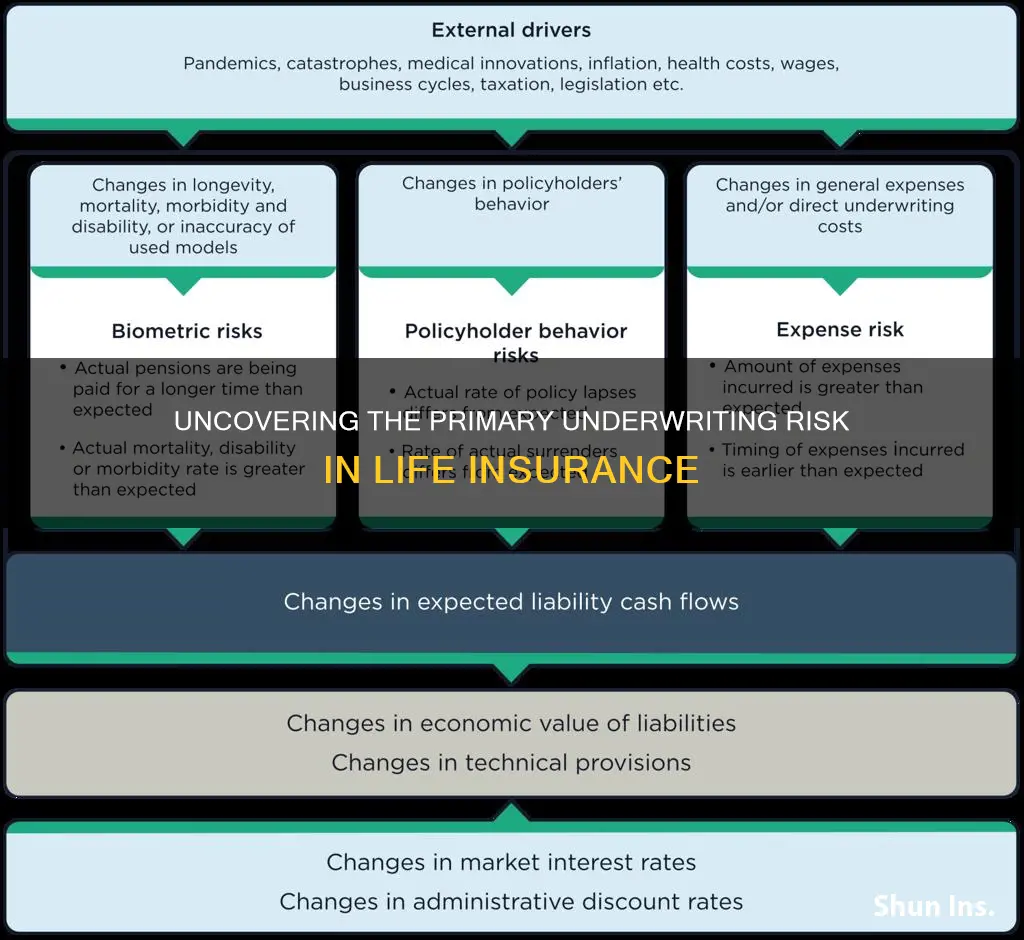
Life insurance underwriting involves assessing the risk associated with insuring an individual's life, and it is a critical process for insurance companies to ensure financial stability and minimize potential losses. The major source of risk in life insurance underwriting is the inherent uncertainty surrounding an individual's future health and longevity. Underwriters must carefully evaluate factors such as age, medical history, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions to determine the likelihood of the insured individual's premature death or developing severe health conditions. This assessment is crucial as it directly impacts the premium rates and the overall profitability of the insurance policy. Understanding and managing these risks are essential for insurance companies to offer life insurance products that are both financially viable and beneficial to policyholders.
