheduling and resource allocation as providers can focus on providing services that are likely to be covered by insurance.
- It improves communication between healthcare staff and patients about their coverage and out-of-pocket expenses, facilitating discussions about alternative treatment options.
The Insurance Verification Process
The insurance verification process typically involves the following steps:
- Collecting comprehensive patient information, including insurance cards, policy details, and identification documents.
- Contacting the insurance provider to confirm the validity and specifics of the patient's insurance coverage.
- Recording accurate information about the patient's insurance coverage to create a solid foundation for the medical claim.
- Following up with the patient as needed to clarify any concerns or questions about insurance information.
Best Practices for Insurance Verification
- Verify insurance coverage before scheduling appointments or performing elective procedures so that patients are aware of their financial responsibilities.
- Develop standardised workflows and protocols for insurance verification to maintain consistency and reduce variations in the process.
- Utilise technology and automation to streamline the insurance verification process. Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and practice management software often offer integrated insurance verification modules.
- Establish collaborative relationships with insurance companies and payers to streamline the verification process and resolve any coverage issues.
Get in Touch: A Guide to Contacting Momentum Short-Term Insurance
You may want to see also

The insurer's reimbursement depends on the data format compatibility
The billing process for medical services is a complex one, involving many stakeholders and a multitude of steps. It is important to understand the intricacies of this process to ensure that reimbursements are made accurately and efficiently. One critical aspect of this process is data format compatibility, which can have a significant impact on the insurer's reimbursement.
When a patient receives medical treatment, the date of service is recorded, along with other relevant information, for billing and insurance purposes. This information is then submitted by the healthcare provider to the patient's insurance company in the form of a claim or bill. The claim details the services provided, including medical transportation, and any relevant medical codes. It is essential that the data in this claim is compatible with the insurer's system to avoid delays or issues in reimbursement.
Incompatible data formats can lead to errors and delays in the reimbursement process. If the claim contains errors or fails to meet the insurer's formatting requirements, it may be rejected, resulting in a delay in reimbursement. To mitigate this, clearinghouses play an important role by standardizing and screening medical claims before sending them to the insurer. This helps to ensure that the data is in the correct format and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Additionally, the timely reimbursement of claims is crucial for healthcare providers to maintain their cash flow and financial stability. Delays in reimbursement can impact their ability to provide services and manage their operations effectively. Therefore, ensuring data format compatibility is essential to facilitate prompt and accurate reimbursement.
Moreover, the use of standardized coding systems, such as CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System), plays a vital role in streamlining the billing process. These coding systems enable healthcare providers and insurers to communicate and track billing more efficiently. Standardized codes help ensure that services are accurately described and billed, reducing potential errors and discrepancies.
In conclusion, data format compatibility is critical in the medical billing process as it directly impacts the insurer's reimbursement. Incompatible data formats can lead to errors, delays, and additional costs. By ensuring compatibility and adhering to standardized coding systems, healthcare providers can streamline the billing process, receive timely reimbursements, and ultimately provide better care to their patients.
Decorrelation's Impact: Unraveling the Intricacies of Insurance Risk Management
You may want to see also

The patient may need to pay a co-payment
Co-payments are usually lower for standard doctor visits than for specialists, and emergency room visits tend to have the highest co-payments. The amount of the co-payment is determined by the insurance plan and is outlined in the policy document. It is important to carefully review the terms and conditions of the policy to understand the co-payment requirements.
Co-payments are different from deductibles, which are a fixed amount that must be paid by the patient before the insurance company begins covering any expenses. Deductibles are often annual, and once met, the patient typically pays co-insurance, which is a certain percentage of costs, until they reach their out-of-pocket maximum for the year.
The purpose of co-payments is to encourage policyholders to be more involved in their healthcare decisions and to discourage unnecessary medical expenses. It also helps to keep insurance premiums lower since the policyholder shares a portion of the cost. Additionally, co-payments prevent the misuse of insurance policies by discouraging unnecessary claims.
While co-payments can help lower insurance premiums, high co-payments may deter people from seeking necessary medical care. It is important for individuals to carefully consider their health status, financial situation, and comfort with risk when deciding whether to opt for a policy with a co-payment.
The Renewal Riddle: Unraveling the Mystery of Level Term Insurance
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The date of service is the date on which a patient has been given medical treatment. It is recorded for billing purposes, as well as for a patient's medical record.
A bill is a printed summary of your medical bill. An EOB, on the other hand, is a report sent by the insurance company to show what they did when they received the bill from the doctor's office. An EOB is not a bill.
The No Surprises Act (NSA) protects you from surprise billing for emergency services if you have a group health plan or group or individual health insurance coverage. It limits the amount of surprise bills for emergency services from an out-of-network provider or facility without prior authorization.
A surprise medical bill is an unexpected bill, often from an out-of-network provider or facility. It can also be a bill for services received from a healthcare provider or facility that you did not know was out-of-network until you were billed.