Life insurance is a financial safety net for your loved ones in the event of your death. It is a contract between you and an insurance company, where the company agrees to pay a sum of money, known as a death benefit, to your chosen beneficiaries. This money can be used to cover living expenses, pay off debts, fund children's education, or keep a family business going.
There are two main types of life insurance: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a certain period, usually between 10 and 30 years, and is generally the more affordable option. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, offers lifelong coverage and often includes a cash value component that can be accessed while the insured is still alive.
When considering life insurance, it is important to evaluate your financial situation and determine how much money would be needed to maintain your beneficiaries' standard of living. Factors such as age, health, and lifestyle can affect the cost of premiums, with younger and healthier individuals typically paying lower rates.
Life insurance can provide peace of mind and financial security for you and your loved ones. It ensures that your family will be taken care of, even if something unexpected happens to you.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide financial support to surviving dependents or other beneficiaries after the death of an insured policyholder |
| Policy types | Term life insurance, Permanent life insurance, Whole life insurance, Universal life insurance, Variable universal life insurance, Indexed universal life insurance, Credit life insurance, Burial insurance, Survivorship life insurance, etc. |
| Policy components | Death benefit, Premium, Cash value |
| Beneficiaries | Spouse, Dependents, Children, Parents, Siblings, Business partners, etc. |
| Requirements | Permission from the insured, Insurable interest, Medical exam, etc. |
What You'll Learn
- You need an insurable interest and permission to get life insurance for someone else
- Credit life insurance covers specific loans, like a home or vehicle loan
- Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance with a savings component
- Life insurance beneficiaries can receive the death benefit in a lump sum, annuity, or specific income payout
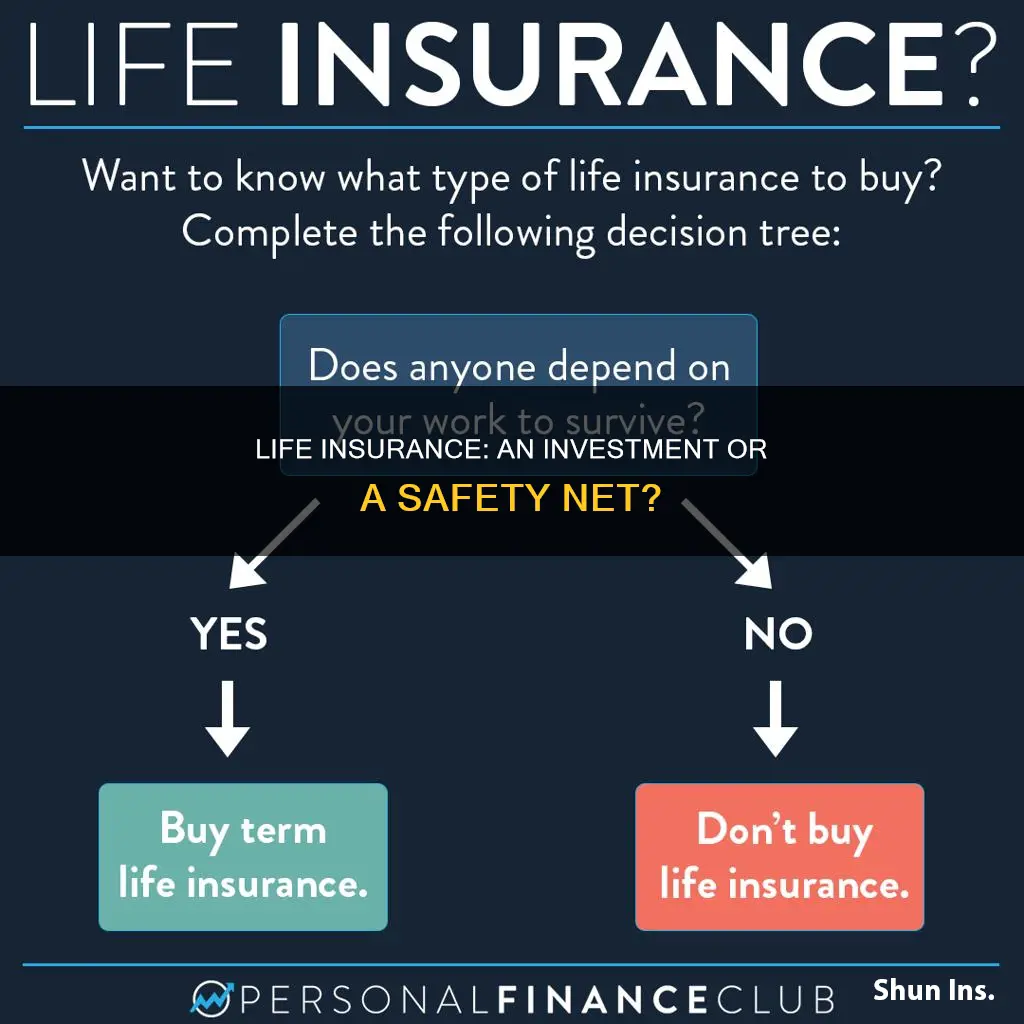
- Life insurance is not always necessary; it depends on whether your death would financially impact others

