Paying insurance bills is unlikely to build your credit score, even if you've been doing so for years. This is because insurance companies don't lend money and don't report to credit bureaus. However, if you don't pay your insurance bills, your account may be sent to collections, which can damage your credit score. One way to indirectly build your credit score with insurance payments is to pay your insurance bills with a credit card and make timely payments on that card.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Do insurance bills build credit? | No, insurance companies do not lend money and do not report to credit agencies. |
| How can insurance payments indirectly build credit? | By paying insurance bills with a credit card and making timely payments. |
| What happens if insurance bills are not paid? | It will not impact the credit score but may affect ongoing coverage. |
| Can insurance companies check credit scores? | Yes, some insurance companies may check credit scores before quoting an insurance premium. |
What You'll Learn

Paying insurance bills with a credit card
Advantages of paying insurance with a credit card
Using a credit card to pay for insurance can have several benefits:
- On-time payments: Setting up autopay ensures timely payments and helps avoid late fees.
- Paying in full: Credit cards make it easier to pay the policy in full and take advantage of discounts offered by insurers for annual payments.
- Rewards: Using a credit card that offers rewards can help accumulate points for travel or other benefits.
- Convenience: Paying insurance with a credit card helps keep all payments in one place and makes expense tracking easier.
Disadvantages of paying insurance with a credit card
There are also some drawbacks to consider when paying insurance with a credit card:
- Credit score damage: A higher card balance can negatively impact your credit score, especially if the utilisation tops 30%.
- Accumulating interest: Credit cards charge high interest rates, so it's important to pay off the balance each month to avoid extra charges.
- Additional fees: Some insurance companies charge extra fees for credit card payments, which can negate the benefits.
Factors to consider when paying insurance with a credit card
When deciding whether to pay insurance with a credit card, it's important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Check for fees: Ensure there are no additional fees for using a credit card, as this could increase the overall cost of insurance.
- Pay the balance in full: Make sure you can pay off the credit card balance in full and on time to avoid interest charges and maintain a good credit score.
- Compare insurance companies: Not all insurers accept credit card payments, so it's important to check with your provider.
- Evaluate your financial situation: Only use a credit card if you can afford to pay the insurance bill. Routinely using a credit card for bills you can't afford can lead to high-interest debt.
Telemedicine's Role in Term Insurance: Revolutionizing Access and Efficiency
You may want to see also

How insurance companies view credit scores
Insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to determine insurance premiums. These scores are based on credit reports and are designed to predict the likelihood of filing an insurance claim that will lead to a loss for the insurer. While insurance scores are based on credit scores, they are not the same thing. Lenders use credit scores to determine how likely someone is to repay a loan, whereas insurance scores are used to determine the likelihood of filing a claim.
In most states, insurers can use credit-based insurance scores to determine premiums. However, eight states forbid home and auto insurance companies from using credit-based insurance scores when offering or renewing a policy, or deciding how much to charge in premiums. These states are California, Hawaii, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Nevada, Oregon, and Utah.
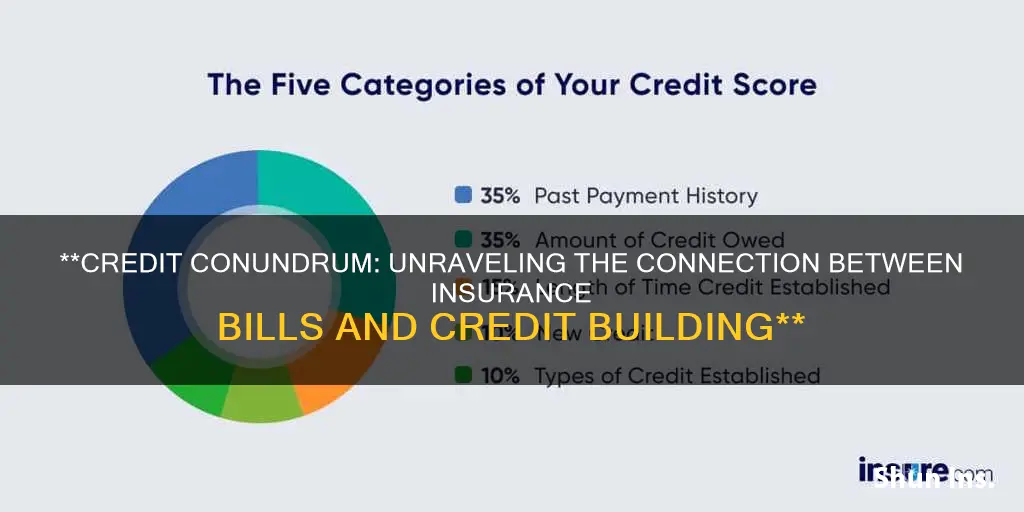
Insurance scores typically take credit scores into account and may be referred to as credit-based insurance scores. Insurance companies may also consider other factors, including insurance claim history and car accident history. While insurance companies generally do not disclose the specific factors and weightings used in their scores, FICO uses the following to determine credit scores:
- Payment history (40%)
- Outstanding debt (30%)
- Length of credit history (15%)
- Pursuit of new credit (10%)
- Credit mix (5%)
A higher insurance score indicates a lower risk to the insurance company and may result in lower insurance premiums. Conversely, a lower score suggests a higher risk and could lead to higher premiums.
Understanding Rider Benefits: Maximizing Your Term Insurance Coverage
You may want to see also