What You'll Learn
- Health and Lifestyle: Underwriting risk is heavily influenced by an individual's health and lifestyle choices
- Age and Gender: Older individuals and men may face higher underwriting risks due to statistical trends
- Financial Status: Wealth and income can impact risk assessment, especially for high-net-worth individuals
- Family Medical History: Genetic predispositions and family medical history play a role in underwriting decisions
- Occupational Hazards: Certain professions expose individuals to higher risks, impacting insurance underwriting

Health and Lifestyle: Underwriting risk is heavily influenced by an individual's health and lifestyle choices
Underwriting risk in life insurance is significantly impacted by an individual's health and lifestyle, which are critical factors that insurers consider when assessing the likelihood of a policyholder's future claims. This aspect of underwriting is essential as it directly influences the premium rates and the overall viability of the insurance policy.
Health status is a primary concern for insurers. Pre-existing medical conditions, chronic illnesses, and physical ailments can significantly increase the risk of mortality or morbidity, which in turn affects the underwriting process. For instance, individuals with a history of heart disease, diabetes, or cancer may be considered higher-risk candidates, leading to higher premiums or even denial of coverage. The severity and management of these conditions are also crucial; a well-controlled diabetes patient might be offered more favorable terms compared to one who is not.
Lifestyle choices play an equally important role in underwriting risk. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use are well-documented risk factors for various health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, lung cancer, and liver damage. Insurers often request detailed health and lifestyle information, including smoking habits, alcohol intake, and any recreational drug use, to accurately assess the potential risks associated with insuring an individual.
Additionally, certain lifestyle activities can also be considered high-risk behaviors. High-risk occupations, such as those in construction or mining, can increase the likelihood of accidents and injuries. Similarly, participation in extreme sports like skydiving or rock climbing can lead to higher underwriting risks due to the increased potential for physical harm.
In summary, health and lifestyle are critical components in the underwriting process for life insurance. Insurers use this information to assess the risk profile of potential policyholders, ensuring that the coverage provided is appropriate and financially viable. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their insurance coverage and potentially improve their chances of securing favorable terms.
Life Insurance After Being Fired: What's the Timeline?
You may want to see also

Age and Gender: Older individuals and men may face higher underwriting risks due to statistical trends
Age and gender play significant roles in life insurance underwriting, often influencing the assessment of risk and the subsequent premium rates. When it comes to life insurance, older individuals and men may encounter higher underwriting risks due to various statistical trends and factors.
As individuals age, their overall health and life expectancy tend to decline. Older adults are generally considered higher-risk candidates for life insurance due to the increased likelihood of pre-existing medical conditions, chronic illnesses, and a higher mortality rate. Insurance companies often use age as a significant determinant in their underwriting process, with older applicants potentially facing higher premiums or even being deemed uninsurable. For instance, a 65-year-old male with a history of heart disease may be considered a higher-risk case, leading to more expensive insurance or a denial of coverage.
Gender also contributes to underwriting risk assessment. Statistically, men have historically faced higher mortality rates than women, particularly in younger age groups. This trend is often attributed to various factors, including biological differences, lifestyle choices, and societal influences. Insurance underwriters take these statistical trends into account when evaluating risk. As a result, men, especially those in certain age brackets, may be offered higher premiums or face more stringent underwriting requirements. For example, a 35-year-old male with a history of smoking and a sedentary lifestyle might be considered a higher-risk profile, leading to more expensive life insurance or a need for additional medical exams.
The impact of age and gender on underwriting risk is further emphasized by the presence of certain health conditions. Older individuals are more prone to age-related diseases such as Alzheimer's, cancer, and cardiovascular issues. Men, on the other hand, may have higher rates of certain cancers, such as prostate and lung cancer, and are also more likely to engage in risky behaviors, including smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These factors contribute to the overall risk assessment and can result in higher insurance premiums or limited coverage options.
In summary, age and gender are critical considerations in life insurance underwriting. Older individuals and men may face higher risks due to statistical trends, health conditions, and mortality rates. Insurance companies use these factors to assess the likelihood of claims and determine premium rates, ensuring that the coverage provided aligns with the potential risks associated with each individual's profile. Understanding these trends is essential for both applicants and insurance providers to make informed decisions regarding life insurance coverage.
