In Washington State, there are two types of work injury claims: L&I claims and self-insured employer claims. L&I claims are funded by the state, while self-insured employer claims are funded by employers and private insurance companies. Self-insured employers manage their L&I claims in-house or with the help of a service company, and they must follow the same Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedules as L&I. If you are treating an injured worker insured by their employer rather than the State Fund, you should submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Who manages self-insured claims? | Self-insured claims are managed by the self-insurer or their service company. |
| Who funds self-insured claims? | Self-insured claims are funded by employers and private insurance companies. |
| Who is responsible for paying benefits? | Self-insured employers are responsible for paying benefits while the work injury claim is open. |
| How to determine if an employer is self-insured? | Check the list of self-insured employers with contact information or call L&I's Self-Insurance Program at 360-902-6901. |
| How to apply for self-insurance? | Submit the following documents: Application for Self-Insurance Certification, Self-Insurance Certification Questionnaire, three years of audited financial statements, list of physical locations and addresses, copy of the Accident Prevention Program, Self-Insurance Electronic Data Reporting System enrollment form, and other required forms. |
| How to maintain self-insured status? | File Self-Insurance Quarterly Reports, submit audited annual financial statements, submit the Annual Report of Self-Insured Business, submit monthly claim data, report payment of medical bills, maintain the required surety, retain a licensed Third Party Administrator, and notify L&I of business status changes. |
| How to bill a self-insured employer? | Submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative. |
What You'll Learn

Submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative
When treating a worker injured by their employer's insurance rather than the State Fund, submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative.
To determine if an employer is self-insured, you can check the list of self-insured employers with contact information, which also includes a list of third-party administrators. Alternatively, you can call L&I's Self-Insurance Program at 360-902-6901.
Self-insured employers must pay bills according to the same Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedules as L&I. If you disagree with a payment received from a self-insurer, you must follow WAC 296-20-125(9) and inquire about it within 90 days of payment. You can also bill the self-insured employer interest on the balance due when payment is not made within 60 days of receipt of a proper bill, using the L&I local code 1159M. Calculate the interest due using the Self-Insurance Medical Bill Interest Calculator.
If you need to dispute a bill underpayment, complete and submit the Self-Insurance Medical Provider Billing Dispute form (F207-207-000). For other disputes, include the L&I claim number on your fax cover sheet and fax all information to 360-902-6900. Contact L&I's Self-Insurance Program at 360-902-6901 if you need help identifying the department claim number. The employer should be the worker's first point of contact, but if there is an issue that cannot be resolved, you can use the online system to report problems with time-loss compensation, medical care, and other issues.
The Mystery of BGA in Insurance: Unraveling the Acronym's Significance
You may want to see also

