Insurance is a contract, represented by a policy, in which a policyholder receives financial protection or reimbursement against losses from an insurance company. Most people have some form of insurance, whether it be for their car, house, healthcare, or life.
North Americans pronounce the word insurance in two different ways: i→nsurance and insur→ance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Protect high-value items | House, car, jewelry |
| Protect property and possessions | Fire, flood, overseas travel |
| Provide financial protection | Lawsuits, debts, living expenses, medical expenses, funeral costs |
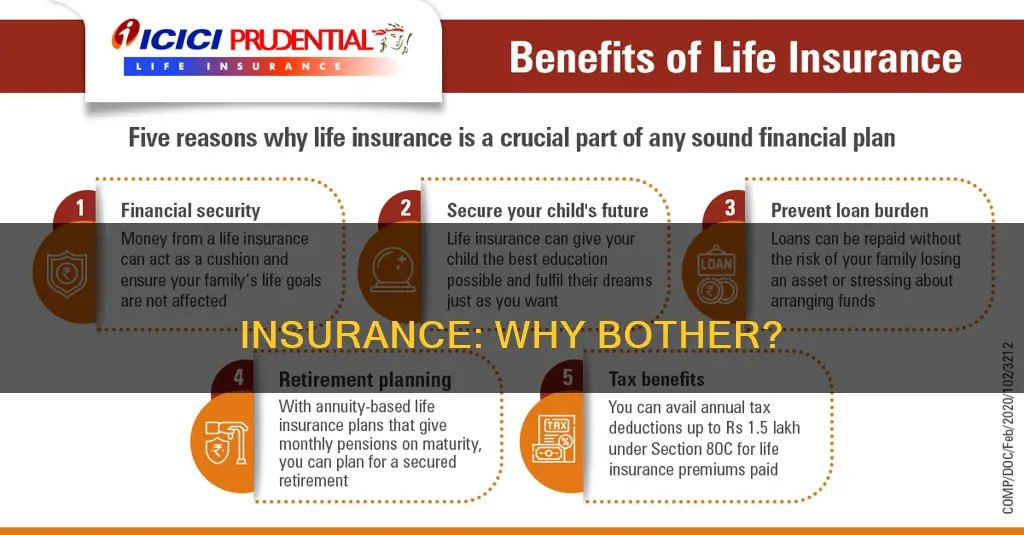
| Fulfill financial planning goals | Death, terminal illness |
| Peace of mind | Safety, security, stability |
| Support family and business | Income replacement, inheritance, family stability |
| Compulsory | Auto insurance, workers' compensation |
| Commerce | Lenders require insurance |
What You'll Learn
- Protection against financial losses resulting from accidents, injury, or property damage
- Covering costs associated with liability for damage or injury caused to a third party
- Protection against financial losses resulting from business-specific risks
- Protection against financial losses resulting from very specific risks
- Protection against financial losses resulting from travel-related issues

Protection against financial losses resulting from accidents, injury, or property damage
Insurance is a risk-sharing business that provides protection against possible financial loss. People buy insurance to protect themselves from financial losses resulting from accidents, injury, or property damage.
Insurance companies provide protection against financial losses resulting from accidents, injury, or property damage. This protection can take many forms, including:
- Automobile insurance: This type of insurance covers the risks associated with driving or owning a vehicle, such as collision, liability, comprehensive, medical, and uninsured motorist coverage.
- Homeowner's insurance: This type of insurance provides protection for residences and their associated financial risks, such as damage to personal property and injuries to others.
- Health insurance: This type of insurance provides coverage for medical expenses and can include disability insurance, which provides income for those who are unable to work due to illness or injury.
- Life insurance: This type of insurance provides financial protection for loved ones in the event of the insured's death.
- Property insurance: This type of insurance covers loss or damage to real or personal property from a variety of perils, including fire, theft, and natural disasters.
- Liability insurance: This type of insurance protects against legal liability resulting from negligence, carelessness, or failure to act, which can lead to property damage or personal injury.
By purchasing insurance, individuals and businesses can protect themselves from financial losses resulting from accidents, injury, or property damage. Insurance companies assess the risks and provide coverage to help mitigate these risks, giving peace of mind to their customers.
ACA's Impact: Insured Americans Surge
You may want to see also

