Auto insurance premiums are the amount of money an individual pays for an insurance policy. Auto insurance premiums are usually paid monthly, every six months, or annually. The cost of auto insurance premiums depends on a variety of factors, including age, gender, driving record, location, and the type of vehicle. The national average premium for a full-coverage auto insurance policy in 2024 is $2,314 per year.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is an auto insurance premium? | The amount of money an individual pays for an auto insurance policy. |
| Who decides the premium? | The insurance company. |
| How often are premiums paid? | Monthly, every six months, or annually. |
| What factors influence the premium? | Driving record, age, demographics, type of car, mileage, coverage, deductible, location, gender, credit score, etc. |
| What is the difference between a premium and a deductible? | The premium is the amount paid for the policy, while the deductible is the amount paid out of pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. |
| Can premiums be paid in installments? | Yes, some insurance companies allow premiums to be paid in installments such as monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually. |
| What is the average premium cost? | The national average premium for a full-coverage policy in 2024 is $2,314 per year, while the minimum coverage average is $644 per year. |
What You'll Learn

How auto insurance premiums are calculated
Auto insurance premiums are calculated based on a variety of factors, and the calculation methods vary from company to company. Here is a detailed overview of the factors that influence how auto insurance premiums are determined:
Personal Details
The personal details of the policyholder play a significant role in calculating auto insurance premiums. These details include:
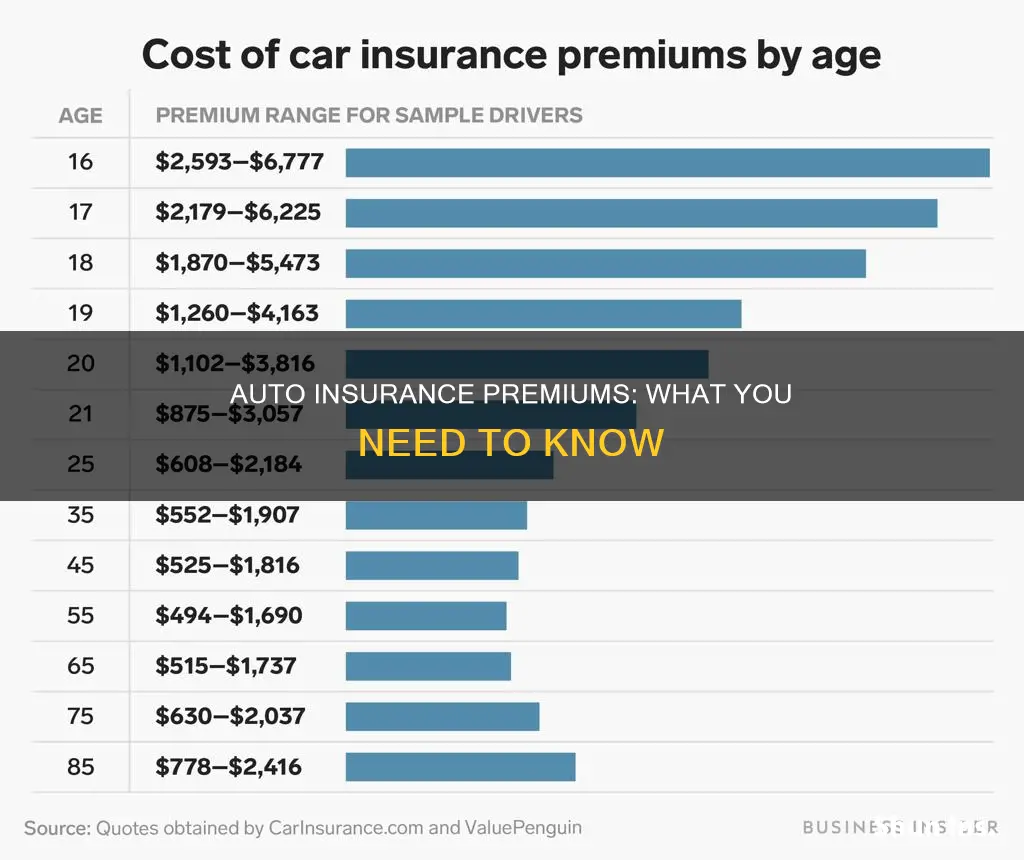
- Age: Younger and less experienced drivers, especially teenagers and those under 25, often face higher premiums due to their higher risk of being involved in accidents. Premiums generally decrease as drivers get older, with the lowest rates often offered to drivers in their 50s and 60s. However, premiums may rise again after the age of 75.