Determine if an employer is self-insured
There are several ways to determine if an employer is self-insured.
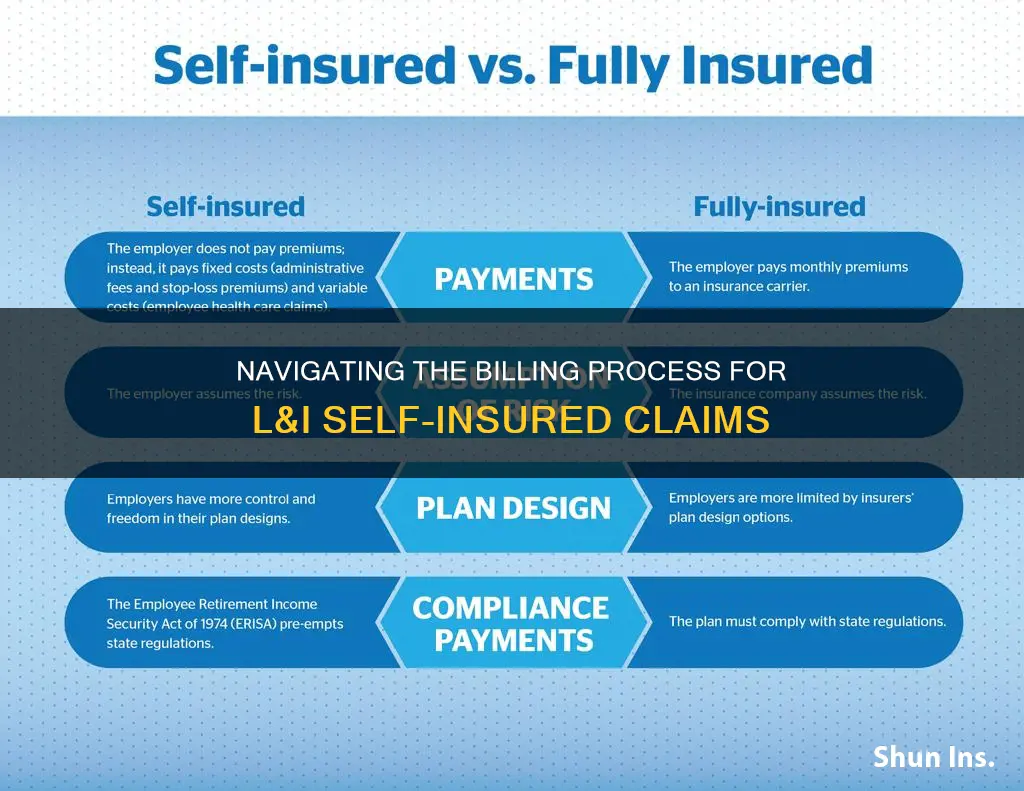
Firstly, it is important to understand the difference between self-insured and fully-insured plans. A self-insured plan means that the employer takes on the financial risk of providing health care benefits to their employees, paying for each claim out of pocket as they are incurred. In contrast, with a fully-insured plan, the employer pays a fixed premium to an insurance carrier, who then assumes the risk of paying employees' health claims.
According to a 2022 Kaiser Family Foundation analysis, 65% of U.S. employees with employer-sponsored health insurance are in self-insured plans. This is more common among larger businesses with 200 or more employees, where 82% of covered workers are enrolled in self-insured plans. This is because larger businesses tend to have the financial resources to take on the risk associated with employees' medical claims.
Therefore, one way to determine if an employer is self-insured is to consider the size of the company. However, this is not a foolproof method, as some smaller employers may also choose to self-insure.
Another way to determine if an employer is self-insured is to examine the employees' insurance ID cards or plan documents. These may bear the name of an insurance carrier, leading enrollees to assume that the insurer is providing their coverage. However, in some cases, the insurance company is only acting as an administrator, and the employer is still taking on the financial risk.
Additionally, self-insured plans are regulated at the federal level under ERISA, while fully-insured plans are mostly regulated at the state level. Therefore, checking the applicable laws and regulations for an employer's health plan can provide an indication of whether it is self-insured or fully-insured.
Finally, self-insured employers typically set up a special trust fund to earmark money for paying incurred claims. Therefore, enquiring about the financial arrangements and funding sources for an employer's health plan can provide insight into whether it is self-insured or fully-insured.
Haven Insurance: Understanding the Fine Print
You may want to see also

Self-insured employers must authorize treatment and pay bills
When treating a worker insured by their employer, submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative. You can determine if an employer is self-insured by checking the list of self-insured employers with contact information or by calling L&I's Self-Insurance Program at 360-902-6901.
For bill underpayment disputes, complete and submit the Self-Insurance Medical Provider Billing Dispute form (F207-207-000). For all other disputed issues, include the L&I claim number on your fax cover sheet and fax all information to 360-902-6900. The employer should be a worker's first point of contact. However, if there is an issue that you have been unable to resolve, use the online system to report problems with time-loss compensation, medical care, and other issues.
L&I doesn't require self-insured employers to develop or change existing automated payment systems. However, they will require self-insured employers to process proper billings. If an approved provider submits a complete billing to a self-insured employer for proper and necessary medical services with the ICD coding as described below, the self-insured employer should respond to the billing as follows:
- Before October 1, 2015: For billing submitted with ICD-9 codes, the SIE would be required to pay based on ICD-9 coding if the bill is otherwise payable. The SIE may pay or may return the billing to the provider for proper ICD-10 coding.
- After October 1, 2015: For billing submitted with ICD-10 codes, the SIE may pay or may return the billing to the provider for proper ICD-10 coding. The SIE would be required to pay based on ICD-10 coding if the bill is otherwise payable. The SIE must consistently apply whichever approach it takes.
Comprehensive Guide to Purchasing 1 Cr Term Insurance
You may want to see also

