Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and death benefit adjustments. It also provides lifelong coverage and allows policyholders to build cash value over time. The interest rate on the cash value is set by the insurance company and can change frequently, though there is usually a guaranteed minimum rate. This means that interest rates can vary for universal life insurance policies.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Permanent life insurance |
| Coverage | Lifelong |
| Cash value | Grows over time based on an interest rate set by the insurance company |
| Premium payments | Adjustable |
| Death benefit | Adjustable |
| Interest rate | Set by the insurance company |
| Interest rate frequency | Can change frequently |
| Minimum interest rate | Guaranteed |
What You'll Learn

Interest rates and cash value growth
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and death benefit adjustments. It also has a cash value component that grows over time based on an interest rate set by the insurance company. This cash value can be accessed through loans or withdrawals, but it is important to note that doing so may reduce the death benefit and accrue owed interest.
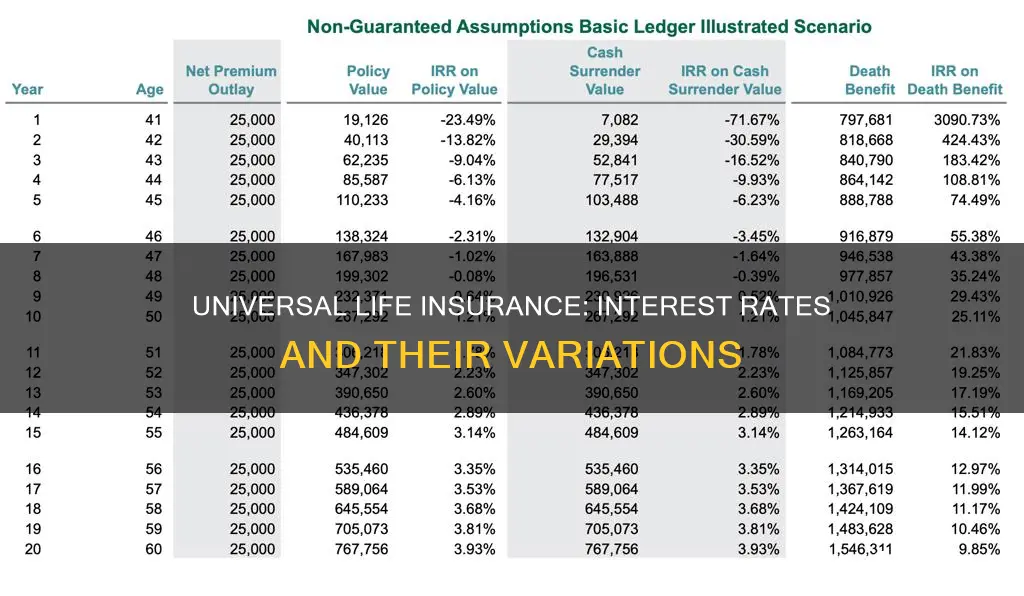
The interest rate on universal life insurance policies is not fixed and can change frequently. However, these policies typically have a guaranteed minimum interest rate to protect policyholders from significant losses. The interest rate on the cash value component of universal life insurance policies can vary depending on the insurance company and the market performance. The insurance company sets the interest rate, and it may be based on the current market rate or the policy's minimum interest rate, whichever is higher.
Universal life insurance offers more flexibility than whole life insurance when it comes to premium payments and death benefit adjustments. Policyholders can choose to pay more than the minimum premium, and the additional funds, minus administrative charges, will be added to the cash value. Alternatively, they can pay less than the minimum premium as long as there is sufficient cash value to cover the insurance costs and expenses. However, if the cash value is insufficient, the policy may lapse.
The cash value in a universal life insurance policy can be used in several ways. It can be borrowed against, used as collateral for a loan, or used to pay premiums. Withdrawing cash from the policy permanently reduces both the cash value and the death benefit and may have tax implications. On the other hand, policy loans do not require repayment and are not taxed, but any unpaid loans will reduce the death benefit.
Overall, universal life insurance provides policyholders with flexible coverage options and the potential for cash value growth. However, it is important to actively monitor the policy to ensure sufficient cash value and avoid large payment requirements or policy lapse.
Term Life Insurance: Cashing Out and Claiming Benefits
You may want to see also