- Gender: In some states, gender influences insurance premiums. Women tend to have fewer and less severe accidents than men, resulting in lower premiums in states that consider gender.
- Marital Status: Married individuals often benefit from lower premiums since data suggests they are less likely to file auto insurance claims. Additionally, married couples with multiple cars may receive discounts for insuring more than one vehicle.
Driving History and Habits
An individual's driving history and habits are crucial factors in determining auto insurance premiums:
- Driving Record: A clean driving record with no accidents, speeding tickets, or traffic violations results in lower premiums. Conversely, a history of moving violations, accidents, or DUIs will lead to higher rates.
- Driving Experience: New drivers without an established insurance track record may be subject to higher premiums until they gain more experience.
- Vehicle Usage: The more you drive, the higher the chances of an accident. Therefore, those who drive for work or long commutes will likely pay more. Usage-based insurance programs can offer discounts to drivers who don't use their vehicles frequently.
- Driving Safety: Safe driving habits can lead to lower premiums. Avoiding speeding tickets and aggressive driving can reduce costs, and some companies offer discounts for accident-free periods or completing defensive driving courses.
Location
Where you live and park your car impacts your auto insurance premium:
- Urban vs. Rural: Urban drivers typically pay higher premiums due to higher rates of vandalism, theft, and accidents compared to small towns or rural areas.
- Specific Location: The state or area you live in can affect premiums due to varying costs of medical care, car repairs, litigation, insurance fraud, and weather-related risks.
- Parking Location: Parking your car in a secure garage instead of on the street may result in lower premiums.
Vehicle Type and Value
The type and value of your vehicle are essential considerations for insurance providers:
- Vehicle Cost and Repair: More expensive vehicles or those with higher repair costs will generally lead to higher premiums.
- Theft Risk: If your vehicle is popular with thieves, your insurance premium is likely to be higher.
- Engine Size: Larger engines may result in higher premiums.
- Safety Record and Features: Vehicles with a better overall safety record and advanced safety equipment may qualify for premium discounts.
- Potential Damage to Others: If your vehicle model has a higher chance of inflicting damage on another car in an accident, your liability insurance premium may be higher.
Insurance Coverage and Deductibles
The type and amount of insurance coverage you choose, as well as your deductibles, will influence your premium:
- Coverage Type: Opting for comprehensive, collision, or full coverage will likely increase your premium. Additionally, choosing higher coverage limits and lower deductibles will drive up costs.
- Deductibles: A higher deductible usually results in a lower monthly payment, while a lower deductible leads to a higher monthly payment.
- Minimum Requirements: State laws mandate a minimum amount of liability coverage, and some states also require personal injury protection insurance. Lenders may have additional insurance requirements for financed vehicles.
Credit Score and History
Your credit score and history can also impact your auto insurance premium:
- Credit-Based Insurance Score: Insurance companies use this score to predict the likelihood of you filing a claim. A higher score typically leads to lower premiums.
- Credit History: Maintaining good credit may positively impact your auto insurance costs, while a history of late payments or financial issues may increase premiums.
Additional Factors
Other factors that may influence auto insurance premiums include:
- Claims History: Filing multiple claims suggests a higher risk of future claims, leading to increased premiums.
- Insurance Company: Different insurance providers may offer varying premiums for the same type and amount of coverage. Shopping around and comparing quotes can help identify the most cost-effective options.
