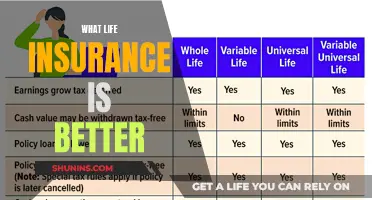
Suicide is a serious health problem in Australia, and it's important to understand how it is treated by life insurers. Generally, life insurance will cover suicide after a specific exclusion period, which is often around 13 months, to prevent people from taking out life insurance for the sole purpose of committing self-harm. After this exclusion period, life insurance funds will pay out as normal. However, this depends on the terms and conditions in your product disclosure statement (PDS), and wider exclusions may apply.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Does life insurance cover suicide? | Yes, but only after a specific exclusion period. |
| How long is the exclusion period? | Usually 13 months, but can be up to 2 years. |
| What happens if someone commits suicide within the exclusion period? | No death benefit will be given. Some insurers may refund paid premiums instead. |
| What happens after the exclusion period? | The clause will be waived or open to reassessment, depending on the insurer's guidelines. |
| What should I do if I have attempted suicide in the past? | You may still be able to get sufficient coverage, but it will likely be more difficult. Insurers will assess your risk factors to determine coverage. |
| What questions might insurers ask when assessing risk? | How long ago the attempt took place, factors leading to the attempt, diagnosis date, whether professional help was sought, medications taken, and family history of mental health problems or suicide. |
| What happens if someone fails to disclose medical information during the application? | The insurer has the right to deny a claim or pay a lesser amount, regardless of the cause of death. |
| What are some other instances when insurers may not pay out on a policy? | Claims connected to dangerous activities, participation in illegal activities, and drug or alcohol abuse. |
What You'll Learn
- Life insurance will not cover suicide if it occurs within the exclusion period, which is usually 13 months
- Life insurance companies will investigate the circumstances of death and review the deceased's medical history
- Life insurance companies will pay out for suicide after the exclusion period
- Life insurance companies may deny a claim if the policyholder failed to disclose medical information
- Life insurance companies will not pay out for suicide if it is listed as an exclusion in the policy

Life insurance will not cover suicide if it occurs within the exclusion period, which is usually 13 months
Life insurance is a complex issue, and it's important to understand the terms and conditions of your specific policy. In general, life insurance will not cover suicide if it occurs within the exclusion period, which is typically around 13 months from the start of the policy. This exclusion period is designed to prevent people from taking out life insurance with the sole intention of committing self-harm and to protect those who may be at risk. After this exclusion period, life insurance will usually cover suicide, although there may be additional requirements and conditions.
The exclusion period for suicide in life insurance policies varies but is often around 13 months. This period starts from the inception of the cover and is intended to safeguard the insurance company from policyholders who take out cover with the intention of harming themselves. It also acts as a protective measure for those who may be at risk, giving them time to seek help and potentially change their minds.
It's important to note that some life insurance companies may have different exclusion periods, and it's crucial to refer to the product disclosure statement (PDS) to understand the specific terms and conditions of your policy. While many insurers will pay a death benefit after the exclusion period, most will not cover claims related to self-inflicted injuries or attempted suicide under Trauma, Total and Permanent Disability (TPD), or Income Protection policies.
Additionally, it's worth mentioning that insurers may apply exclusions or higher premiums based on an individual's mental health history and risk factors. If you have experienced mental health challenges or attempted suicide in the past, insurers may still offer you cover but with certain exclusions or higher premiums. They may also deny your application altogether, depending on their policies and your specific circumstances.
In conclusion, while life insurance can provide financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your death, it's important to understand the exclusions and limitations of your specific policy. Suicide is generally not covered within the first 13 months of the policy, and there may be additional conditions or exclusions depending on the insurer. Always refer to the PDS and seek professional advice if needed to ensure you have a clear understanding of your life insurance coverage.
Life Insurance Interest: Myth or Reality?
You may want to see also

