Internal rate of return (IRR) is a measurement used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs, and can be used to compare life insurance to other asset classes. It is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow. IRR is a useful tool for comparing permanent life insurance product performance, such as whole life and universal life insurance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | The internal rate of return (IRR) is the compound rate of return that results in a net present value equal to zero. |
| Use | IRR is used to evaluate life insurance policy designs and compare life insurance to other asset classes. |
| Inputs | IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow. |
| Types | There are two different IRR measurements: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. |
What You'll Learn
- IRR is a financial analysis tool to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams
- IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs
- IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow
- IRR is the discounting rate which sets the NPV of a cash flow stream to zero
- There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR

IRR is a financial analysis tool to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a financial analysis tool used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs, and can be useful in comparing life insurance to other asset classes. IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow. It provides an indicator of the efficiency, quality, or yield of an investment.
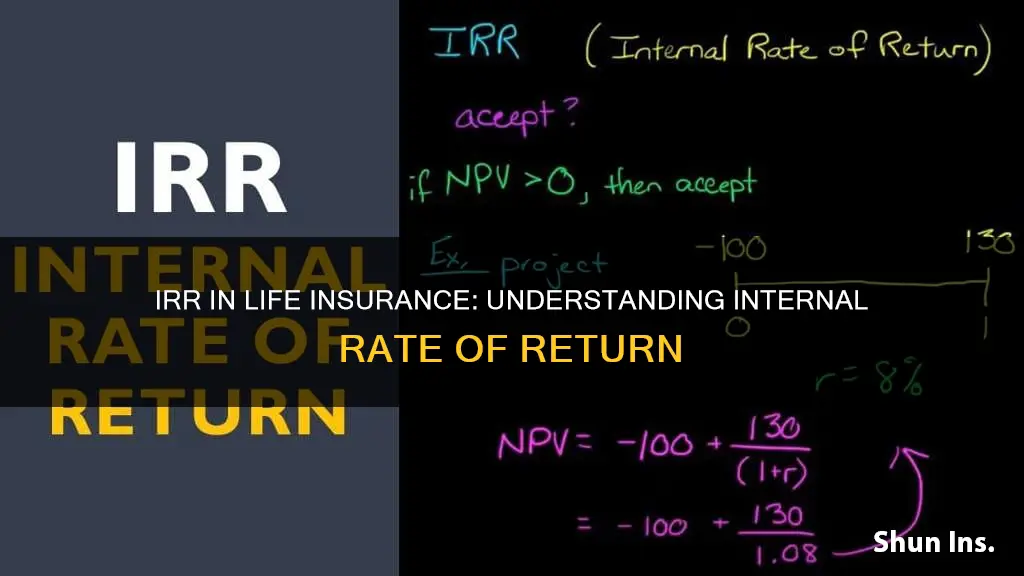
The IRR involves the concept of Net Present Value (NPV), which is the present value of all cash flows in the present and future expected from an investment. The present value of money is always higher than the same amount in the future. This is due to uncertainty in the interim period and price inflation, which reduces your purchasing power. Any future value (FV) of money must be “discounted”, or reduced, at some discounting rate to arrive at its present value (PV).
The IRR is that discounting rate which sets the NPV of a cash flow stream to zero. In other words, the IRR represents the interest rate at which the amount(s) you invest will get compounded to fetch you the maturity amount(s).
There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. CV IRR is the cumulative internal rate of return on the cash surrender value (factoring in policy surrender charges).
Canceling Stonebridge Life Insurance: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs
Internal rate of return (IRR) is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs. IRR is a financial analysis tool used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. It is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow. IRR is well-equipped to tell us what sort of return we are achieving on these types of life insurance.
There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. CV IRR is the cumulative internal rate of return on the cash surrender value (factoring in policy surrender charges). DB IRR, on the other hand, is the internal rate of return on the death benefit.
The IRR is the discounting rate that sets the net present value (NPV) of a cash flow stream to zero. In other words, the IRR represents the interest rate at which the amount(s) you invest will get compounded to fetch you the maturity amount(s). The present value of money is always higher than the same amount in the future due to uncertainty in the interim period and price inflation, which reduces your purchasing power.
The IRR is a useful metric for comparing life insurance to other asset classes. It provides an indicator of the efficiency, quality, or yield of an investment. However, it is important to note that an IRR calculated today is purely hypothetical and its output is only as accurate as its inputs.
U.S.A.A. Term Life Insurance: Level or Decreasing Coverage?
You may want to see also

IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow
Internal rate of return (IRR) is a commonly quoted measurement when talking about whole life and universal life insurance. IRR is a financial analysis tool to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. It is defined as the compound rate of return that results in a net present value equal to zero. In other words, the IRR is the rate at which an investment breaks even in today’s dollars. IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs, and can be useful in comparing life insurance to other asset classes.
Cash flow, the second input, refers to the movement of money in and out of the investment. In the context of life insurance, the premiums paid into the policy represent negative cash flows, while the payouts or benefits received constitute positive cash flows. The timing and amount of these cash flows significantly impact the IRR. For example, a policy with higher premiums paid over a shorter period may result in a different IRR compared to a policy with lower premiums paid over a longer duration.
By considering both time and cash flow, IRR provides an indicator of the efficiency, quality, or yield of an investment. It helps individuals and financial professionals assess the potential returns and performance of life insurance policies, making it a valuable tool in financial planning and decision-making.
There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. CV IRR focuses on the cumulative internal rate of return on the cash surrender value, taking into account any policy surrender charges. On the other hand, DB IRR likely considers the internal rate of return on the death benefit offered by the policy.
Life Insurance: Comprehensive Cover for Peace of Mind
You may want to see also

IRR is the discounting rate which sets the NPV of a cash flow stream to zero
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a financial analysis tool used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs, and can be useful in comparing life insurance to other asset classes. IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow. It provides an indicator of the efficiency, quality, or yield of an investment.
The IRR is the discounting rate which sets the Net Present Value (NPV) of a cash flow stream to zero. In other words, the IRR represents the interest rate at which the amount(s) you invest will get compounded to fetch you the maturity amount(s). The present value of money is always higher than the same amount in the future. This is due to uncertainty in the interim period and price inflation, which reduces your purchasing power. Any future value (FV) of money must be “discounted”, or reduced, at some discounting rate to arrive at its present value (PV).
There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. CV IRR is the cumulative internal rate of return on the cash surrender value (factoring in policy surrender charges). IRR is a commonly quoted measurement when talking about whole life and universal life insurance.
Life Insurance Payouts: Are They Taxable?
You may want to see also

There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR
The Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a financial analysis tool used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams. IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs, and can be used to compare life insurance to other asset classes. IRR is dependent on two inputs: time and cash flow.
Understanding Life Insurance: Cash Surrender Value Explained
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
IRR stands for Internal Rate of Return. It is a financial analysis tool used to compare the returns from two different cash flow streams.
IRR involves the concept of Net Present Value (NPV), which is the present value of all cash flows in the present and future expected from an investment. The present value of money is always higher than the same amount in the future. This is due to uncertainty in the interim period and price inflation, which reduces your purchasing power. Any future value (FV) of money must be “discounted”, or reduced, at some discounting rate to arrive at its present value (PV).
IRR is an important metric for evaluating life insurance policy designs and can be useful in comparing life insurance to other asset classes. IRR is well equipped to tell us what sort of return we are achieving on these types of life insurance.
There are two different IRR measurements that are useful when comparing permanent life insurance product performance: Cash Value (CV) IRR and Death Benefit (DB) IRR. CV IRR is the cumulative internal rate of return on the cash surrender value (factoring in policy surrender charges).







