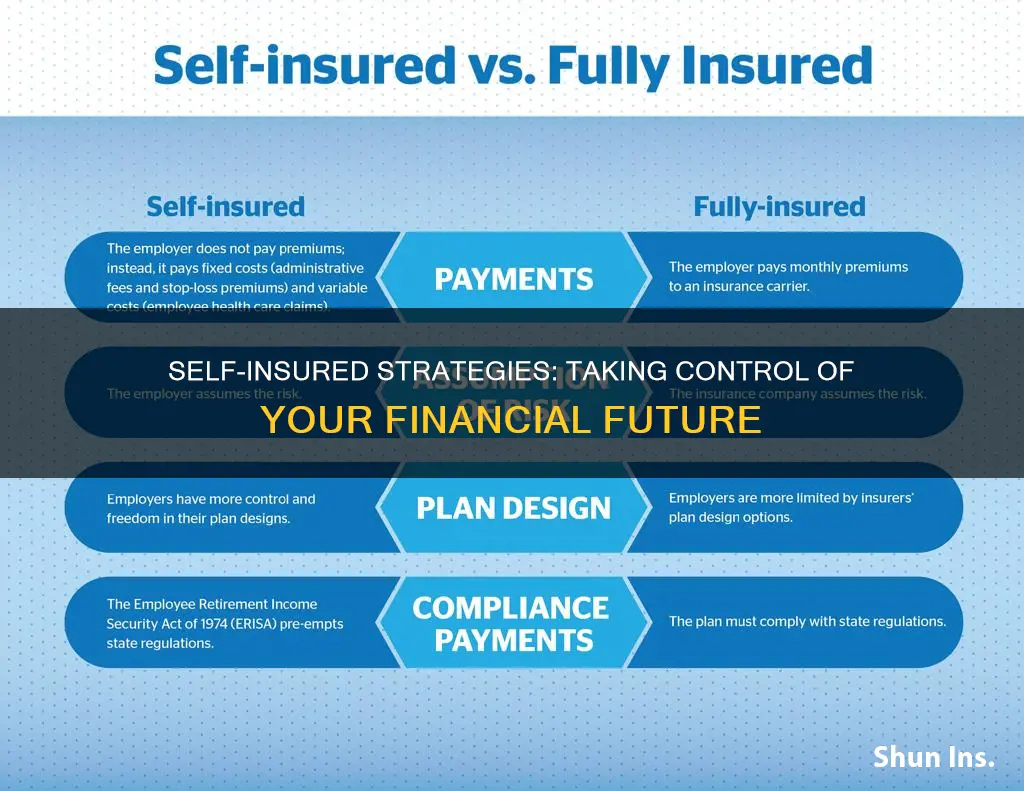
Self-insurance is a risk management technique where individuals set aside a pool of money to cover unexpected losses. This can be more economical than buying insurance from a third party, especially for predictable and smaller losses. For example, tenants may choose to self-insure instead of purchasing renter's insurance. However, most people opt for insurance from a company for unpredictable and significant losses, such as car accidents or severe illness. To become self-insured, individuals need to assess their financial situation, including savings, spending, and future expenses, and ensure they have enough money set aside to cover potential losses. They can also consult insurance professionals for guidance on the feasibility of self-insurance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| When to self-insure | When you have enough money to cover a potential loss |
| Who can self-insure | Individuals and companies |
| What you need | A pool of money to cover unexpected losses |
| When it's not a good idea | When you don't have enough money to cover financial losses |
| Self-insurance vs. no insurance | Self-insurance is when you have the means to cover a loss but choose not to insure |
| Where to get the money | Savings, assets, emergency funds, or self-insurance funds |
| Application process | Submit a non-refundable application fee, financial statements, loss history, and other required information |
| Requirements | Submit quarterly and annual reports, maintain surety, notify of business status changes, etc. |
What You'll Learn

