Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that an individual is responsible for paying and that may or may not be reimbursed later. The term is most often used to describe an employee's work-related expenses that the company later reimburses. It also indicates a health insurance policyholder's nonreimbursable share of medical expenses such as deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. An out-of-pocket expense is a payment you make with your own money that an employer may reimburse later.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that an individual is responsible for paying and that may or may not be reimbursed later. | Deductibles, copays, coinsurance, airfare, car rentals, tolls, parking, lodging, meals, work-related supplies and tools |
| Out-of-pocket medical expenses are the amount a policyholder pays for a service or item their health insurance plan doesn’t cover. | 10% to 100% of the total cost of the item or service |
| Out-of-pocket costs refer to the portion of your covered medical expenses that you can expect to pay during the course of a plan year. | In-network costs for essential health benefits |
| Out-of-pocket healthcare expenses include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. | Set by federal law |
What You'll Learn

Deductibles
The 1095 tax forms are used by exchanges, employers, and health insurance companies, to report health insurance coverage to the IRS. Out-of-pocket costs refer to the portion of your covered medical expenses that you can expect to pay during the course of a plan year, although they typically only refer to in-network costs for essential health benefits, as there are no regulations in place to cap how much people spend on out-of-network care, and insurers are not required to cover services that aren't considered essential health benefits.
Georgia Medicaid Coverage: Ozempic and Diabetes Management
You may want to see also

Copays
The amount of copay varies depending on the type of service and the specific insurance plan. Copays are usually lower for in-network providers and higher for out-of-network providers.
It's important to note that copays are not the same as monthly premiums, which are paid to the insurance company to maintain coverage. Copays are paid directly by the policyholder and may or may not be reimbursed by the insurance company.
Understanding copays and other out-of-pocket expenses is crucial for managing healthcare costs and ensuring that policyholders are aware of their financial responsibilities under their health insurance plan.
Understanding Medical Insurance Coverage for STD Testing
You may want to see also

Coinsurance
Health insurance plans have out-of-pocket maximums that are set by federal law. This means that policyholders are responsible for paying the cost of a service or item their health insurance plan doesn't cover. Depending on the plan and the care received, policyholders could pay between 10% and 100% of the total cost of the item or service.
Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that an individual is responsible for paying and that may or may not be reimbursed later. The term is most often used to describe an employee's work-related expenses that the company later reimburses. It also indicates a health insurance policyholder's nonreimbursable share of medical expenses such as deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
Out-of-pocket healthcare expenses include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Health insurance plans have out-of-pocket maximums that are set by federal law. This means that policyholders are responsible for paying the cost of a service or item their health insurance plan doesn't cover. Depending on the plan and the care received, policyholders could pay between 10% and 100% of the total cost of the item or service.
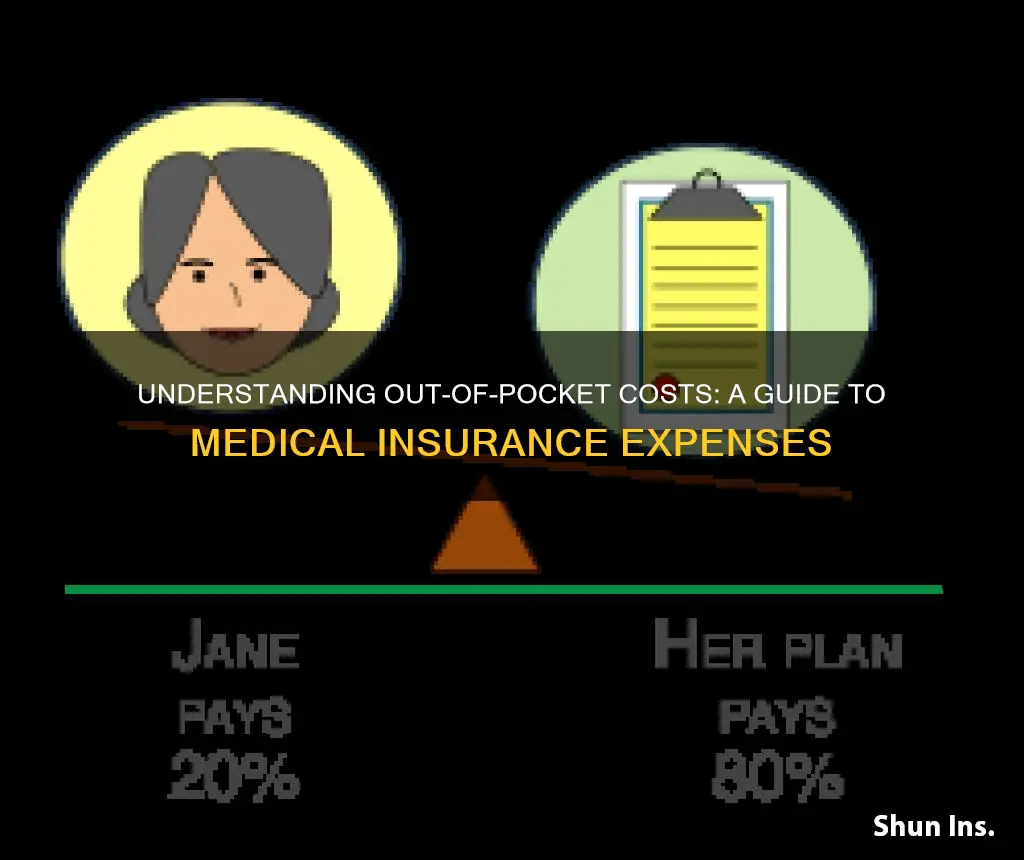
Out-of-pocket costs refer to the portion of a medical cost that the insurance company doesn't cover. Out-of-pocket costs are your share of the medical costs you incur and may include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
Understanding Medical Evacuation Insurance: Costs and Coverage Explained
You may want to see also

