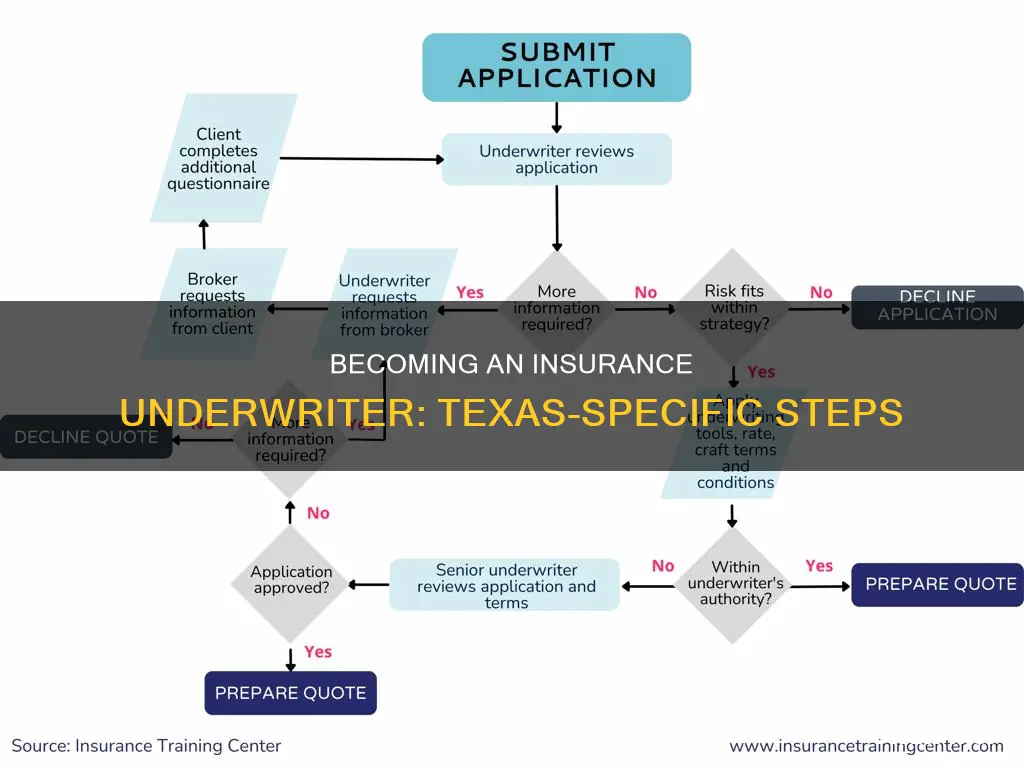
Becoming an insurance underwriter in Texas involves a blend of formal education, specialized training, and practical experience in the field of insurance or finance. While it is not always necessary to have a college degree, most firms prefer candidates with a bachelor's degree in a related field, such as finance, economics, or business. Candidates with an associate's degree or a high school diploma may also be considered if they have relevant work experience. In addition to education, building a strong professional network, gaining practical experience, and obtaining certifications are crucial steps to enhance one's employability and advance in the field of insurance underwriting.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Education | Bachelor's degree in business, finance, economics, mathematics, or a related field |
| Work Experience | Entry-level positions within insurance organizations or internships |
| Skills | Analytical, computer, communication, decision-making, attention to detail, math |
| Certification | Chartered Property and Casualty Underwriter (CPCU), Life Underwriter Training Council Fellow (LUTCF), Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU), Associate in Commercial Underwriting (ACU), Associate in Personal Insurance (API) |
What You'll Learn
- Pursue a bachelor's degree in business, finance, economics, or mathematics
- Gain professional experience through internships or entry-level positions
- Seek relevant certifications to advance your career
- Develop key skills such as analytical, communication, and decision-making abilities
- Build a professional network and stay informed about industry trends and regulations

