Life insurance is a financial product that provides a financial safety net for beneficiaries in the event of the insured's death. The payment for life insurance, often referred to as the death benefit, is a predetermined sum of money that the insurance company pays out to the designated beneficiaries upon the insured's passing. This payment is designed to offer financial security and peace of mind to the insured's loved ones, helping them cover essential expenses and maintain their standard of living. The amount of the death benefit can vary widely depending on the type of policy, the insured's age, health, and lifestyle factors, and the insurance company's terms and conditions. Understanding the payment structure of life insurance is crucial for individuals to choose the right policy that aligns with their financial goals and provides adequate coverage for their loved ones.
What You'll Learn
- Premiums: The cost of insurance, paid regularly (monthly, annually)
- Term Length: Duration of coverage, e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years
- Death Benefit: Payout upon death, often a lump sum
- Types of Plans: Term, whole life, universal life, and more
- Factors Affecting Cost: Age, health, coverage amount, and policy type

Premiums: The cost of insurance, paid regularly (monthly, annually)
When considering life insurance, understanding the concept of premiums is crucial. Premiums are the regular payments made by the policyholder to the insurance company to maintain their life insurance coverage. These payments are typically made on a monthly or annual basis, depending on the policyholder's preference and the insurance provider's offerings.
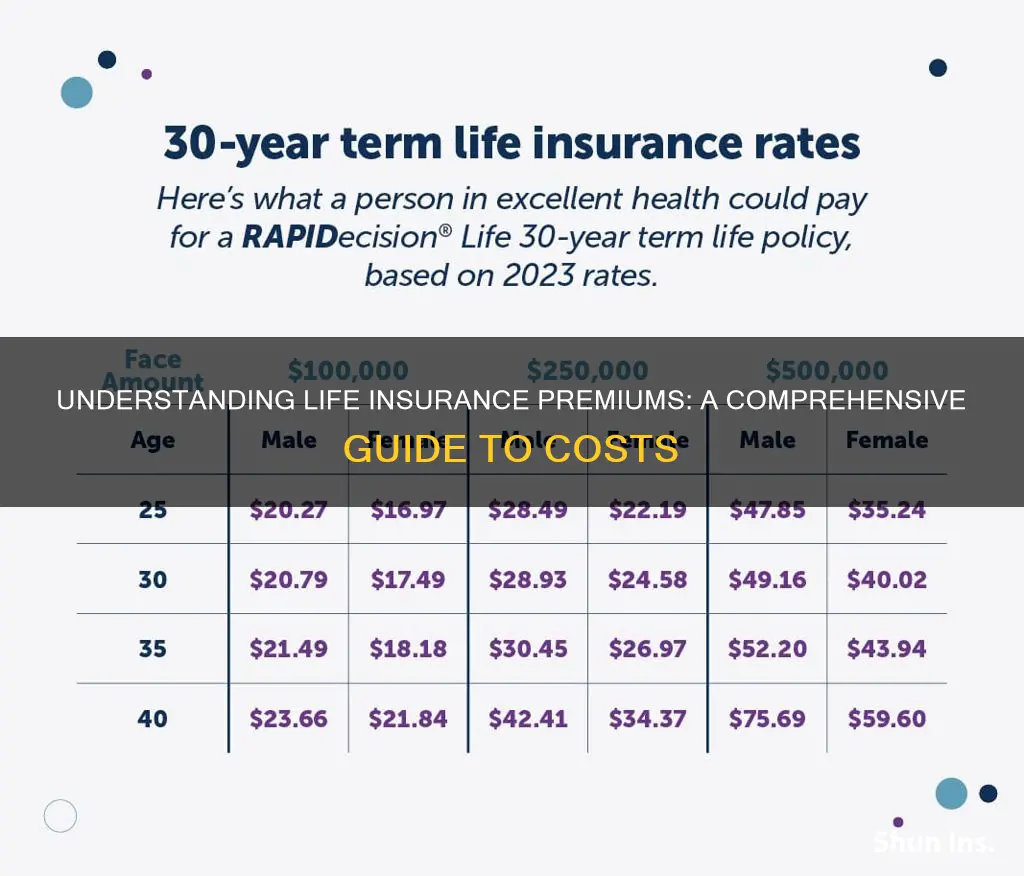
The amount of premium paid can vary significantly depending on several factors. Firstly, the type of life insurance policy plays a major role. Term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specified period, often has lower premiums compared to permanent life insurance, which offers lifelong coverage. Additionally, the amount of coverage, or death benefit, directly impacts premium costs. Higher death benefits generally result in higher premiums as the insurance company assumes a greater risk by promising a larger payout upon the insured individual's death.
Age and gender are other critical factors influencing premium rates. Younger individuals, especially those in their 20s and 30s, often benefit from lower premiums due to their perceived lower risk of death. Similarly, men and women may have different premium rates, with statistical data sometimes indicating that men pay more for life insurance. However, it's important to note that these factors are just a starting point, and insurance companies consider a comprehensive set of criteria to determine premiums.
Furthermore, the overall health and lifestyle of the insured individual can significantly impact premium costs. Non-smokers, for instance, may be offered lower premiums compared to smokers, as smoking increases the risk of various health issues, which can lead to higher insurance claims. Similarly, individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those who engage in high-risk activities may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of potential health complications.
In summary, premiums are a fundamental aspect of life insurance, representing the cost of maintaining coverage. The amount paid can vary based on policy type, coverage amount, age, gender, and individual health factors. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions when choosing and managing their life insurance policies.
Life Insurance Agent: Is It a Tough Job?
You may want to see also

