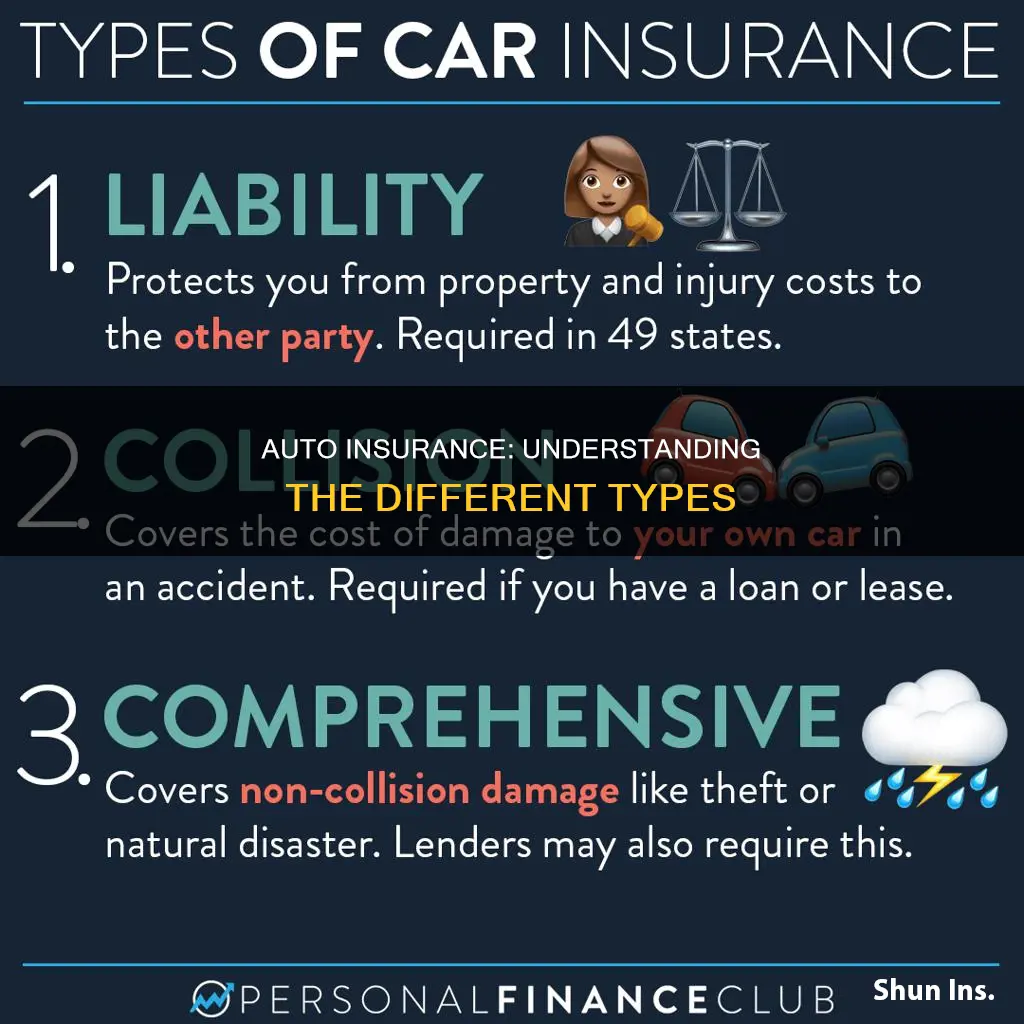
There are several types of auto insurance, and while most people don't need all of them, it's important to understand the different options to ensure you're adequately protected. The most common types of auto insurance coverage include liability insurance, collision coverage, comprehensive insurance, uninsured motorist coverage, medical payments coverage (MedPay), and personal injury protection (PIP). While some of these coverages are mandatory in certain states, others are optional. Liability insurance, which covers bodily injury and property damage, is required in most states. Collision coverage pays for repairs to your vehicle, regardless of who is at fault, while comprehensive insurance covers damage to your car from non-collision incidents, such as weather events, vandalism, or accidents with animals. Uninsured motorist coverage protects you if you're hit by an uninsured driver, and underinsured motorist coverage kicks in when the at-fault driver's insurance isn't sufficient. Medical payments coverage and personal injury protection cover medical expenses after an accident.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Covering medical bills, repair costs, and other expenses after a car accident |
| Coverage | Liability, collision, comprehensive, uninsured motorist, medical payments, personal injury protection, and gap insurance |
| Requirements | Varies by state and insurance provider; some types are mandatory, while others are optional |
| Deductibles | May apply for collision and comprehensive coverage, ranging from $100 to $1,000 |
What You'll Learn