Pursue a bachelor's degree in business, finance, economics, or mathematics
Aspiring insurance underwriters in Texas will need a bachelor's degree in business, finance, economics, or mathematics. This educational background will provide them with the fundamental knowledge required for a career in underwriting, and help develop the analytical skills that are so crucial to success in this field. Courses in risk management, insurance, and financial analysis will be particularly beneficial.
A bachelor's degree in business will equip future underwriters with a solid understanding of business procedures and practices. They will learn about the principles of accounting, including objectives, theories, and practices aligned with the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). They will also gain insights into the fundamentals of the accounting cycle, from transactions through financial statement preparation, and explore the application of managerial accounting data in business decision-making. Additionally, descriptive and inferential business statistics will be covered, providing a strong foundation for data analysis.
For those pursuing a degree in finance, they can expect to study similar topics but with an added focus on the fundamentals of business finance. This includes asset valuation, capital budgeting, and an introduction to the financial markets. They will also delve into investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds, as well as portfolio management and the international monetary environment. This knowledge will enable them to understand the financial landscape and make informed decisions about insurance applications.
A degree in economics will provide a strong foundation in economic theory, which is essential for understanding the broader context in which insurance companies operate. Economics students will learn about economic trends and factors that influence the financial decisions of individuals and organizations. This knowledge will be invaluable when assessing the risks associated with insuring people, property, and assets.
Lastly, a degree in mathematics will equip future underwriters with strong quantitative skills, including advanced mathematical and statistical techniques. These skills will be applied when calculating premiums and assessing risks, ensuring accuracy and informed decision-making.
While a bachelor's degree is the typical starting point for a career in insurance underwriting, further specialization or certifications can enhance an underwriter's credentials and demonstrate a commitment to the profession. For example, pursuing certifications such as the Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter (CPCU) or the Associate in Commercial Underwriting (AU) can set candidates apart and showcase their expertise.
In summary, pursuing a bachelor's degree in business, finance, economics, or mathematics is an essential step for aspiring insurance underwriters in Texas. This educational foundation will provide the knowledge, skills, and credentials needed to embark on a successful career in underwriting.
E-Health Short-Term Insurance: Exploring the Digital Revolution in Healthcare Coverage
You may want to see also

Gain professional experience through internships or entry-level positions
Gaining professional experience is an important step in becoming an insurance underwriter. Entry-level positions within insurance organisations are a great way to get started in this field. Some roles to consider include insurance policy processing clerk or procurement clerk. These positions will help you develop the skills and knowledge needed to succeed as an insurance underwriter. For example, you will learn about policy analysis, risk assessment, and the underwriting process.
Another option to gain experience is to pursue internships. Many colleges and universities partner with local businesses to offer internships, which can provide valuable knowledge and practical experience. As an intern, you will likely work under the supervision of senior underwriters and gain exposure to basic applications and common risk factors.
Starting in a support role within a financial institution, such as a loan processor or junior risk analyst, can also provide a solid foundation for a career in underwriting. These roles often involve a practical understanding of financial products, risk assessment, and the regulatory environment, which are all transferable skills for underwriting.
It is worth noting that some employers may hire recent graduates for insurance underwriter roles, so gaining experience through internships or entry-level positions may not always be necessary. However, it is beneficial to have some knowledge of the industry and the required skills before applying for underwriter positions.
Unveiling the NCB: A Rewarding Feature of Insurance Policies
You may want to see also

Seek relevant certifications to advance your career
While a certification is not necessary to become an insurance underwriter, it can help you advance your career by demonstrating your skills and expertise to employers. Here are some relevant certifications to consider as you pursue a career as an insurance underwriter in Texas:
Chartered Property and Casualty Underwriter (CPCU)
The CPCU certification is widely recognised and respected in the property and casualty insurance industry. It is offered by The Institutes and focuses on fundamental risk management and property-casualty insurance knowledge. To be eligible for this certification, you must have at least two years of insurance underwriting experience and pass a series of online courses and exams.
Associate in Commercial Underwriting (AU)
The AU certification is another option offered by The Institutes. This certification covers topics such as financial statements, risk analysis, and premium determination in commercial underwriting. It consists of four core classes, along with elective and concentration courses, and typically takes about a year to complete.
Life Underwriter Training Council Fellow (LUTCF)
The LUTCF certification is offered by the National Association of Insurance and Financial Advisors. It consists of three courses that cover practice management, life insurance, investment products, and risk management. After completing the curriculum, you must pass an exam to earn the certification.
Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU)
The CLU certification is offered by the American College of Financial Systems and is designed for candidates with three years of work experience in life insurance. The program includes five core courses and three elective courses covering life insurance planning, law, estate planning, and business owner/professional planning. Passing the exam is required to achieve this certification.
Associate in General Insurance (AINS)
The AINS certification is also offered by The Institutes and provides comprehensive knowledge of insurance principles, practices, policies, and coverages. It is suitable for those seeking a career in insurance underwriting as it covers relevant topics and allows you to focus on areas aligned with your professional goals through optional electives.
Certified Insurance Examiner (CIE)
The CIE certification is awarded by the Insurance Regulatory Examiners Society to insurance regulatory professionals who have attained expertise in both the property-casualty and life-health educational paths. To earn the CIE, you must meet specific employment and experience requirements, in addition to completing the required coursework.
These certifications can enhance your resume, showcase your expertise, and open doors to senior-level positions in insurance underwriting. Remember to consider your area of specialisation, time commitment, and the reputation of the certifying organisation when choosing the right certification for your career goals.
Dental Fear: No Insurance, No Visit
You may want to see also