Term Length: Duration of coverage, e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years
When considering life insurance, one of the most crucial factors to determine is the term length, which refers to the duration of coverage provided by the policy. This term length is a significant decision that can impact the overall cost and benefits of the insurance. Here's a breakdown of how to approach this:
The term length options typically range from 10 to 30 years, offering policyholders flexibility in choosing a plan that aligns with their specific needs. For instance, a 10-year term is suitable for those seeking temporary coverage, often for a specific financial goal, such as paying off a mortgage. In contrast, a 30-year term provides long-term financial security, ensuring that your loved ones are protected throughout the majority of your working years. The 20-year term is a popular choice, offering a balance between affordability and extended coverage.
When selecting a term length, it's essential to consider your financial situation and life goals. Younger individuals often opt for longer terms, as they are typically in better health and can afford the potentially higher premiums. As you age, you may choose to convert to a permanent life insurance policy, ensuring lifelong coverage. Additionally, some policies offer the option to increase the term length later, providing an opportunity to extend coverage if needed.
The payment structure for life insurance is directly tied to the chosen term length. Longer terms generally result in lower monthly premiums, making it more affordable for individuals with limited budgets. However, this may mean that the coverage might not be as comprehensive as shorter-term policies. Conversely, shorter-term policies often have higher premiums but provide more extensive coverage during the initial years.
In summary, the term length is a critical aspect of life insurance, influencing both the cost and the level of protection. It is a decision that should be made after careful consideration of your personal circumstances, financial goals, and the level of coverage required. Consulting with an insurance advisor can help you navigate these options and make an informed choice.
Life Insurance Application: A Step-by-Step Guide to Filling It Out
You may want to see also

Death Benefit: Payout upon death, often a lump sum
The death benefit is a crucial component of life insurance, and it is the primary reason why people purchase this type of coverage. When you buy life insurance, you are essentially making a financial agreement with an insurance company. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurer promises to provide a financial payout to your beneficiaries in the event of your death. This payout is known as the death benefit, and it serves as a safety net for your loved ones, ensuring they have the financial support they need during a difficult time.
The death benefit is typically paid out as a lump sum, which is a significant advantage for the policyholder's family. This lump sum payment can be used to cover various expenses associated with the deceased's passing, such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, or even the day-to-day living expenses of the beneficiaries for a period of time. It provides immediate financial relief and helps ensure that the family can maintain their standard of living and cover essential costs without going into debt.
One of the key advantages of the death benefit is its flexibility. The amount paid out can vary depending on the policyholder's preferences and needs. Some policies offer a fixed death benefit, ensuring a predetermined sum is paid out regardless of the cause of death. Others provide an adjustable benefit, allowing the policyholder to increase or decrease the payout amount over time. This flexibility is particularly useful for those who want to ensure their family's financial security and can adapt the policy as their circumstances change.
Furthermore, the death benefit can be tailored to suit specific requirements. For instance, some policies offer an additional benefit called "accelerated death benefit" or "critical illness benefit." This feature allows the policyholder to receive a portion of the death benefit early if they are diagnosed with a critical illness or suffer a severe medical condition. This early payout can be used to cover medical expenses, modify living arrangements, or provide financial support while the policyholder is still alive, ensuring they have access to the necessary resources during challenging times.
In summary, the death benefit is a vital aspect of life insurance, providing financial security and peace of mind. It ensures that your loved ones receive a lump sum payment upon your passing, helping them cover essential expenses and maintain their financial stability. With the option to customize the benefit amount and include additional features, life insurance policies offer a comprehensive solution to protect your family's future.
Life Insurance and Taxes: What's the Connection?
You may want to see also

