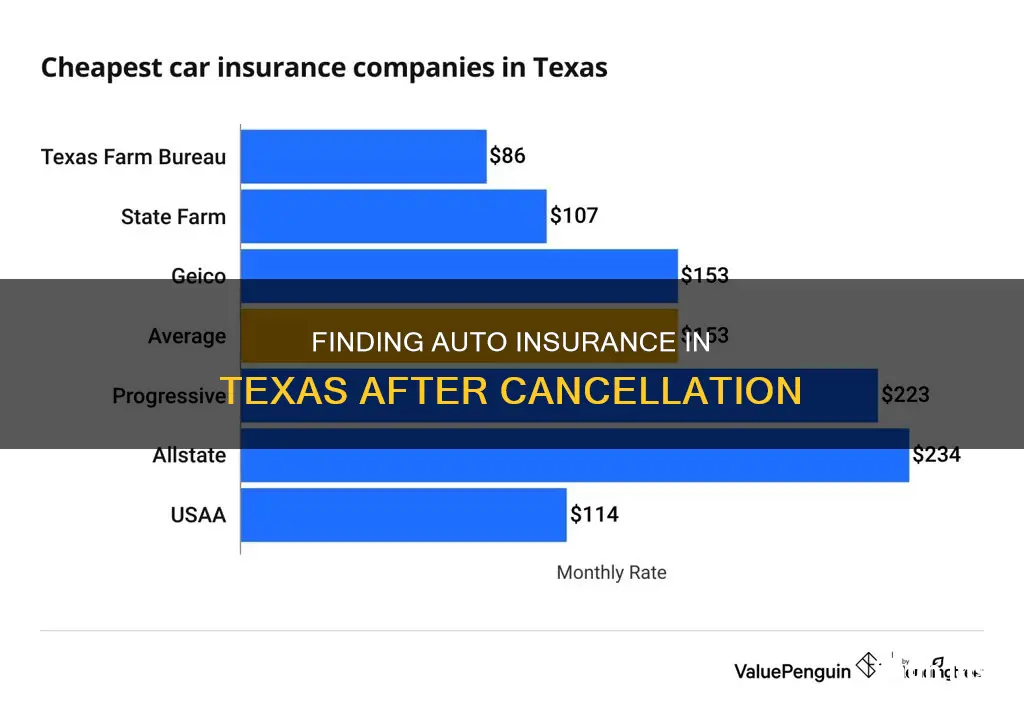
If your auto insurance policy has been cancelled in Texas, you can get minimum auto insurance from the Texas Automobile Insurance Plan Association (TAIPA). TAIPA provides basic liability coverage for drivers who have been turned down by two insurance companies. The average annual cost for minimum coverage in Texas is $788, or about $66 per month.
TAIPA coverage is more expensive than coverage from other insurance companies, and it does not sell collision or comprehensive coverage. If you still owe money on your car, your lender will require you to have collision and comprehensive coverage, which you can get from another insurance company.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What to do if your policy is cancelled | Contact your insurance agent to explore reinstatement options or seek a new policy |
| Time period to find new coverage | As soon as possible to avoid the legal and financial risks of driving uninsured |
| Options for high-risk drivers | Get coverage through the Texas Automobile Insurance Plan Association (TAIPA) |
| Reasons for policy cancellation | Non-payment of premium, license suspension, fraud or misrepresentation, too many claims |
What You'll Learn