Life insurance companies will investigate the circumstances of death and review the deceased's medical history
When a life insurance claim is made, the onus is on the beneficiary or policy owner to provide proof of death and the circumstances surrounding it. As suicide is labelled as an "unnatural cause of death", an autopsy will likely be performed. If death was due to a strange circumstance, such as a car accident, a police report and/or coroner's report may also be required when lodging a claim.
In addition to these documents, the following information is also required when lodging a life insurance claim:
- Fully completed claim forms
- Medicare and Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme Release forms
- General Medical History Release forms
In some cases, the insurer may review the deceased's full medical history to check for any significant mental health issues that may not have been disclosed during the underwriting process. If the insurer finds that the deceased did not disclose all relevant information, and these details are considered to have been a material factor in the death, the claim may be denied.
Kansas Withholding Tax on Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Life insurance companies will pay out for suicide after the exclusion period
Life Insurance and Suicide in Australia
Suicide is a serious health problem in Australia, and it is the dominant cause of death for Australians between the ages of 15 and 44. Life insurance companies in Australia will pay out for suicide after a specific exclusion period, which is generally around 13 months but can vary depending on the insurer and the policy. This exclusion period is to prevent people from taking out life insurance with the sole intention of committing suicide and receiving a payout for their loved ones.
Life Insurance and Suicide: What You Need to Know
- Understanding the Exclusion Period: The exclusion period for suicide in life insurance policies is typically 13 months, but it can range from one to two years. During this time, no death benefit will be paid if suicide occurs. After the exclusion period, the clause is waived or open to reassessment, and life insurance companies will generally pay out for suicide.
- Reading the Fine Print: It is crucial to carefully review your Product Disclosure Statement (PDS) to understand the terms and conditions of your policy. While many insurers will pay a death benefit due to suicide after the exclusion period, they may not cover Trauma, Total and Permanent Disability (TPD), or Income Protection for self-inflicted injuries or attempted suicide.
- Applying for Life Insurance after a Suicide Attempt: If you have previously attempted suicide, you may still be able to obtain life insurance, but your mental health history can complicate the process. Insurers will assess your risk factors and may request information about your mental health history, diagnosis, treatment, and medication. They may also inquire about your family history of mental health issues. Based on this information, they will determine your eligibility and premium rate.
- Submitting a Claim for a Spouse's Suicide: If your spouse commits suicide, you can submit a life insurance claim provided they meet certain criteria: their policy must be older than the exclusion period, they must have disclosed their medical and personal information truthfully, and you must be the nominated beneficiary.
- Understanding General Exclusions: In addition to suicide and self-harm, life insurance policies typically have general exclusions for reckless and negligent behaviour, dangerous activities, illegal activities, and drug or alcohol abuse. These exclusions vary among insurers, so it is essential to carefully review your policy's specific terms and conditions.
Seeking Support
If you or someone you know is struggling with suicidal thoughts or mental health issues, it is crucial to seek help. Lifeline Australia (13 11 14) and similar support services are available to provide confidential advice and assistance.
First Citizens Bank: Life Insurance Offerings and Benefits
You may want to see also

Life insurance companies may deny a claim if the policyholder failed to disclose medical information
In Australia, life insurance companies may deny a claim if the policyholder failed to disclose medical information. This is known as non-disclosure and is considered a breach of the duty of disclosure, as outlined in the Insurance Contracts Act 1984 (ICA). The duty of disclosure states that the insured person must provide all relevant information that may influence the insurer's decision to insure them and the terms of the policy. This includes medical history, lifestyle, and occupation details.
If a policyholder fails to disclose medical information, the insurer has the right to deny a claim or pay a lesser amount, regardless of the cause of death. This is because non-disclosure is seen as a misrepresentation of the insured person's risk profile. In other words, the insurer's decision to offer coverage and the terms of the policy may have been different had they been aware of the full medical history.
To investigate non-disclosure, insurers will typically review the policyholder's medical records, including Medicare and Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) data, and may contact the policyholder's doctors to request medical history. They may also review social media profiles for any discrepancies in the information provided.
In some cases, non-disclosure may result in the insurer voiding or cancelling the policy altogether, treating it as if it never existed. This is more likely to occur if the non-disclosure is deemed fraudulent or intentional. However, each insurer has different underwriting guidelines, and the outcome may vary depending on the specific circumstances.
To prevent issues arising from non-disclosure, it is essential to provide complete and accurate information when applying for life insurance. Policyholders should disclose any pre-existing conditions and be transparent about their medical history, even if they believe it is unrelated to the policy. Seeking professional advice or consulting a specialist broker can also help ensure that all relevant information is disclosed.
Life Insurance and College Loans: What's Covered?
You may want to see also

Life insurance companies will not pay out for suicide if it is listed as an exclusion in the policy
Most life insurance plans have a suicide and self-harm clause that withholds benefits in claims involving suicide or attempted suicide if it occurs within the first 13 months of the policy. This exclusion period is designed to prevent applicants from taking out life insurance with the intention of harming themselves to provide financial benefits for their families. After this exclusion period, the clause may be waived or open to reassessment, depending on the insurer's guidelines.
Some insurers may choose to refund paid premiums instead of providing death benefits in cases of suicide within the exclusion period. It is important to note that even after the exclusion period, certain policies, such as trauma cover, total and permanent disability (TPD) cover, and income protection insurance, may not cover suicide or attempted suicide.
Additionally, failing to disclose medical information, including any history of mental illness, during the application process can also lead to a denied claim. This is because an insurance company will generally investigate your medical records in the event of a claim. Therefore, it is crucial to be honest and upfront when completing the application form and complying with your duty of disclosure.
Before purchasing a life insurance policy, carefully review the product disclosure statement (PDS) to understand the specific exclusions and conditions of your policy.
Divorce and Life Insurance: What Happens to Your Policy?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, life insurance generally covers suicide after a specific exclusion period, which is often around 13 months but can vary depending on the insurer and the policy. During this exclusion period, insurers will not pay out for suicide or attempted suicide.
Yes, it is possible to get life insurance if you have attempted suicide in the past, but it may be more difficult and insurers will likely ask detailed questions about your mental health history and may charge a higher premium.
If your partner has committed suicide, you should lodge a claim with your insurer for a death benefit, provided that your partner's policy was held for longer than the exclusion period, did not exclude death by suicide, and you are the nominated beneficiary.