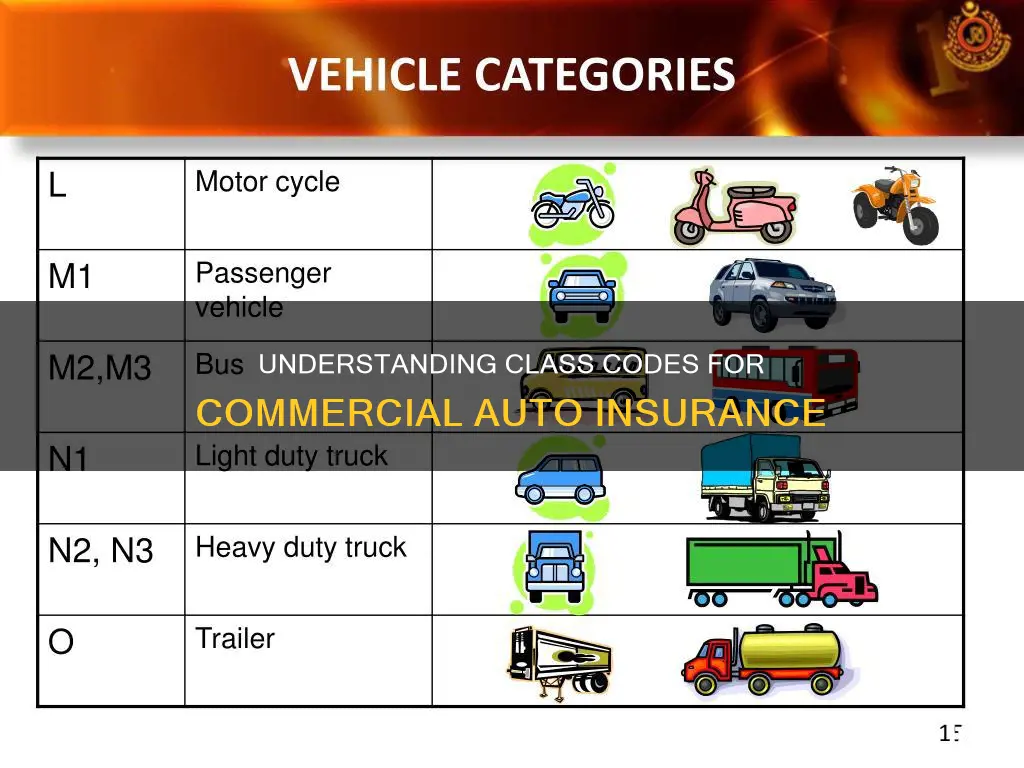
Commercial auto insurance class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of vehicles and drivers to help insurance companies determine the level of risk associated with insuring them. The codes are based on factors such as vehicle usage, the nature of the work performed by the insured, and the risk level of the industry. These codes are important because they impact the cost of insurance, with higher-risk classifications leading to higher premiums. While specific codes may vary between insurance providers, understanding the classification system is crucial for business owners to ensure they are properly covered at the correct rate.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To determine the risk level of a business |
| Usage | To set insurance rates and coverage |
| Management | Handled by organisations like Insurance Services Office (ISO), National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI), North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), and Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) |
| Types | General liability class codes, workers' compensation class codes, vehicle insurance class codes |
| Impact | Affects insurance cost, coverage, and exclusions |
| Examples | Barbershops – 10113, Consultants – 41677, Photographers – 16471, Technology businesses – 91555 |
What You'll Learn

How class codes impact insurance cost
Class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs and vehicles. They are a crucial aspect of commercial auto insurance as they help insurance providers determine the level of risk associated with various occupations and vehicles. This, in turn, impacts the cost of insurance.
In the context of workers' compensation insurance, class codes are used to assess the risk level of different occupations. Each type of job is assigned a specific code based on the nature of the work and the associated risks. These codes help insurance companies determine the premium employers need to pay for their workers' compensation insurance. The higher the risk, the higher the premium.
For example, a clerical office employee might have a class code of 8810, indicating a relatively low-risk occupation. In contrast, a construction worker or a carpenter might have a class code of 5437, reflecting the higher risks inherent in their work.
Class codes also play a role in determining insurance rates for commercial vehicles. The business use class, which is a classification based on commercial vehicle usage, is a factor in the rating process for commercial auto insurance. There are three main business use classifications: service, retail, and commercial. The specific class code assigned to a vehicle will impact the insurance cost, with higher-risk classifications resulting in higher premiums.
Insurers use class codes to quantify the risk they assume when providing coverage. Each class code has a rate associated with it, which helps calculate premiums. For instance, a bank in New Jersey might have a class code rate of $0.30 per hundred square feet. This rate would be applied to all banks seeking general liability coverage, as they fall within the same risk class.
Accurate class codes are essential for businesses to ensure they are paying the correct premiums for their level of risk. Incorrect codes can result in overpayment or underpayment, both of which can have financial implications. By understanding class codes and how they impact insurance costs, businesses can better manage their insurance policies and ensure they are getting the best value for their money.
Insufficient Auto Insurance: Risks and Financial Burdens
You may want to see also