- Discounts: Various discounts may be available, such as good student discounts, safe driver discounts, multi-policy discounts, and more.
Keep Auto Insurance Claim Money?
You may want to see also

How to pay auto insurance premiums
Auto insurance premiums are the amount of money you pay to an insurance provider in exchange for coverage for yourself and your vehicle. The cost of your premium will depend on a variety of factors, including your driving record, age, location, and the type of coverage you choose.
There are several ways to pay your auto insurance premium, depending on your provider. Here are some common methods:
- By mailing a check to your insurance provider
- Online through the insurer's website or smartphone app
- Automatically through autopay, with the money drafted from your bank account each month
Most insurers require that you pay your premium every six or twelve months, though many offer monthly payment plans as well. You may be able to get a discount on your premium if you pay the full amount upfront or enroll in autopay.
In addition, there are a few strategies you can use to lower your auto insurance premium:
- Drop unnecessary coverage, especially for older vehicles
- Compare rates from multiple providers and switch insurers if you find a better deal
- Take a driver safety course
- Choose usage-based insurance if it suits your driving habits
- Bundle your auto insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners' or renters insurance
- Pay your premium in advance to take advantage of potential discounts
Auto Insurance: Essential or Excessive?
You may want to see also

How to save on auto insurance premiums
Auto insurance premiums can be costly, but there are many ways to save money. Here are some strategies to reduce your auto insurance premiums:
- Shop around for insurance: Prices differ from company to company, so it's worth getting multiple quotes from different insurers and types of insurance providers. Ask friends and family for recommendations, and research the company before committing. Remember that the lowest price isn't always the best option; choose a reputable company with good customer service.
- Compare insurance costs before buying a car: Auto insurance premiums are based on the car's price, repair costs, safety record, and theft likelihood. Insurers often offer discounts for features that reduce theft or enhance safety. Research insurance costs for different vehicles before buying.
- Raise your deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can significantly lower your premium. Ensure you have enough savings to cover the higher deductible if needed.
- Reduce optional insurance on older cars: If your older car is worth less than ten times the insurance premium, consider dropping collision or comprehensive coverage. Evaluate the value of your car and check if it's cost-effective to keep the coverage.
- Bundle your insurance policies: Many insurers offer discounts if you purchase multiple types of insurance from them, such as homeowners and auto insurance, or insure more than one vehicle. Some companies also provide loyalty discounts for longtime customers. Compare costs to find the best deal.
- Maintain a good credit history: Establishing a solid credit history can lead to lower insurance costs. Insurers use credit information to price auto insurance policies, as those who manage their credit effectively tend to make fewer claims. Regularly check your credit record to ensure its accuracy.
- Take advantage of low-mileage discounts: Some insurers offer discounts for motorists who drive less than the average number of miles per year or carpool to work.
- Ask about group insurance: Certain companies provide reductions for drivers insured through employer group plans or professional, business, or alumni associations. Check with your affiliated organizations to explore potential discounts.
- Seek out other discounts: Insurers may offer various other discounts, such as those for accident-free driving records, taking a defensive driving course, or having a young driver with good grades on your policy. Ask your insurer about potential discounts, but remember that the final policy cost is what matters most.
- Improve your driving record: Speeding tickets, accidents, and traffic violations increase insurance premiums. Consider taking a driver safety course to improve your skills and potentially reduce your rates.
- Choose a vehicle that's cheap to insure: Before buying a car, compare insurance rates for different models. Safe and moderately priced vehicles, such as small SUVs, tend to have lower insurance premiums.
- Increase your deductible for collision and comprehensive insurance: Raising your deductible can lead to significant savings on these coverages. Compare quotes with different deductible levels to find the best option.
- Improve your credit: In most states, your credit history can significantly impact your insurance rates. Focus on making timely loan and credit card payments, maintaining low credit card balances, and only opening new credit accounts when necessary.
- Consider usage-based insurance: If you're comfortable with your driving behavior being tracked, usage-based or pay-per-mile insurance can reduce costs. These programs typically involve using an app or installing a device in your car to transmit data to the insurer.