Know when self-insurance is a good idea
Self-insurance is a good idea when you have enough money to cover a potential loss. It is a risk management technique where you set aside a pool of money to remedy an unexpected loss. This is a good strategy for mitigating the possibility of future losses by putting aside a set portion of your money, rather than buying insurance and having a company reimburse you.
Self-insurance is a good idea when you have no debt and a considerable amount of assets. In this case, you could consider self-insuring for life insurance. The idea is that since insurance companies aim to make a profit by charging premiums in excess of expected losses, a self-insured person can save money by setting aside the money that would have been paid as insurance premiums.
However, it is critical to amass and put aside enough funds to cover you, your family, and your possessions if an accident or natural catastrophe occurs. For example, if you have children depending on your income, you need to ensure that your savings, investments and assets will be able to support them if you pass away.
Self-insurance is also a good idea for charges that are likely to be minimal, as it may cost less than paying for monthly or annual insurance premiums. It may also be a good idea for those who want to avoid paying high premiums to insure against a potentially expensive but unlikely event.
In addition, self-insurance is a good idea for predictable and small losses. For example, some tenants prefer to self-insure rather than purchase renter's insurance to protect their assets. Similarly, instead of purchasing extended warranties on appliances, you can choose to self-insure by paying for any repairs out of your savings.
However, it is important to note that self-insurance is not a good idea if you do not have enough money to cover a financial loss. For example, most people choose to buy auto insurance and health insurance from an insurance company rather than self-insure against car accidents or severe illness.
HSA: Insurance or Not?
You may want to see also

Understand the risks of self-insurance
Understanding the risks of self-insurance is crucial before making any decisions about your insurance coverage. Self-insurance involves a significant financial risk, as you bear the full cost of any losses or damages. This can be a heavy financial burden, especially if the loss is substantial or if there are multiple claims. Unlike traditional insurance, self-insurance lacks the safety net of risk transfer to a third party, which can leave you vulnerable to financial strain.
Another risk to consider is the lack of risk pooling and spreading. Traditional insurance operates on the principle of risk pooling, where policyholders' premiums collectively fund the claims of those who experience losses. This spreading of risks reduces the financial impact on individuals and ensures that resources are available when needed. Self-insurance does not offer this benefit, and your financial exposure may be concentrated, leaving you susceptible to a catastrophic event that could deplete your resources.
Self-insurance also has limited coverage compared to traditional insurance policies. Commercial insurance often provides comprehensive protection for a wide range of risks, including property damage, liability claims, medical expenses, and more. With self-insurance, you may overlook certain risks or underestimate their impact, leaving you exposed to unexpected expenses that could be challenging to manage.
The unpredictability of losses is another disadvantage of self-insurance. It can be difficult to predict or plan for potential losses, and you are responsible for covering the full cost of any retained losses. This unpredictability highlights the potential financial risks associated with self-insurance, and it's crucial to evaluate whether you have sufficient resources to cover unforeseen losses.
Additionally, self-insurance can be administratively burdensome. It requires expertise in managing retained risks, including policy wording, risk management, claims handling, and financial management. Small organisations or individuals may not have the necessary resources to effectively handle these responsibilities, making self-insurance less feasible for them.
Pharmacists' Support: Pharmacy Techs and Insurance Billing
You may want to see also

Assess your financial situation
To assess your financial situation, you need to determine if you have enough money to cover a potential loss. This means understanding the worst-case scenario financially and ensuring you are prepared for it.
Firstly, it is important to note that self-insurance is not always a good idea for every insurance need. For example, health insurance and car insurance are types of coverage where being self-insured is not practical because the potential risk and cost are too high to pay out of pocket. Similarly, home insurance is important to have, but it can be challenging to self-insure due to the high costs of repairing or rebuilding a home after a disaster.
However, life insurance is a type of coverage where being self-insured can make sense under very specific conditions. When you are self-insured for life insurance, you have enough money on hand to forgo an insurance policy and enjoy some savings. This typically happens when you are debt-free and have enough savings, investments, and assets to ensure your family can live off the income generated by these sources if you were to pass away.
To assess your financial situation, you should calculate your annual income and the return on investment (ROI) you are currently getting on everything. If your ROI exceeds your income, you are likely in a good position to consider self-insurance. Additionally, consider your savings and assets and whether you have enough to cover your losses in the event of a disaster.
It is also important to note that self-insurance does not mean making your dependents rich. It is about having enough to replace your income and provide for your loved ones after you're gone.
The Evolution of Term Insurance: A Historical Perspective
You may want to see also