Life Insurance: Haven's Affiliate Program Explained
You may want to see also

Financial Status: Wealth and income can impact risk assessment, especially for high-net-worth individuals
The financial status of an individual is a critical factor in life insurance underwriting, particularly when assessing the risk for high-net-worth individuals. Wealth and income significantly influence the underwriter's decision-making process, as they provide insights into the individual's ability to meet financial obligations and manage potential risks. For high-net-worth individuals, their financial resources can either mitigate or exacerbate certain risks associated with life insurance.
Wealth plays a pivotal role in risk assessment as it directly correlates with an individual's capacity to fulfill financial commitments. High-net-worth individuals often possess substantial assets, investments, and property, which can serve as collateral or security in the event of a claim. This financial security can reduce the perceived risk for underwriters, as they know that the policyholder has the means to honor the insurance obligations. For instance, a person with a large estate and diverse investments may be considered less risky, as their financial resources can be utilized to settle any potential claims, ensuring the insurance company's interests are protected.
Income is another essential aspect of financial status that underwriters consider. High-income earners may present a different set of risks compared to those with lower incomes. While a high income can indicate financial stability and the ability to afford premium payments, it might also suggest a higher level of debt or investment risk. Underwriters need to carefully evaluate the source and stability of income to assess the individual's long-term financial health. For instance, a high-income professional with a stable career might be considered a lower risk, but if their income is heavily dependent on a single employer or industry, it could introduce a new layer of uncertainty.
In the context of life insurance, the financial status of high-net-worth individuals can also impact the type of coverage and premium rates. Wealthier individuals may require more extensive coverage, such as higher death benefits, to protect their extensive assets and liabilities. However, their financial resources can also enable them to afford more expensive policies, which might include additional riders or benefits. Underwriters must carefully consider these factors to ensure that the policy is tailored to the individual's needs while maintaining a balanced risk assessment.
Moreover, the financial status of high-net-worth individuals can influence the underwriting process in terms of speed and efficiency. With substantial financial resources, these individuals may be able to provide quick access to necessary documentation and assets, streamlining the underwriting process. This can be particularly beneficial for time-sensitive cases or when quick decisions are required. However, underwriters must also be cautious and verify the accuracy of the provided information to ensure fair and accurate risk assessment.
Life Insurance: Strategies for Better Coverage and Peace of Mind
You may want to see also

Family Medical History: Genetic predispositions and family medical history play a role in underwriting decisions
Family medical history and genetic predispositions are crucial factors that significantly influence life insurance underwriting decisions. Insurers use this information to assess the risk associated with insuring an individual, as certain medical conditions and genetic traits can increase the likelihood of developing specific health issues. By evaluating family medical history, underwriters can identify patterns and trends that may indicate a higher risk for the applicant or their beneficiaries.
When considering family medical history, underwriters look for a variety of factors. Firstly, they examine the presence of chronic diseases or conditions within the family. For example, a history of heart disease, diabetes, or certain types of cancer can raise concerns about the insured individual's future health. These conditions may be influenced by genetic factors, making it essential for underwriters to understand the family's medical background. Additionally, the age at which these conditions appeared in family members can provide valuable insights. Younger onset of diseases might suggest a stronger genetic predisposition, which could impact the underwriting process.
Genetic predispositions are another critical aspect. Some individuals may have a genetic makeup that increases their susceptibility to particular illnesses or health complications. For instance, certain genetic markers are associated with a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, while others may predispose individuals to cardiovascular issues. Insurers use advanced medical databases and genetic testing results to identify these predispositions. By understanding these genetic risks, underwriters can make more informed decisions regarding premium rates and policy terms.
Moreover, family medical history helps underwriters assess the likelihood of hereditary conditions. Some medical conditions, such as cystic fibrosis or Huntington's disease, have a genetic basis and can be inherited. If a close family member has one of these conditions, it may indicate a higher risk for the applicant. Underwriters carefully consider the type and severity of the condition, as well as the family's medical tree, to determine the appropriate level of coverage and premium.