What to do if your policy is cancelled
If your auto insurance policy has been cancelled, there are several steps you should take to ensure you remain protected and comply with the law.
Firstly, if your policy has been cancelled, your insurance company is required to notify you at least 10 days before the cancellation takes effect. This gives you time to find a new policy and avoid a lapse in coverage. You should also receive a refund for any unearned premiums within 15 days of the cancellation.
Next, start shopping for a new insurance policy right away. You can use resources such as the Texas Department of Insurance's HelpInsure tool to compare prices and policies from different companies. It is important to note that if you still owe money on your car, your lender will require you to have collision and comprehensive coverage. You may also want to consider additional coverages such as uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, personal injury protection, and rental reimbursement coverage.
While comparing policies, look at the company's complaint record and financial rating to get a sense of their customer service and stability. You can also ask about discounts that may be available, such as those for taking defensive driving courses or having multiple policies with the same company.
Once you have found a new policy that meets your needs and budget, be sure to get written confirmation of your coverage before cancelling your previous policy. This will help you avoid any gaps in coverage and ensure you are continuously protected.
Finally, if you are having trouble finding a new insurance policy, you can consider getting coverage through the Texas Automobile Insurance Plan Association (TAIPA). TAIPA provides basic liability, personal injury protection, and uninsured/underinsured motorist coverages and can be an option if you have been turned down by other insurance companies.
Understanding Progressive's Comprehensive Auto Insurance Deductible
You may want to see also

Reasons for cancellation
Auto insurance can be cancelled for a variety of reasons, and these reasons are often dictated by state laws. Here are some common reasons for the cancellation of auto insurance:
Non-Payment of Premium
If you fail to pay the premium on time, your insurance company may cancel your policy. It is important to stay on top of your payments to avoid this issue.
Material Misrepresentation
Providing false or incomplete information on your auto insurance application can lead to cancellation. This includes failing to accurately report your vehicle's garaging address or not disclosing necessary information such as accidents or traffic violations.
Fraudulent Claims
If you file a claim or someone makes a claim against your policy, you are expected to provide complete and accurate information. Purposely failing to do so may result in your policy being cancelled.
Suspended or Revoked License/Registration
If your driver's license or vehicle registration is suspended or revoked, your insurance company may cancel your policy. This also applies if a regular driver on your policy has their license suspended.
Medical Conditions Affecting Driving Ability
Certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy or heart attacks, may require a certificate from a physician confirming your ability to drive safely. If you cannot provide this certificate, your insurance company may cancel your policy.
Conviction of DUI, DWI, or OUI
If you or a regular driver on your policy is convicted of driving under the influence, your insurance rates may increase significantly. In some cases, your current insurer may choose to cancel your policy instead.
Unsafe Vehicle
If your car has mechanical problems that endanger public safety, or if it fails a required state inspection, your insurance policy may be cancelled.
Business Use of Vehicle
Personal auto insurance policies typically do not cover business use of your vehicle. If you use your car for work, such as visiting job sites or making deliveries, you may need a commercial auto policy.
Ridesharing or Carrying Passengers for Hire
Using your personal vehicle for ridesharing services like Uber or Lyft without informing your insurer may result in policy cancellation or claim denial. A personal policy only covers personal vehicle use, and a separate rideshare insurance policy is required.
It is important to note that insurance companies are required to provide advance notification of cancellation, usually sent by mail or electronic delivery. The time frame for this notification varies by state and the reason for cancellation.
Evaluating Auto Insurance Companies: Key Factors to Consider
You may want to see also

Getting a refund
If your auto insurance policy is cancelled, you may be entitled to a refund for the remaining months of the policy. If you paid a full year of premiums and cancel after one month, for example, you should receive 11 months' worth of premiums back. The insurance company must refund any unearned premium within 15 days of the cancellation date. The unearned premium is the amount you paid in advance that didn't go towards coverage.
The amount of the refund will be calculated on a pro-rata basis, depending on how many days of the policy are remaining. Some insurance companies may charge a cancellation fee, which will be taken out of the refund. This fee is either a flat fee or a short-rate fee, which is a percentage (usually 10%) of the unearned premium.
In some cases, the refund may be sent to a finance company if you financed your premium through them, rather than directly to you.
Auto Insurance: Wisconsin's Minimum Requirements and You
You may want to see also