Calculate how much you need to save
Self-insurance means that you act as your own insurer and can prove that you have the financial capacity to pay out of pocket for any accidents or incidents that would usually be covered by an insurance company.
Self-insurance is a good idea when you have enough money to cover a potential loss. For example, if you have enough money to cover the cost of replacing stolen items, or repairing a car after an accident, then you may want to consider self-insurance.
However, self-insurance is not always a good idea. For example, health insurance is not recommended to be self-insured, as medical bills can quickly become unaffordable without insurance coverage.
If you are thinking about self-insurance, you need to calculate whether you have the means to cover any potential losses. This will depend on your income, your ROI, and the stage of life your family is in. For example, if you have children who are financially dependent on you, you will need more savings to self-insure.
You can also use an investment calculator to find out how much you need to save each month to become self-insured. This will help you understand whether self-insurance is a feasible option for you and ensure that you have enough money set aside to cover any potential losses.
Additionally, if you are considering self-insurance for your car, you will need to complete an application and provide proof of financial responsibility, such as a security bond or cash deposit. This is because car accidents can be expensive, especially if there are high-tech features on the vehicle or associated medical costs. As such, you will need to have a significant amount of capital available to cover potential losses, usually between $40,000 and $60,000.
In summary, self-insurance can be a great way to save money on insurance premiums, but it is important to carefully calculate whether you have enough savings to cover any potential losses.
Billing Strategies for School Psychology Residents: Navigating Insurance Claims
You may want to see also

Choose a savings strategy
To become self-insured, you must have enough money to cover anything an insurance company would usually pay for. This means that you need a robust savings strategy to ensure you can cover any potential losses. Here are some tips to help you choose a savings strategy:
Define your savings goal
Firstly, you need to decide what you're saving for. Are you saving for a vacation, a college education for your children, a down payment on a house, or for retirement? Having a clear and specific savings goal will help you stay focused and motivated.
Set a timeline
Determine how much money you need to save and by when. For example, if you need $10,000 to buy a car next year, you'll need to save around $833 per month for the next 12 months. Setting a deadline will help you stay on track and ensure you're saving enough.
Create a budget
Figure out your monthly expenses and create a budget that outlines your essential spending, such as housing, transportation, food, and utilities. This will help you identify how much money you can realistically save each month towards your goal.
Automate your savings
Consider setting up automatic transfers from your checking account to your savings account. That way, you don't have to remember to transfer the money manually, and it's easier to stick to your savings plan. You can also split your direct deposit so that a portion of your paycheck goes directly into your savings account.
Choose the right accounts
Utilise different types of savings accounts to maximise your savings. For short-term goals, consider high-yield savings accounts, money market accounts, or certificates of deposit (CDs). For medium-term goals, you can also use these accounts, and for long-term goals, look into employer-sponsored retirement accounts, IRAs, or securities like stocks or mutual funds.
Break your goal into smaller chunks
To make your savings goal more manageable, break it down into smaller, more achievable milestones. For example, if you want to save $5,000 in 12 months, focus on saving around $416 each month or $104 per week. This smaller target may feel more attainable and help you stay motivated.
By following these steps, you can design a savings strategy that aligns with your goals and financial situation, helping you on your journey to becoming self-insured.
Insurance Emergencies: What Counts as an Accident?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Self-insurance is when you have enough money saved to cover any financial losses that you would have otherwise passed on to an insurance company. This means you are acting as your own insurance provider.
You should self-insure when you have enough money to cover a loss of income, property, or other expenses. You can determine this by assessing your savings and spending, including current and future expenses.
Self-insurance can save you money on insurance premiums, and you avoid the need for a medical exam and the application process. However, it is important to note that self-insurance does not provide a financial safety net, and you must be willing to risk losing money in an emergency.