Develop key skills such as analytical, communication, and decision-making abilities
Aspiring insurance underwriters in Texas should focus on developing key skills such as analytical, communication, and decision-making abilities. These skills will enable them to excel in their roles and advance in their careers. Here are some ways to develop these abilities:
Analytical Skills
- Critical Thinking: Enhance your ability to question preconceived notions and identify areas for improvement. This skill is valuable as it helps organizations move beyond traditional practices and is often the catalyst for innovation.
- Data and Information Analysis: Focus on developing skills to analyze data and information effectively. Collecting and interpreting data allows for better decision-making and can lead to process improvements.
- Research: Strengthen your research skills by seeking information from various sources, including experienced colleagues and external research. Knowing where to find valuable information is essential for effective problem-solving.
- Problem-Solving: Practice identifying issues and designing creative solutions. This involves gathering feedback, testing potential solutions, and making adjustments as needed.
Communication Skills
- Active Listening: Pay close attention to others by engaging, asking questions, and rephrasing their thoughts to ensure understanding. This builds respect and increases understanding among colleagues.
- Confidence: Present your ideas with confidence by maintaining eye contact, using a clear speaking voice, and avoiding filler words. Confidence in your communication can help your ideas gain traction.
- Friendliness: Foster trust and understanding with colleagues by communicating with a positive attitude and showing genuine interest in their well-being. Small gestures, such as asking about their life and offering praise, can build strong relationships.
- Empathy: Understand and share the emotions of your colleagues to build effective connections. This skill is valuable in both one-on-one and team settings, helping you acknowledge and address their emotions appropriately.
- Responsiveness: Respond promptly to phone calls, emails, and other forms of communication. Being a fast communicator demonstrates efficiency and strengthens trust with colleagues and clients.
Decision-Making Skills
- Problem-Solving: Develop strong problem-solving skills by considering different viewpoints and observing challenges from a neutral, non-emotional perspective. This enables you to make well-informed decisions.
- Leadership: Cultivate leadership skills to motivate your team and promote teamwork. Building strong relationships with your coworkers creates an environment where they feel comfortable sharing their ideas and working collaboratively.
- Reasoning: Take the time to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each possible solution. Weighing the pros and cons carefully will help guide your decision-making process.
- Intuition: Trust your instincts and past experiences to guide your decisions. Reflect on how your core values and lessons learned can inform your choices and potential actions.
- Time Management: Effective time management ensures that you meet deadlines and keep all stakeholders informed with timely updates. This skill is especially valuable when quick decisions are required.
Developing these key skills will not only enhance your resume but also make you a well-rounded and highly effective insurance underwriter.
Uninsured and Unnecessary Deaths
You may want to see also

Build a professional network and stay informed about industry trends and regulations
Building a professional network is an investment in yourself and your business. It takes time and effort, but the payoff can be substantial. A strong network can help you learn about alternative ways to operate or improve your business, boost your career and personal growth, and open the door to new sales opportunities. Here are some steps you can take to expand your professional network:
- Make the most of your existing contacts: Think about your family and friends, neighbours, social network connections, and people you went to school with. See what shared interests you have, find common ground, and arrange a meeting to talk about what you do and what they do. You may be surprised at how you can benefit each other.
- Identify people you want to connect with: Make a list of people you don’t know yet but want to connect with. These could be people you are one or two connections away from on LinkedIn, industry professionals you could reach through a trade group, alumni association, or industry event. Figure out how you’re connected (or could be) and craft a careful introduction message.
- Rehearse your pitch: Develop and practice a short introduction about yourself and what you do. This can be adapted depending on who you are talking to, but the core should be consistent. Include a simple “hello”, share information about who you are and what you do, discuss what you want to improve or focus on in the future, and talk about how you can help others.
- Attend networking events: Networking events, whether in-person or online, are a great way to expand your professional network. Look for events sponsored by trade groups, business groups (including Chambers of Commerce), EventBrite, school alumni associations, and others.
- Get involved with professional and community organisations: Joining and being active in a professional or community organisation is a fantastic way to build your profile and expand your network. Many organisations are always looking for event organisers or Board Members, so consider getting involved if your schedule permits.
In addition to building a professional network, it is important to stay informed about industry trends and regulations. This is especially true in the insurance industry, where regulations and policies are constantly changing. One way to stay informed is to subscribe to industry publications and newsletters, such as the Insurance Broker Blog and Monster's newsletters. You can also follow relevant insurance industry websites and influencers on social media. Attending industry conferences and events can also help you stay up-to-date on the latest trends and regulations.
Marketplace Insurance: Are Investments Counted as Income?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Most insurance underwriters need a bachelor's degree in a field like finance, economics, business, or mathematics. However, some employers may accept candidates with an associate's degree or a high school diploma, as long as they have relevant work experience.
Certification is not always required to get an entry-level insurance underwriter job in Texas. However, it may be beneficial and can help you advance to senior positions. Some common certifications for insurance underwriters include Chartered Property and Casualty Underwriter (CPCU) and Life Underwriter Training Council Fellow (LUTCF).
Insurance underwriters need strong analytical, computer, communication, and math skills. They must be detail-oriented and have good decision-making abilities.