Auto Insurance and Broken Frames: What's Covered?
You may want to see also

How auto insurance premiums differ from quotes
An auto insurance premium is the amount of money an individual pays for an auto insurance policy. Auto insurance premiums are paid periodically, and the failure to pay may result in the cancellation of the policy. The premium amount depends on several factors, including the type of coverage, the area in which the individual lives, and any claims filed in the past.
On the other hand, a car insurance quote is an estimate of how much an individual may pay for a policy. It is based on the coverage selected and the information provided by the individual during the initial quote process. A car insurance quote is not a binding contract but rather an introduction to the potential policy.
- Missing or Incorrect Information: Providing incomplete or inaccurate information during the quote process can lead to discrepancies between the quote and the final premium. This can include forgetting to disclose traffic violations, convictions, or accidents on the individual's driving record, or misstating the year, make, or model of the vehicle.
- Not Using a Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): During the quote process, an insurer may not ask for the VIN and instead base the quote on the year, make, and model of the vehicle provided by the individual. However, when writing the policy, the insurer will need the VIN to ensure accurate information, which may result in a change in the premium.
- Changes in Coverage: If an individual realizes they need additional coverage beyond the state's minimum insurance requirements, the premium amount will increase.
- Taxes and Fees: Taxes and fees vary from state to state and company to company, and they may not be included in the initial quote, leading to a higher premium.
To prevent discrepancies between quotes and premiums, it is essential to provide accurate and complete information during the quote process, including checking the driving record and using the VIN for the vehicle.
Allstate Auto Insurance: Available in Florida?
You may want to see also

How auto insurance premiums change over time
Auto insurance premiums are the amount of money an individual pays for an auto insurance policy. They are calculated based on several factors, and they can change over time for various reasons.
Firstly, premiums are influenced by the type of coverage, the area in which the individual lives, any claims filed in the past, and moral hazard and adverse selection. The price of a premium is typically higher if the individual chooses collision and comprehensive insurance policies, which cover accidents and non-collision-related damages, respectively. Premiums also tend to be more expensive in urban areas due to higher rates of accidents, vandalism, and theft.
Secondly, an individual's personal details and driving history can impact their premiums. For example, younger and less experienced drivers often pay higher premiums because they are at a higher risk of accidents. A poor driving record, including speeding tickets, accidents, and DUIs, will also increase premiums for a set period, usually around three years. Additionally, factors such as gender, credit score, and marital status can affect premiums, although some states prohibit using these factors in rate calculations.
Moreover, premiums can change over time due to inflation and increasing expenses across the state. As the costs of healthcare, salaries, and living expenses rise, insurers need to collect higher premiums to offset these expenses and pay out claims. Inflation is a significant factor contributing to premium increases, affecting various economic sectors.
In addition to economic factors, regional factors can also influence premium changes. For instance, if a state introduces legislation to control auto insurance costs, individuals may see lower rates in their next policy period. Conversely, if a state experiences an increase in insurance claims, such as after a hurricane, premiums may rise to compensate for the higher number of claims.
Lastly, premiums may fluctuate due to changes in the individual's circumstances. Adding or changing a vehicle or driver on the policy, increasing coverage limits, or reducing deductibles can lead to higher premiums. Even without any apparent reason, rates can increase due to factors beyond the individual's control, such as rising car repair and replacement costs or an increase in claims in their area.
Insurers and Your Auto History: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A car insurance premium is the amount of money you pay your auto insurance provider. It is the cost of your auto insurance policy and is sometimes called an insurance rate.
Most insurers require that you pay your premium every six or 12 months, though many offer month-to-month payment plans too.
Many factors determine your insurance premium, including your driving record, age, gender, credit score, location, and the type of car you drive.
There are several ways to save on car insurance premiums, including shopping around for quotes, taking a driver safety course, choosing usage-based insurance, and bundling your policies.