Liability insurance
Liability coverage typically includes two types: property damage and bodily injury. Property damage coverage insures against damage to another person's property caused by your vehicle, while bodily injury coverage provides payment for others injured in an accident.
The cost of liability insurance depends on various factors, such as the amount of coverage selected. Higher coverage limits will generally result in higher costs. The required limits vary by state, and it's important to check the specific requirements for your state. Liability coverage limits are usually expressed as three numbers, such as 25/50/10, indicating the coverage for bodily injury per person, bodily injury per accident, and property damage per accident, respectively.
Understanding liability coverage limits is crucial when deciding on the amount of coverage you need. While states have minimum coverage requirements for bodily injury and property damage liability, drivers can opt to purchase additional coverage based on their specific situation.
Direct Auto Insurance: Grace Period?
You may want to see also

Collision insurance
The deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company covers the rest of the expenses. Deductibles can vary, and a higher deductible can lower your monthly premium. It is important to weigh the cost of collision coverage against the value of your car and your chosen deductible. For example, if your car is only worth a few thousand dollars and your deductible is high, collision coverage may not be beneficial.
Collision coverage is different from comprehensive coverage, which protects your car from damage caused by non-collision-related incidents, such as weather-related damage, theft, vandalism, or damage caused by falling trees or objects. While collision coverage focuses on accidents involving a collision with another vehicle or object, comprehensive coverage is for situations that are typically out of your control.
U.S. Auto Insurance: Who Qualifies?
You may want to see also

Comprehensive insurance
The cost of comprehensive insurance will depend on several factors, including the value of your car, its make and model, your driving history, and the deductible you choose. The deductible is the amount you agree to pay out of pocket before your insurance company covers the remaining expenses. Generally, a higher deductible will result in lower insurance premiums, while a lower deductible will increase the cost of your premium.
Burning Vehicle for Insurance: The 'How-To' Guide
You may want to see also

Uninsured motorist insurance
Uninsured motorist coverage, often referred to as UM or UMBI, pays for medical expenses and, in some cases, property damage if you or your passengers are injured in an accident caused by an uninsured driver. This includes hit-and-run incidents, where the at-fault driver flees the scene, as well as accidents caused by a driver whose insurance company denies coverage or goes out of business.
There are two main types of uninsured motorist coverage: Uninsured Motorist Bodily Injury (UMBI) and Uninsured Motorist Property Damage (UMPD). UMBI covers medical bills for both you and your passengers, while UMPD covers repairs or replacement of your vehicle and other damaged property. In some states, you can also purchase UMPD coverage separately to protect against property damage caused by uninsured drivers.
Underinsured motorist coverage, or UIM, is similar but separate coverage that is sometimes packaged with UM. UIM pays for medical bills and other expenses when the at-fault driver has insufficient insurance to cover the full cost of your damages. This includes situations where the driver only has the minimum mandatory insurance, which may not be enough to cover all your expenses.
When deciding on uninsured motorist coverage, it is important to understand the requirements and options in your specific state. Additionally, consider your own insurance coverage and whether you would be adequately protected without this type of insurance. While it may increase your overall insurance costs, uninsured motorist coverage provides valuable peace of mind and financial protection in the event of an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver.
Switching Auto Insurance: A Smooth Transition
You may want to see also

Medical payments coverage
MedPay is different from personal injury protection (PIP) coverage, which is mandatory in 12 "no-fault" states. While MedPay only covers medical bills, PIP covers a wider range of expenses, including wage reimbursement if injuries force someone to miss work. PIP limits and costs are typically much higher than MedPay limits.
The availability of MedPay varies by state, and it is mandatory in some states, optional in others, and not offered at all in a few. MedPay limits typically range from $1,000 to $10,000, but can go up to $50,000 or even $100,000. The cost of increasing coverage from $2,000 to $10,000 is approximately $10 per year.
After an accident, MedPay can provide peace of mind and help avoid the financial burden of medical expenses. It is a valuable option for those who may not be able to afford medical bills after a car accident.
Jet Ski Gap Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Basic car insurance is known as liability insurance. It covers medical bills for other drivers in an accident where you’re at fault, as well as damage to their vehicle.
The five basic types of car insurance are liability insurance, collision coverage, comprehensive insurance, uninsured motorist coverage, and either medical payments coverage or personal injury protection.
The most basic car insurance policy is minimum coverage car insurance. The amount of insurance required varies by state.
Full coverage car insurance combines liability, comprehensive, and collision insurance to provide coverage for most scenarios.
Liability insurance covers damages to other people. Collision insurance covers repairs to your vehicle after an accident, regardless of who is at fault. Comprehensive insurance covers damage to your car from events outside your control, like weather events, vandalism, or hitting an animal.