In summary, family medical history and genetic predispositions are vital tools for life insurance underwriters. They provide valuable insights into an individual's potential health risks, allowing insurers to make informed decisions. By evaluating these factors, underwriters can offer suitable coverage options while managing the underwriting risk effectively. It is essential for applicants to provide comprehensive medical information to ensure accurate risk assessment and fair underwriting practices.
How to Get Life Insurance for Your Adult Daughter
You may want to see also

Occupational Hazards: Certain professions expose individuals to higher risks, impacting insurance underwriting
The concept of occupational hazards is a critical aspect of life insurance underwriting, as certain professions inherently carry higher risks that can significantly impact the assessment of an individual's insurability. When evaluating life insurance applications, underwriters must consider the unique challenges and dangers associated with specific occupations, which can influence premium rates and coverage decisions.
One of the primary sources of risk in life insurance underwriting is the nature of the job itself. Some professions are inherently more dangerous due to the inherent risks involved in the work. For instance, construction workers, miners, and loggers face a higher likelihood of workplace injuries or fatalities due to the physical demands and hazardous conditions of their jobs. Similarly, emergency responders like firefighters and police officers are exposed to extreme physical and mental stress, often in dangerous situations, which can lead to long-term health issues and increased mortality rates. These occupations are considered high-risk, and individuals in these lines of work may be charged higher premiums or may even be deemed uninsurable due to the potential for severe and sudden health complications.
Underwriters also consider the physical demands and environmental factors associated with different professions. Jobs requiring heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or exposure to extreme temperatures and harsh environments can lead to various health issues, including musculoskeletal disorders, respiratory problems, and heat-related illnesses. For example, manual laborers, warehouse workers, and outdoor sports professionals may face a higher risk of injuries and chronic health conditions, which can impact their insurability.
Furthermore, certain occupations may involve exposure to hazardous substances or materials, such as chemicals, heavy metals, or radiation. These substances can have long-term health effects, including cancer, respiratory diseases, and organ damage. Industries like manufacturing, mining, and healthcare often involve such risks, and individuals in these fields may require specialized assessments and higher insurance premiums to account for the potential health impacts.
In addition to physical risks, some professions also carry higher mental health risks. Jobs with high-stress levels, demanding work schedules, or those involving public safety and emergency response can contribute to increased rates of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These mental health concerns can significantly impact an individual's overall well-being and longevity, making them a relevant factor in life insurance underwriting.
In summary, occupational hazards play a significant role in life insurance underwriting, as certain professions expose individuals to higher risks that can affect their insurability and premium costs. Underwriters must carefully assess the unique challenges and dangers associated with specific occupations to make informed decisions regarding coverage and pricing, ensuring that the risks are appropriately managed and communicated to policyholders.
Bank's Interest: Insuring Debtor's Life, Ethical or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Underwriting risk in life insurance primarily stems from the inherent uncertainty of human life expectancy and the potential for adverse health events. The major sources of risk include age, health status, lifestyle factors, family medical history, and the individual's occupation.
Age is a critical factor as the risk of death increases with age. Younger individuals generally face lower underwriting risks due to longer life expectancies, while older applicants may be considered higher risk, especially if they have pre-existing health conditions.
Health status significantly influences underwriting decisions. Individuals with chronic illnesses, such as heart disease, diabetes, or cancer, may be considered higher risk and could face higher premiums or even denial of coverage. Underwriters assess health through medical exams, lab tests, and health questionnaires.
Yes, lifestyle choices can impact underwriting risk. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and a sedentary lifestyle are considered high-risk behaviors. These factors can lead to an increased likelihood of health issues and, consequently, higher underwriting risks.
Family medical history is an important consideration. Underwriters review genetic predispositions to certain diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, or certain types of cancer. A family history of these conditions may indicate a higher risk for the individual, potentially affecting underwriting terms.