How to find the correct class code
Commercial auto insurance class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs to help insurance companies determine the level of risk associated with various occupations. These codes are important because they impact the cost of insurance, with higher-risk jobs requiring higher premiums.
To find the correct class code for your business, you can take the following steps:
- Consult your insurance provider: They can help you verify that the codes assigned to your business are accurate. They will take into account the nature of the work your employees perform and can provide guidance on the appropriate class codes.
- Review job descriptions: Ensure that job descriptions are up-to-date and accurately reflect the work being performed. This is important because class codes are based on the inherent risks of specific job roles. By having detailed and current job descriptions, you can more accurately determine the correct class codes.
- Use state resources: Many states provide resources to help businesses find the correct class codes. These resources can include information specific to your state's regulations and guidelines. You can typically find these resources through your state's website or by contacting relevant departments or agencies.
- Refer to industry resources: In addition to state resources, there are industry-specific resources that can help you identify the correct class codes. For example, the National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI) provides information on class codes for various occupations. You can also refer to resources from organizations or associations within your industry that may offer guidance on class codes relevant to your business.
- Seek professional assistance: Commercial insurance can be complex, and finding the correct class code may require expertise. Consider consulting a professional agent or broker who specializes in commercial insurance. They can help you navigate the process, identify risks, and ensure that your business is properly covered at the correct rate.
By following these steps and staying informed about the latest updates and resources, you can be confident that you have the correct class codes for your commercial auto insurance. This will help ensure that you are paying appropriate premiums and have the right level of coverage for your business needs.
Is Your Gap Flood Insurance Capitalized?
You may want to see also

How insurers use class codes
Class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs or businesses. They are used by insurance companies to determine the level of risk associated with insuring various occupations or business activities. The higher the risk, the higher the premium charged for insurance coverage.
In the context of commercial auto insurance, class codes are determined by commercial vehicle usage and are a part of the rating process in classifying commercial vehicles. There are three main business use classifications: service, retail, and commercial. Service refers to the transportation of tools, equipment, and supplies to and from jobs, while retail involves transporting property to and from individual households. The commercial classification applies to any other type of transportation that does not fall under service or retail.
Insurers use class codes to quantify the risk they assume when providing coverage. Each class code has a rate associated with it, which helps calculate premiums. For example, a class code for a bank in New Jersey might assess a rate of $0.30 per hundred square feet. This rate would be applied to all banks that seek general liability coverage, as they are considered to be in the same class with similar risks.
Class codes are essential for businesses to ensure they are paying the correct premium for their level of risk. Inaccurate class codes can result in overpayment or underpayment, both of which can have consequences. By understanding and verifying their class codes, businesses can better manage their insurance costs and ensure they have the right coverage.
Insurance Gap Referral: Filling the Coverage Void
You may want to see also

How class codes affect coverage and exclusions
Class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs and businesses. In the context of commercial auto insurance, class codes help to determine the level of risk associated with insuring different types of vehicles and drivers. This, in turn, affects the cost of insurance coverage.
When it comes to commercial auto insurance, class codes are based on the usage of the vehicle. There are three main business use classifications: service, retail, and commercial. Service businesses do not transport any property except for tools, equipment, and supplies to and from jobs. Retail businesses transport property to and from individual households. Commercial businesses are involved in any other type of transportation that does not fall under service or retail.
The assigned class code impacts the cost of commercial auto insurance by determining the level of risk associated with the vehicle's usage. A higher-risk classification will result in a higher premium for the insurance coverage. The class code also influences the specific exclusions in the insurance policy, outlining what is not covered by the insurance provider.
For example, let's consider a business that provides both retail delivery services and commercial transportation of goods. The delivery aspect of the business would fall under the retail classification, while the transportation of goods would be classified as commercial. As a result, the insurance provider would take into account the risks associated with both classifications when determining the cost of coverage and the specific exclusions.
It is important to note that class codes can vary depending on the insurance provider and the specific circumstances of the business. Insurance companies may use their own classification systems or refer to standardized lists provided by organizations such as the Insurance Services Office (ISO) or the National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI).
Liability Auto Insurance and Flood Damage: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Examples of class codes
Class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs to help insurance companies determine the risk level associated with various occupations. These codes are essential in the commercial auto insurance industry as they impact the cost of insurance. While workers' comp class codes are specific to workers' compensation insurance, there are also class codes for other types of insurance, including commercial auto insurance. These codes help determine the risk level associated with different types of vehicles and drivers.
8810: Clerical Office Employees
This class code is for employees who work in an office setting and perform clerical tasks such as data entry, filing, and answering phones. The risk level associated with this type of work is typically low, as it does not involve physical labour or hazardous conditions.
8742: Salespersons – Outside
The class code for outside salespersons involves travelling to meet with clients and customers to sell products or services. This type of work may involve driving long distances and visiting various locations, which could increase the risk of accidents or other work-related injuries.
5437: Carpentry – NOC (Not Otherwise Classified)
This class code is assigned to carpenters who do not fall under a specific category. Carpentry work can vary widely, from construction sites to home repairs, each presenting its own set of risks and hazards.
9015: Taxi Drivers and Limousine Services
Taxi drivers and limousine services fall under this class code, which considers the unique risks associated with transporting passengers for a living. This includes factors such as long driving hours, varying routes, and the potential for confrontational situations with passengers.
8390: Delivery Drivers – Local
Local delivery drivers, who transport goods and packages within a limited geographic area, are classified under this class code. The risks associated with local deliveries may be influenced by factors such as traffic conditions, parking difficulties, and the potential for theft or damage to the delivered items.
7380: Long-Haul Truckers
Long-haul truckers, who travel long distances across states or regions to transport goods, have a class code that reflects the unique challenges of their profession. This includes extended periods of driving, fatigue management, and the potential for isolated incidents in remote locations.
Auto Accidents and Medical Insurance: Understanding the Financial Impact
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Class codes are numerical identifiers assigned to different types of jobs. They help insurance companies determine the level of risk associated with various occupations.
Class codes are important because they impact the cost of insurance. Accurate class codes ensure that the correct premium is paid for the level of risk.
You can find your class code by consulting your insurance provider or by using resources such as the National Council on Compensation Insurance (NCCI) or your state's workers' compensation board.







