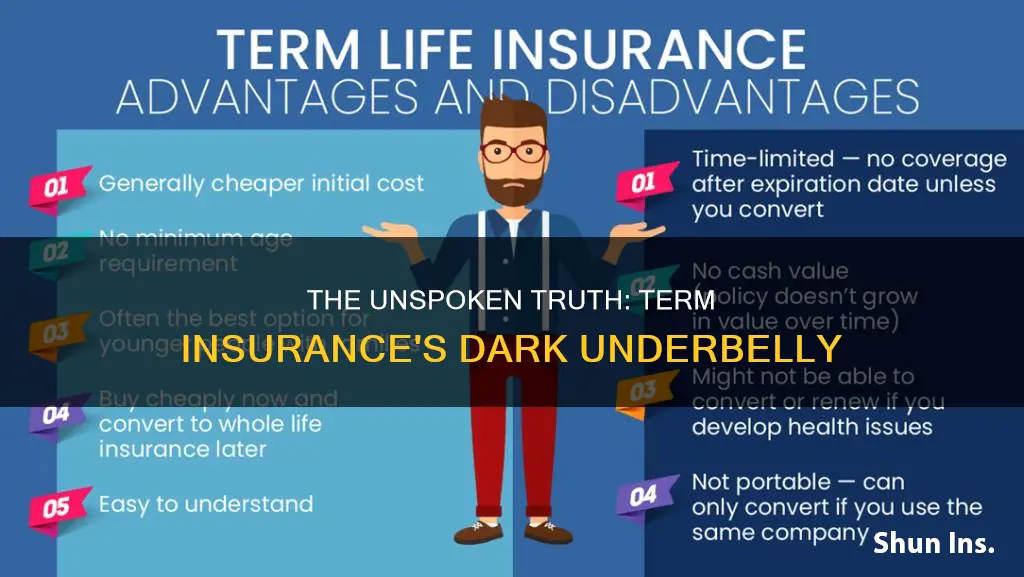
Term life insurance is a popular choice for people seeking a simple, cost-effective way to protect their family financially in the event of their sudden demise. However, it is important to be aware of the disadvantages of term insurance before making a decision. One significant drawback is the increase in cost when the policy is renewed, as well as the lack of value if the policy matures or is discontinued. The premiums for term insurance also tend to be higher for older individuals, making it more expensive for those who opt for it later in life. Additionally, term insurance does not offer maturity benefits or serve as an investment instrument, as it is solely a protection plan with death benefits. The policy can be stopped at any time by the policyholder, and there may be no surrender value offered by the insurance company. While term insurance has certain drawbacks, it is important to weigh them against the advantages, such as affordability and flexibility, to make an informed decision that best suits one's needs.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Renewal cost | Increases when the policy is renewed |
| Payout | No payout if the policyholder outlives the term |
| Cash value | No cash value or savings component |
| Premium | Premium may increase if the policyholder's health conditions change |
What You'll Learn

It becomes more expensive when you renew it
Term life insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a specific time frame or term. It is often chosen by younger people who want to protect their family in the case of their early death. It is also a popular option for those who want to cover their family during their prime earning years.
One of the disadvantages of term insurance is that it becomes more expensive when you renew it. This is because the premiums for term insurance depend on the age of the policyholder. The older the policyholder, the higher the premium. This means that if you renew your policy, you will be paying a much higher premium than you did previously.
For example, let's consider a 35-year-old male non-smoker who purchases a $500,000 term-20 policy. The monthly cost of this policy is likely to be relatively low, at around $33.30 per month. However, if he renews the policy after 20 years, the premium could increase to $560.70 per month! That's over 17 times more than what he was paying before!
The reason for this increase is that insurance companies expect that people who renew their term insurance policies are more likely to be in poor health, and therefore more likely to make a claim. So, while you don't have to medically qualify to renew your term insurance policy, you will have to pay a much higher premium.
Another factor that contributes to the increase in cost is that term life insurance premiums are based on a person's age and life expectancy. As you get older, your life expectancy decreases, and insurance companies view this as an increased risk. This is reflected in the higher premiums charged for renewed term insurance policies.
In addition to the increased cost, there are a few other disadvantages to term insurance. Unlike whole life insurance, term insurance does not offer any maturity benefits such as bonuses. It also does not have a cash value or investment component, so it cannot be used as an investment instrument. Finally, term insurance is only valid for a specific term, and if you outlive the term, there is no payout or financial benefit unless you purchase an optional return of premium (ROP) rider.
Understanding Pure Term Insurance: Unraveling the Basics of This Essential Financial Safety Net
You may want to see also