Policy loans and withdrawals
- Policy loans allow you to borrow money from the insurance company, using the cash value of your policy as collateral. The loan accrues interest, but there is usually no requirement to repay it during your lifetime. However, if the loan and interest are not repaid, the outstanding balance will reduce the death benefit paid to your beneficiaries.
- Withdrawals allow you to directly withdraw cash from the policy's cash value. Withdrawals permanently reduce both the cash value and the death benefit. They do not accrue interest and do not need to be repaid.
- Both policy loans and withdrawals can have long-term consequences. If the cash value falls too low, it could lead to higher premiums or even cause your policy to lapse. Therefore, careful monitoring of the cash value is necessary to ensure the policy remains in force.
- The interest rates on policy loans are typically set by the insurance company and can be either fixed or variable. Compared to traditional loans, policy loans often have lower interest rates, and there is usually no credit check or income verification required.
- Policy loans and withdrawals provide flexibility and quick access to funds, which can be useful for unexpected expenses, debt consolidation, or investment opportunities. However, it's important to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks, such as reduced death benefits and the risk of policy lapse.
- Before taking out a policy loan or withdrawal, it is recommended to consult a financial advisor to understand the full financial implications and ensure it aligns with your long-term financial goals.
Life Insurance and Taxes: What's the Write-Off Story?
You may want to see also

Whole life insurance vs universal life insurance
Whole life insurance and universal life insurance are both permanent life insurance policies, but they have some key differences. Whole life insurance offers fixed premiums and a guaranteed death benefit, meaning you won't have to worry about increasing payments or a changing benefit. This makes it a more stable and predictable option. On the other hand, universal life insurance provides flexibility, allowing you to adjust your premiums and death benefit as your circumstances change. This adaptability can be beneficial if you have a fluctuating income or evolving needs.
When it comes to the cash value component, whole life insurance offers a guaranteed cash value build-up over the life of the policy, with a fixed interest rate. This means you know exactly what to expect in terms of growth. In contrast, universal life insurance policies have the potential to accumulate cash value, but it may fluctuate over time based on market performance, the way you fund the policy, and other factors. Universal life insurance typically has a guaranteed minimum interest rate, with the potential for higher returns when the market performs well. However, there is also the risk of lower returns when the market underperforms.
Another distinction between the two types of policies lies in their complexity and management requirements. Whole life insurance is generally simpler and requires less management, as the premiums, death benefit, and interest rate are fixed. Universal life insurance, on the other hand, may necessitate careful monitoring of the cash value to ensure it remains sufficient as insurance charges increase with age. This active management is essential to avoid lapses in coverage or unexpected increases in premiums.
In terms of cost, whole life insurance tends to have higher premiums due to the guaranteed nature of its benefits. Universal life insurance, with its flexibility and potential for higher returns, usually comes with lower premiums. However, it's important to note that universal life insurance can be more expensive than term life insurance, which offers sufficient coverage for most families.
Ultimately, the choice between whole life and universal life insurance depends on your unique circumstances and preferences. If you prioritise stability, predictability, and guaranteed benefits, whole life insurance may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you value flexibility, customisation, and the potential for higher returns, universal life insurance could be the better option. Consulting with a financial advisor can help you weigh these factors and make an informed decision based on your long-term goals and financial plan.
How Life Insurance Loans Affect Your Interest Charges
You may want to see also