Types of Plans: Term, whole life, universal life, and more
When considering life insurance, understanding the different types of plans and their associated payments is crucial. Here's an overview of some common types of life insurance plans and how their payments work:
Term Life Insurance: This is a straightforward and affordable type of coverage that provides protection for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. The payment structure is simple: you pay a fixed premium for the chosen term. During this period, the insurance company guarantees a death benefit if the insured individual passes away. Term life insurance is ideal for those seeking temporary coverage, often used to cover mortgage payments, provide for dependents, or ensure financial security during specific life stages. The payment remains consistent throughout the term, making it easy to budget.
Whole Life Insurance: In contrast to term life, whole life insurance offers permanent coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured individual. The payments, or premiums, are typically higher compared to term plans. However, whole life insurance provides a guaranteed death benefit and an accumulation of cash value over time. The initial payments might be higher, but they remain level for the policy's duration. This type of plan offers financial security and a savings component, making it a long-term financial strategy.
Universal Life Insurance: This plan provides flexible coverage and allows policyholders to adjust their payments and death benefits. The payments can vary, and you can choose to pay the minimum required or more to build up cash value. Universal life insurance offers a degree of customization, allowing you to increase or decrease payments as your financial situation changes. It provides a higher level of flexibility compared to traditional whole life, but it's essential to carefully manage the payments to ensure the policy remains in force.
Other types of life insurance plans include variable life insurance, which offers investment options, and participation life insurance, where the death benefit is influenced by the insurer's investment performance. Each plan has its own payment structure and benefits, catering to different financial goals and risk preferences. It's essential to review and compare these options to find the best fit for your needs and budget. Understanding the payment structure is key to making an informed decision when choosing life insurance.
Term Life Insurance: Getting Money Back
You may want to see also

Factors Affecting Cost: Age, health, coverage amount, and policy type
When considering life insurance, understanding the factors that influence the cost of your policy is crucial. The payment or premium you pay for life insurance is determined by several key elements, each playing a significant role in the overall expense. Here's an overview of the primary factors that impact the cost:
Age: One of the most significant determinants of life insurance premiums is your age. Younger individuals typically pay lower rates compared to older adults. This is because younger people are generally considered less risky to insure. Insurance companies often offer more competitive rates to younger policyholders as they are expected to have a longer lifespan, reducing the likelihood of claiming the policy early. As you age, the risk of health-related issues increases, leading to higher premiums. This is especially true for older adults with pre-existing medical conditions, as their life expectancy may be shorter, and the potential for claims is higher.
Health and Medical History: Your health and medical background significantly influence the cost of life insurance. Insurance providers assess your overall health and medical history to determine the risk associated with insuring you. People with a history of chronic illnesses, such as heart disease, diabetes, or cancer, may face higher premiums. Additionally, lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or a sedentary lifestyle can also impact the cost. Insurers may request medical exams or health questionnaires to evaluate your health status and determine the appropriate premium.
Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage you choose directly affects the cost of your life insurance policy. Higher coverage amounts result in higher premiums. This is because the insurance company needs to compensate for the larger payout in the event of the insured's death. The coverage amount should be carefully considered based on your financial obligations and dependents. It's essential to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordable premiums.
Policy Type: There are various types of life insurance policies, each with its own pricing structure. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. The cost of term life insurance is generally lower compared to permanent life insurance, which offers lifelong coverage. Permanent life insurance, such as whole life or universal life, includes an investment component and accumulates cash value over time. While it provides lifelong coverage, the cost is typically higher due to the additional features and benefits. The choice of policy type should align with your long-term financial goals and risk tolerance.
In summary, the cost of life insurance is influenced by age, health, coverage amount, and the type of policy chosen. Younger individuals with good health and lower coverage amounts may benefit from more affordable premiums. Conversely, older adults with health concerns and higher coverage needs will likely face higher costs. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions when selecting a life insurance policy that suits your needs and budget.
Retaining Life Insurance Policy Requirements: How Long is Necessary?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The payment, or premium, for life insurance is calculated based on several factors, including the type of policy, the insured individual's age, health, and lifestyle, and the desired coverage amount. Younger and healthier individuals typically pay lower premiums as they pose less risk to the insurance company. The premium is the amount the policyholder pays to maintain the insurance coverage and can vary significantly depending on the specific circumstances.
Yes, life insurance policies can have different payment structures. The most common is a level premium, where the insured pays a fixed amount at regular intervals (annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly) for the entire term of the policy. However, some policies offer a variable premium, where the payments increase or decrease based on the insured's age and the policy's performance. There are also single-premium policies, where the entire coverage cost is paid upfront, and the policy provides benefits over a specified period.
In many cases, yes. Most life insurance companies offer flexibility in payment frequency. You can typically choose to pay annually, semi-annually, quarterly, or monthly. Some insurers might also provide the option to pay via direct deposit, online banking, or even through payroll deductions if you have a policy linked to your employment. It's essential to review the payment terms and conditions when selecting a policy to understand any associated fees or penalties for missed payments.
Missing a payment can have consequences for your life insurance policy. The specific terms and conditions will depend on the insurance company and the type of policy. Generally, a grace period is usually provided after the due date, allowing you to make up for the missed payment without losing coverage. However, if the payment is not made within this grace period, the policy may lapse, and you could lose the coverage. It's crucial to ensure timely payments to maintain the insurance benefit and consider setting up automatic payments to avoid any potential issues.