Disputing a bill underpayment
If you believe you have been underpaid by a self-insured employer, there are a few steps you can take to dispute the bill. Firstly, it is important to act promptly. You must follow WAC 296-20-125(9) and inquire about the payment within 90 days of receiving it. You can then complete and submit the Self-Insurance Medical Provider Billing Dispute form (F207-207-000). This form is specifically for bill underpayment disputes. You can also call L&I's Self-Insurance Section at 360-902-6708 for assistance.
If you are not satisfied with the response from the Self-Insurance Section, you may need to take further action. You can try contacting the employer directly, as they should be the first point of contact. You can speak to their HR department or a service company, depending on how they manage their claims. Ask for an explanation of the payment and express your concerns. If you believe they are wrong, tell them so and request a review of the payment.
If you still do not receive a satisfactory response, you can communicate with the L&I Self-Insured Section about the employer's behaviour. This is separate from the Self-Insurance Section and their job is to oversee self-insured employers and ensure they are following the law. You can call them at 360-902-6901. Encourage them to look into your claim and help you resolve the issue.
If all else fails, you can request an L&I audit of your employer's compliance with self-insured employer requirements. You can also speak to an L&I lawyer who can provide legal assistance and help you stand up for your rights. Remember, self-insured employers are required to follow the same Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedules as L&I, and you have the right to dispute any unfair or incorrect payments.
The Insurance Conundrum: Unraveling the Mystery of T-Bill Insurance Coverage
You may want to see also

Maintaining self-insured status
Once you are approved for certification as a self-insured employer, there are several requirements that need to be met to maintain that certification. These requirements are:
- File Self-Insurance Quarterly Reports.
- Submit audited annual financial statements within six months after the close of the company’s financial year-end.
- Submit the Annual Report of Self-Insured Business by March 1 of each year.
- Submit monthly claim data to L&I via the Self-Insurance Electronic Data Reporting System (SIEDRS).
- Report payment of medical bills via the medical bill electronic data interchange (EDI).
- Maintain the required surety.
- Retain a licensed Third-Party Administrator (TPA), or if self-administered, employ certified claim administrators in accordance with RCW 51.14.170.
- Notify L&I of any business status changes.
- Refer to self-insurer’s reporting requirements in WAC 296-15-221.
Self-insured employers must authorize treatment and pay bills according to the same Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedules followed by L&I. If you disagree with a payment received from a self-insurer, you must follow WAC 296-20-125(9) and inquire about it within 90 days of payment to be considered. You can now bill the self-insured employer interest on the balance due when payment isn't made within 60 days of receipt of a proper bill.
Understanding Solvency: The Lifeline of the Insurance Industry
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can check the list of self-insured employers with contact information on the L&I website or call L&I’s Self-Insurance Program at 360-902-6901.
Submit bills directly to the employer or their claims representative. Self-insured employers must pay according to the same Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedules followed by L&I.
You must follow WAC 296-20-125(9) and inquire about it within 90 days of payment. You can also bill the self-insured employer interest on the balance due if payment is not made within 60 days of receiving a proper bill.
Self-insured employers provide benefits to work injury claimants and are responsible for paying them while the claim is open. The employer remains liable for benefits during a lengthy claim reopening period and even if they surrender their self-insured certification.