Different types of universal life insurance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance, which means it offers lengthy coverage and builds cash value over time. There are several types of universal life insurance policies, each with its own unique features and benefits. Here are some of the most common types:
Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance:
This type of policy offers a guaranteed death benefit and premium payments that remain fixed throughout the policyholder's life. It is often considered a compromise between term and whole life insurance, as it offers lower rates and minimal cash value growth. The policy will not lapse if the cash value is zero, making it a low-risk option.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance:
The cash value growth of indexed universal life insurance is linked to the performance of a stock market index, such as the S&P 500. While this offers the potential for higher returns, there is also a cap on the maximum interest rate that can be earned. Indexed universal life insurance provides downside protection, ensuring that the cash value does not drop below a specified minimum.
Variable Universal Life Insurance:
Variable universal life insurance combines the flexibility of universal life insurance with investment options similar to mutual funds. Policyholders can choose to invest their cash value in various sub-accounts, including stocks, bonds, and money market funds. While this offers the potential for higher returns, it also comes with increased risk and higher management fees.
Standard Universal Life Insurance:
This type of policy allows policyholders to adjust their premium payments and death benefit as their financial situation changes. The cash value of a standard universal life insurance policy grows based on the performance of the insurer's portfolio and can be used to pay premiums or borrow money against it.
Each type of universal life insurance has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best option depends on an individual's financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term needs. It is important to carefully review the features and potential risks of each policy before making a decision.
Health Insurance: A Key to Longevity?
You may want to see also

Pros and cons of universal life insurance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers lifelong coverage and builds cash value over time. It is a flexible option for those who want to adjust their premiums and death benefits as their financial needs change. However, it is important to weigh the pros and cons before deciding if this type of insurance is right for you.
Pros of Universal Life Insurance
- Flexible premium payments: Universal life insurance allows you to adjust your premium payments as your financial situation changes. You can pay more during good financial periods or reduce payments when finances are tight, as long as there is enough cash value to cover the costs.
- Adjustable death benefit: You have the flexibility to increase or decrease the death benefit. Increasing it may require a medical exam, but this option allows the policy to adapt to changing needs.
- Potential cash value growth: The cash value in your account will earn interest at a rate set by your insurer, and that rate can change frequently, offering the potential for higher returns.
- Lifetime coverage: Universal life insurance policies offer lifelong coverage, typically until ages 95 to 121, as long as premiums are paid and a positive cash value balance is maintained.
Cons of Universal Life Insurance
- Active management required: Universal life insurance policies require regular monitoring to ensure the cash value remains sufficient to cover costs. If the cash value drops too low, you may have to pay more to keep the policy in force or risk it lapsing.
- Potential for rising premiums: If you only pay the minimum required premiums, these costs can increase over time, especially as the cost of insurance rises with age.
- Complexity and higher costs: Universal life policies are complex and typically come with higher premiums than other types of life insurance. They may require careful monitoring to ensure the cash value remains sufficient as insurance charges increase with age.
- No guaranteed returns: Universal life insurance policies do not have fixed interest rates, so returns can be unpredictable. If interest rates drop, your cash value may not grow as expected.
Life Insurance: Sickness, Coverage, and Your Options
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and death benefit adjustments. It also has a cash value component that grows over time and can be accessed through loans or withdrawals.
Universal life insurance policies have two components: the cost of insurance (COI) and the cash value. The COI covers the charges for mortality, policy administration, and other expenses. The remaining premium payment goes into the cash value, which accumulates interest over time.
Universal life insurance offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefits, as well as the potential for cash value growth. However, it requires active management to ensure the cash value remains sufficient to cover costs. The interest rates on the cash value can be variable, and some withdrawals may be taxed.
Whole life insurance offers fixed premiums, death benefits, and guaranteed cash value growth. Universal life insurance provides more flexibility, with adjustable premiums and death benefits, but the cash value growth is not guaranteed and may vary with market performance.
There are three main types of universal life insurance: indexed universal life, variable universal life, and guaranteed universal life. Indexed and variable universal life policies offer the potential for higher returns by linking the cash value to market indexes or investments but also carry more risk. Guaranteed universal life provides a fixed premium and coverage for a specified term.