It has no value when it matures or you discontinue your policy
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific time frame or term. It is considered temporary insurance as the policy is only in effect for a relatively short period of time. One of the main disadvantages of term insurance is that it has no value when it matures or the policyholder discontinues the policy. This means that if the policyholder outlives the term of the insurance, there is no payout or financial benefit. The policy simply expires, and the policyholder stops paying premiums.
When a term life insurance policy matures, the policyholder has a few options. They can choose to renew the policy for another term, but the premiums will be higher due to the increased age and health risks of the policyholder. Alternatively, they can convert the term policy to permanent coverage, such as whole life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage. However, this option may not be available with all insurance companies, and there may be specific qualifications or deadlines for conversion. The policyholder may also choose to discontinue the policy altogether, but this is generally not recommended as life insurance is an important financial decision.
Another option is to specify a return of premium plan, where the insurer returns all or a portion of the premiums paid when the policy matures. However, this option does not build interest or earn dividends, so it is not a useful investment tool. Additionally, policyholders are not entitled to any returns if they cancel their coverage before it matures.
Overall, while term insurance offers affordable coverage for a specific period, it is important to carefully consider the implications of the policy maturing or being discontinued. The lack of value at maturity or discontinuation can be a significant disadvantage, and policyholders may need to explore other options to ensure continued coverage.
Understanding Rebating in Insurance: Unraveling the Practice and Its Implications
You may want to see also

It has no investment or savings component
Term life insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for a specific time frame, usually between 10 and 40 years. It is considered temporary insurance as it is only in effect for a relatively short period of time. One of the main disadvantages of term insurance is that it does not have an investment or savings component. This means that policyholders do not accumulate cash value over time and there are no benefits if the policyholder outlives the term.
Term insurance is often chosen by young families as it is more affordable compared to whole life insurance. This is because the premiums paid for term insurance are much lower and more flexible, as they do not include an investment component. However, this also means that there is no opportunity to build up a cash value over time, which could be used for retirement savings or as an emergency fund.
Term insurance is a good option for those who want affordable coverage for a specific period, especially if they are young and healthy. It can provide financial protection for the policyholder's family in the event of their death. However, if the policyholder outlives the term, there is no payout or financial benefit unless they purchase an additional rider. This is a significant disadvantage compared to whole life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage and allows policyholders to build cash value.
While term insurance does not offer an investment or savings component, it is important to note that policyholders can invest the money saved on premiums in other ways. This could potentially generate higher returns than the cash value growth in a whole life policy. Ultimately, the decision between term and whole life insurance depends on an individual's personal and financial goals.
Selecting the Right Term Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide to Making the Best Choice
You may want to see also

It does not offer maturity benefits
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides financial protection for a specific period of time, often 10, 20, 30, or even 40 years. It is considered temporary insurance as it only offers coverage for a limited time and does not accumulate cash value. Instead, it provides a death benefit, guaranteeing a stated payout to the insured's beneficiaries if they pass away during the policy term.
One of the disadvantages of term insurance is that it does not offer maturity benefits. Maturity benefits are the sum assured and bonuses paid out to the policyholder when the insurance policy reaches its maturity date. Term insurance, being a pure protection plan, only offers death benefits and, in some cases, survival benefits. It does not provide any returns or payouts if the policyholder outlives the policy term. This is because the premiums paid for term insurance are primarily allocated to cover the cost of providing life insurance, with minimal administrative charges, and do not include a savings component.
The absence of maturity benefits in term insurance means that the policyholder does not receive any refund of premiums or accumulated value upon surviving the policy term. This is in contrast to other types of life insurance, such as whole life insurance or endowment plans, which offer both death benefits and maturity benefits, providing a payout to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder's death or a refund of premiums and accumulated value if the policy matures and the policyholder survives.
However, it is important to note that term insurance plans with maturity benefits do exist and can be purchased. These plans offer the additional benefit of returning the premiums paid by the policyholder at the end of the term if they survive the policy period. This feature ensures that the policyholder's premiums are not 'wasted' in case they outlive the policy and can be reinvested or used for other financial goals.
While term insurance without maturity benefits may not provide a payout if the policyholder outlives the term, it is important to consider the primary purpose of this type of insurance, which is to provide financial protection to loved ones in the event of the policyholder's death. Term insurance is designed to offer high sum assured amounts at affordable premiums, making it an attractive option for those seeking life insurance coverage without a long-term commitment.
The Perils and Pitfalls of Insurance: Understanding the Risks Covered by Your Policy
You may want to see also

It cannot be used as an investment instrument
Term insurance is a type of life insurance that provides financial protection to the beneficiaries of the policyholder in the event of their death. It is a temporary form of insurance, usually taken out for a fixed period, and does not offer any investment or savings component. This means that term insurance cannot be used as an investment instrument.
Term insurance is a simple and popular form of insurance, which is often chosen by young families due to its affordability. The premiums are usually paid monthly, quarterly, or yearly, and the policyholder can decide whether the sum assured is paid out in a lump sum or in parts. However, if the policyholder outlives the policy term, there is no maturity benefit.
In contrast, whole life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides coverage for the entire life of the policyholder. Whole life insurance policies have a savings or investment component, which allows policyholders to build cash value over time. This cash value can be used to take out loans or make withdrawals, and it may also be used to pay premiums.
Term insurance is a good option for those who cannot afford the higher monthly premiums of whole life insurance. However, it is important to note that term insurance premiums increase with age, so it is best to purchase a policy as early as possible.
Unveiling the NCB: A Rewarding Feature of Insurance Policies
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Term insurance increases in cost when you renew it.
Term insurance has no value when it matures or you discontinue your policy.
Term life insurance does not have a cash value component, so there is no investment or savings benefit.