You need an insurable interest and permission to get life insurance for someone else
To get life insurance for someone else, you need to prove that you have an insurable interest in them. This means that you would experience financial hardship or loss if they were to pass away. For example, if you share finances with the insured, such as a spouse or business partner, their death could cause you financial hardship.
In addition to having an insurable interest, you must also get permission from the person you want to insure. The insured person must sign the insurance application, giving the insurance company permission to collect their data, including their medical history and hobbies. They will also likely have to undergo a medical exam. Therefore, it is not possible to take out a life insurance policy on someone without their knowledge and consent.
- You want to manage your parents' coverage as they age.
- You co-signed a loan, and the borrower dies, leaving you responsible for the remainder of the debt.
- You receive alimony or child support from an ex-spouse or former partner.
- You have business partners, and you want to fund a buy-sell agreement.
How to Cancel a Life Insurance Application
You may want to see also

Credit life insurance covers specific loans, like a home or vehicle loan
Credit life insurance is a type of life insurance policy designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding debts if the policyholder dies. It is typically used to ensure that large loans, such as mortgages or car loans, can be paid off in the event of the borrower's death. The face value of a credit life insurance policy decreases over time as the loan is paid off, in proportion to the outstanding loan amount. This means that the death benefit of a credit life insurance policy also decreases as the policyholder's debt decreases.
Credit life insurance is usually offered when someone borrows a significant amount of money, such as for a mortgage, car loan, or large line of credit. The policy then pays off the loan in the event of the borrower's death. This type of insurance is particularly relevant if there is a co-signer on the loan, as it would protect them from having to make loan payments after the policyholder's death. In most cases, heirs who are not co-signers are not obligated to pay off the loans of the deceased. However, in the few states that recognize community property, a spouse could be liable for the debts of their deceased partner.
Credit life insurance is a specialised type of policy with a term that corresponds to the maturity of the loan. It is worth noting that credit life insurance is always voluntary, and it is against the law for lenders to require it as a condition of a loan. The beneficiary of a credit life insurance policy is the lender, not the family of the deceased. If your goal is to protect your beneficiaries from inheriting your debts, a conventional term life insurance policy may be a better option. Term life insurance is usually more affordable than credit life insurance for the same coverage amount and the benefit will be paid to your chosen beneficiary, rather than the lender.
Credit life insurance can be purchased in two ways. Firstly, as a "single premium" purchase, where the full premium is calculated upfront and added to the loan amount. Alternatively, it can be based on the "monthly outstanding balance", where the payment varies according to the loan balance.
Smart Strategies for Investing in Bank-Owned Life Insurance
You may want to see also

Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance with a savings component
Whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that covers the insured person for their entire life. It is more expensive than term life insurance but offers a guaranteed death benefit and combines this with a savings component. This savings component, known as the cash value, can be used to take out loans or pay premiums, and it accumulates on a tax-deferred basis.
Whole life insurance policies typically feature level premiums, meaning the amount paid every month remains the same. The cash value of a whole life policy usually earns a fixed rate of interest, although some policies may earn a variable rate. Withdrawals and outstanding loan balances will reduce the death benefit.
Whole life insurance is different from term life insurance, which only provides coverage for a certain number of years and does not have a cash savings component. Term life insurance is also generally much cheaper than whole life insurance.
Whole life insurance policies are distinguished as participating and non-participating plans. With a non-participating policy, any excess of premiums over payouts becomes profit for the insurer. With a participating policy, any excess is redistributed to the insured as a dividend. Dividends can be used to make payments or increase coverage limits, but they are not guaranteed and will vary depending on the company's financial performance.
Whole Life Insurance: Are Dividend Scales Guaranteed?
You may want to see also

Life insurance beneficiaries can receive the death benefit in a lump sum, annuity, or specific income payout
Life insurance beneficiaries can receive the death benefit in a few different ways. The death benefit is a payout to the beneficiary of a life insurance policy, annuity, or pension when the insured person or annuitant dies. The death benefit can be received as a lump sum, annuity, or specific income payout.
Lump Sum
The death benefit is commonly issued as a lump-sum payment in the full amount of the benefit. This means that the beneficiary will receive the entire death benefit amount in one go.
Installments
Another option for beneficiaries is to accept the death benefit in installments. This could be in the form of regular payments, such as quarterly or monthly, until the proceeds are depleted or for a set period.
Annuity
Beneficiaries may also choose to receive an annuity, which makes payments in installments for life. The amount of each payment is determined by the insurer.
Interest Payments
Beneficiaries can also opt to take only the interest payments and then pass on the proceeds to another beneficiary.
The choice of how to receive the death benefit depends on the specific circumstances and preferences of the beneficiary. It is important to carefully consider the options and seek financial advice if needed to make an informed decision.
First Citizens Bank: Life Insurance Offerings and Benefits
You may want to see also

Life insurance is not always necessary; it depends on whether your death would financially impact others
Life insurance is a financial safety net that provides a death benefit to your beneficiaries when you pass away. It is not always necessary and depends on whether your death would financially impact others. Here are some scenarios where life insurance may not be necessary:
- No Dependents or Financial Obligations: If you are a young, single adult with no financial dependents, such as children or aging parents, and no significant financial obligations like debt or mortgage, then life insurance may not be a priority. In this case, your loved ones are unlikely to face financial hardship in your absence.
- Adequate Savings and Investments: If you have substantial savings and investments that can cover end-of-life expenses and support your loved ones financially, life insurance may not be needed. This is especially true if your loved ones can easily support themselves without your income.
- Alternative Financial Plans: You may have alternative plans to provide for your beneficiaries financially. For example, you might have an investment account that you believe can meet their financial needs in the event of your death.
- No Income Replacement Needed: If you are not the primary earner in your family and your income is not essential for supporting your dependents or meeting financial commitments, life insurance may not be necessary.
- Tight Budget: If your budget is tight and you are struggling to meet basic necessities like housing, food, and utilities, life insurance might not be a feasible option.
However, it's important to note that life insurance can provide benefits beyond income replacement. It can also be used for estate planning, tax advantages, and building long-term wealth. Additionally, life circumstances can change, and it's a good idea to periodically reassess your financial situation to determine if life insurance is needed.
Life Insurance 101: Understanding the Basics of Coverage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can finance life insurance through a broker or agent, or directly from an insurance company. You can also get free quotes online.
Term life insurance is temporary, lasting for a set number of years, and is generally the more affordable option. Permanent life insurance covers the insured person's entire life and usually includes a cash value component.
Life insurance is ideal for those who want to provide financial security for their loved ones after they're gone. This includes parents of minor children, stay-at-home parents or spouses, adults who co-own property or have shared debts, and small business owners, among others.