Out-of-pocket maximums
The out-of-pocket maximum is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs. This maximum amount is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs.
The out-of-pocket maximum is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs. This maximum amount is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs.
The out-of-pocket maximum is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs. This maximum amount is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs.
The out-of-pocket maximum is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs. This maximum amount is the total amount a policyholder will pay for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance before the insurance company will start to cover the medical costs.
Medical Insurance Deductions: What Self-Employed Individuals Need to Know
You may want to see also

Nonreimbursable share of medical expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that an individual is responsible for paying and that may or may not be reimbursed later. The term is most often used to describe an employee's work-related expenses that the company later reimburses. It also indicates a health insurance policyholder's nonreimbursable share of medical expenses such as deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. An out-of-pocket expense is a payment you make with your own money that an employer may reimburse later. Work-related out-of-pocket expenses are usually reimbursed by the employer. In health insurance, out-of-pocket expenses are your share of the medical costs you incur and may include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
Out-of-pocket medical expenses are the amount a policyholder pays for a service or item their health insurance plan doesn’t cover. In many cases, these expenses will count toward your plan’s out-of-pocket maximum. If you have a medical bill that includes an out-of-pocket expense, you’ll be responsible for paying the cost on your own. Depending on your plan and the care you receive, you could pay between 10% and 100% of the total cost of the item or service.
Out-of-pocket costs refer to the portion of your covered medical expenses that you can expect to pay during the course of a plan year, although they typically only refer to in-network costs for essential health benefits, as there are no regulations in place to cap how much people spend on out-of-network care, and insurers are not required to cover services that aren't considered essential health benefits.
Employees often spend their own money on business-related expenses, especially if they travel on behalf of a company. These out-of-pocket expenses are typically reimbursed by the employer using a company-approved process. Common examples of work-related out-of-pocket expenses include airfare, car rentals, taxis or ride-sharing fares, gas, tolls, parking, lodging, and meals, as well as work-related supplies and tools.
Health insurance plans have out-of-pocket maximums that are set by federal law. Out-of-pocket healthcare expenses include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. A deductible is the amount of money you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance company will start to cover your medical costs. Until you reach your deductible, you’re responsible for paying a certain amount of your healthcare expenses without the help of your insurer. Your health plan will outline your annual deductible. The amount will vary depending on your coverage’s metallic tier, health insurance company, and plan type.
Steward Medical Group Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide to Coverage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Out-of-pocket expenses are costs that an individual is responsible for paying and that may or may not be reimbursed later. Out-of-pocket healthcare expenses include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
The amount you have to pay out-of-pocket for medical expenses depends on your health insurance plan. The amount will vary depending on your coverage’s metallic tier, health insurance company, and plan type. You could pay between 10% and 100% of the total cost of the item or service.
An out-of-pocket medical expense is the amount a policyholder pays for a service or item their health insurance plan doesn’t cover. Even though you pay for your monthly health insurance premium on your own, your insurer doesn’t consider that payment an out-of-pocket cost. Common examples of out-of-pocket medical expenses include deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.