Cancellation fees
In Texas, you can cancel your insurance policy at any time, but there may be a cancellation fee. This fee depends on the cause of the payment. If you cancel your policy before the expiration date, you may be charged a cancellation fee to cover the administrative process. This fee is not required if you opt out of policy renewal. However, if you need to have another insurance policy in place before cancellation, as is the case with Texas auto insurance policies, it will cost you more to cancel.
If you are required to pay a fee as part of the cancellation process, you must do so. If you fail to pay the fee, the insurer may deduct it from any refund you were meant to receive. Non-payment can also stall the cancellation process and lead to unnecessary complications. The insurer may also place the debt into collections, negatively affecting your credit rating.
To avoid cancellation fees, it is best to wait for the active policy to expire and then decline to renew the policy. Alternatively, you can refuse to renew by stopping premium payments, although this is not a formal process and may not trigger the desired response from the insurance company.
Florida Auto Insurance: Understanding the Basic Coverage Requirements
You may want to see also

Consequences of no insurance
Driving without insurance in Texas can have serious consequences, and it is considered an illegal act in most states. Here are some key points to remember about the consequences of driving without insurance:
Legal Consequences
- Driving without insurance is illegal in Texas and most other states. Only New Hampshire and Virginia allow driving without insurance, but even these states can impose insurance requirements after accidents or serious offenses.
- If caught driving without insurance in Texas, you may face penalties such as fines, court costs, and surcharges. For first-time offenders, this can include a fine of up to $350, plus court costs, and a $250 surcharge per year for three years.
- A second offense can result in a fine of up to $1,000, along with the same surcharge. However, providing proof of insurance and prepaying your six-month premium may reduce the surcharge to $125 per year.
- Texas law allows police officers to tow and impound your vehicle if you are caught driving without insurance. This will result in additional impound fees on top of other penalties.
- Driving without insurance can lead to license suspension. Texas is one of 44 states that will suspend your driver's license if you are caught without proof of insurance.
- If you are involved in an accident while uninsured, the consequences can be even more severe. You may be designated as a high-risk driver, and the other driver's insurance company may sue you for bodily injury or property damage claims.
- Texas has a "no pay, no play" law, which limits the compensation you can receive if you are uninsured, even if you are not at fault in an accident.
Financial Consequences
- Insurance lapse can result in higher future insurance premiums. Insurance companies consider drivers with coverage gaps as higher risks, leading to increased rates.
- If you cause an accident while uninsured, you may be held legally responsible for the other party's medical expenses and vehicle repairs. This can result in significant out-of-pocket expenses.
- The average cost of property damage per vehicle is $5,700, according to the National Safety Council (NSC). The per-person economic and comprehensive costs can range from $23,700 for no injuries to over $260,000 with evident injuries.
- In the event of disabling injuries or fatalities, the costs can be over $1.2 million or even exceed $14 million, respectively.
- If your driver's license and vehicle registration are suspended, you will need to pay reinstatement fees to get them back.
- If your vehicle is impounded, you will be responsible for the towing and storage fees.
Other Considerations
- If you have a loan on your vehicle, your lender will likely require you to maintain collision and comprehensive insurance coverage. Lacking insurance may result in your lender obtaining single-interest coverage, which protects only them, and the cost will be added to your loan payments.
- Driving without insurance can impact your ability to obtain insurance in the future. Insurance companies may consider you a high-risk driver and charge higher premiums or even deny coverage.
- If you are caught driving a business vehicle without insurance, you are not only breaking the law but also putting your business at risk. This can have significant financial and legal implications for your company.
Auto Insurance Policy: What to Carry and Why
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The minimum auto insurance coverage in Texas is $30,000 for bodily injury liability per person, $60,000 per accident, and $25,000 for property damage liability. This basic coverage is often referred to as 30/60/25.
Driving without insurance in Texas is illegal and can result in fines, license suspension, vehicle impoundment, and even jail time if you're involved in an accident.
If your auto insurance policy is cancelled, you will need to find new coverage to avoid legal and financial risks. Contact your insurance agent to explore reinstatement options or seek a new policy.
If your auto insurance policy was cancelled, you can contact the Texas Automobile Insurance Plan Association (TAIPA) to help you secure the state minimum coverage.