How insurance claims impact credit scores
Insurance claims can impact credit scores in several ways, depending on the circumstances and the type of insurance involved. Here are some key points to consider:
Car Insurance Claims
Car insurance claims generally do not have a direct impact on credit scores. Insurance companies do not report premium payments or claims to credit bureaus since insurance is not a form of credit. However, there are a few ways in which car insurance claims can indirectly affect your credit:
- Deductibles and Uncovered Expenses: If you cause an accident and need to pay a deductible or any expenses not covered by your insurance, it may strain your finances. This could affect your ability to manage other credit obligations and, indirectly, your credit score.
- Policy Cancellation: If you fail to pay your insurance premiums on time, your policy may be cancelled. Missed payments or policy cancellation can result in a past-due balance, which the insurance company may report to credit bureaus, negatively impacting your credit score.
- Collections: If you consistently fail to pay your premiums, your insurance provider may consider your account in default and send it to a debt collection agency. Debt collection activities can further damage your credit.
Health Insurance Claims
Health insurance claims themselves do not directly impact your credit score. However, if you incur significant medical expenses not covered by your insurance, it could affect your finances and your ability to manage other credit obligations, which may indirectly influence your credit score.
Other Factors to Consider
- Credit Card Payments: If you pay your insurance premiums using a credit card and fail to make timely payments on the credit card, it will negatively impact your credit score.
- Credit-Based Insurance Scores: Some insurance companies use credit-based insurance scores to assess the likelihood of a policyholder filing a claim. These scores are based on factors such as payment history, outstanding debt, and credit use. While these scores are not the same as credit scores, they can influence the insurance rates you are offered.
- Soft and Hard Inquiries: Getting insurance quotes typically involves soft inquiries, which do not affect your credit score. However, applying for insurance may sometimes result in hard inquiries, which can have a small and temporary impact on your score.
The Fine Line Between Insurance and Utility Bills: Understanding the Difference
You may want to see also

The consequences of unpaid insurance bills
- Collections Calls and Letters: If your insurance bill remains unpaid for an extended period, it will likely be sent to a collection agency. This means you will start receiving frequent calls and letters demanding payment, which can be stressful and overwhelming."
- Lien on Property or Wage Garnishment: If the unpaid insurance bills continue, your creditors may be able to take more severe actions, such as placing a lien on your property or garnishing your wages. A lien gives the creditor the right to possess your property, such as your home or car, and a wage garnishment allows them to deduct debt payments directly from your salary."
- Negative Impact on Credit Score and Report: Unpaid insurance bills can significantly damage your credit score and report. This will make it challenging to secure loans, rent an apartment, or purchase a car, as these situations typically require a credit check."
- Late Fees and Interest: Failure to pay your insurance bills on time can result in late fees and interest charges, increasing the overall amount you owe."
- Loss of Coverage: Prolonged non-payment of insurance bills may result in the cancellation of your insurance policy, leaving you without the necessary protection."
- Legal Consequences: In some cases, unpaid insurance bills can lead to legal consequences, including lawsuits and court judgments. This could further damage your financial situation and creditworthiness."
It is important to stay on top of your insurance payments to avoid these consequences and maintain a positive credit history.
Unraveling the Web of Deceit: Understanding Insurance Deceits and Their Synonyms
You may want to see also

How to build credit
Building credit can be tricky, especially if you don't have a credit history. Here are some tips to help you build your credit:
Get a Secured Credit Card
If you're building your credit score from scratch or have a bad credit history, you'll likely need to start with a secured credit card. A secured card is backed by a cash deposit you make upfront; the deposit amount is usually the same as your credit limit. You'll use the card like any other credit card: buy things and make payments on or before the due date. You'll receive your deposit back when you close the account.
Get a Credit-Builder Product or a Secured Loan
A credit-builder loan is designed to help people build credit. Typically, the money you borrow is held by the lender in an account and not released to you until the loan is repaid. Your payments are reported to credit bureaus. These loans are most often offered by credit unions or community banks.
Become an Authorized User
You can become an authorized user on someone else's credit card account. Authorized users have access to an existing credit card account and might even get their own card, but the primary account holder is ultimately responsible for payments. If the issuer reports authorized user activity to the credit bureaus, positive habits could benefit you.
Get Credit for the Bills You Pay
Rent-reporting services take a bill you are already paying and put it on your credit report, helping to build a positive history of on-time payments. Experian Boost offers a way to have your cell phone and utility bills reflected in your credit report.
Practice Good Credit Habits
Building a good credit score takes time and a history of on-time payments. Make your payments on time, pay more than the minimum if you can, keep your credit utilization low, avoid applying for multiple credit accounts close together, and keep credit card accounts open.
Check Your Credit Scores and Reports
Monitor your credit scores and reports to watch for errors and to see your credit-building efforts pay off. You can request your credit report in Spanish directly from each of the three major credit bureaus: TransUnion, Equifax, and Experian.
Unraveling the Complexities of Hostile Fire in Insurance Policies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Paying insurance bills does not directly build credit. However, paying insurance bills with a credit card can indirectly help build credit.
Insurance companies do not lend money, and they do not report payment histories to credit rating agencies. Credit scores are based on the contents of TransUnion, Equifax, and Experian credit reports, which document our history of borrowing and repaying money via loans and lines of credit.
You can build your credit score by using a credit card to make insurance payments and then paying off your credit card by the due date.
If you don't pay your insurance bills, your provider may cancel your insurance coverage or charge you fees. However, unpaid insurance bills won't impact your credit score unless your debt is sent to collections.
Some insurance companies may check credit scores before quoting an insurance premium. They will assess your score, which may impact the size of your premium.