Covering costs associated with liability for damage or injury caused to a third party
Third-party insurance is a policy purchased by the insured (first party) from the insurance company (second party) for protection against the claims of another (third party). It is a form of liability insurance that covers injury or damage caused to another person or business. This means that it covers the legal costs and payouts for which the insured party is found liable.
Third-party insurance is commonly purchased as auto insurance, to cover damage to another person's vehicle or property, and any medical costs relating to injuries caused to another driver or passenger. This is mandatory in most states and countries. For example, if you crash your car into a neighbour's fence, your third-party insurance will cover the cost of repairing the fence. If you are in an accident deemed your fault and the other driver requires medical attention, your insurance will cover their medical bills.
Third-party insurance can also be purchased as homeowners' insurance. This will cover any injuries sustained by someone on the insured's property, as well as any unintentional damage caused to someone else's property off-premises. For example, if a neighbour's child fell off your deck and broke their arm, your insurance would cover the ambulance and hospital costs.
Businesses can also obtain third-party insurance to protect against claims arising from a client getting injured on the premises, or by a product, or experiencing financial loss due to an error in the business's service. This includes product liability insurance, which covers businesses if a product is faulty and causes damage to the purchaser or another third party.
Informing Lienholder of Insurance Switch
You may want to see also

Protection against financial losses resulting from business-specific risks
Insurance is an economic device that transfers risk from an individual to a company, reducing the uncertainty of risk through pooling. People seek insurance to protect themselves from financial losses resulting from business-specific risks.
Business liability insurance, for example, protects the financial interests of companies and business owners in the event they face formal lawsuits or third-party claims. It covers any direct financial liabilities incurred, as well as legal defence expenses. This includes compensatory damages, non-monetary losses suffered by the injured party, and punitive damages.
Additionally, liability insurance covers the cost of a company's legal defence and any settlement offerings or awards mandated by legal judgments against the company. For businesses that rent their workspaces, general liability insurance also protects against liability from damage suffered due to fire, mould, floods, or other physical catastrophes.
Businesses can also purchase insurance to protect against losses from theft, fraud, operational errors, or other factors. This is known as loss prevention insurance, which aims to safeguard a company's assets, including inventory, equipment, data, and finances.
Insurance is a way for individuals and businesses to protect themselves from financial losses resulting from various risks. By purchasing insurance, individuals and businesses can gain peace of mind and focus on their goals without worrying about potential financial setbacks.
Understanding the Criteria: Unlocking Short-Term Insurance Eligibility
You may want to see also

Protection against financial losses resulting from very specific risks
Financial risk is the likelihood of losing money on a business or investment decision. It is a danger that can translate into the loss of capital and relates to the odds of money loss. Financial risk is an unsystematic risk because it does not impact every company. It is specific to each company as it depends on an organization's operations and capital structure.
Financial risk can be categorised into several types, including market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, and legal risk. These risks can affect businesses, markets, governments, and individuals.
Market risk arises due to movements in the prices of financial instruments, such as stocks, interest rates, and currencies. Credit risk occurs when one fails to fulfil their obligations towards their counterparties. Liquidity risk arises out of an inability to execute transactions due to insufficient buyers or sellers. Operational risk arises out of operational failures such as mismanagement or technical issues. Legal risk arises out of legal constraints such as lawsuits.
Businesses face financial risk due to several macroeconomic forces, fluctuating market interest rates, and the possibility of default by large organisations or sectors. Financial risk for governments arises when they lose control of their monetary policy, are unable or unwilling to control inflation, or default on their bonds. Individuals can also fall prey to financial risk by making poor decisions or engaging in highly speculative investments.
To protect against financial losses, it is important to identify and assess risks, establish risk appetite and tolerance, develop and implement risk response strategies, monitor and review the risk management plan, communicate and consult with stakeholders, and learn and improve from past experiences.
Insurance Options When the Birthday Rule Changes
You may want to see also

Protection against financial losses resulting from travel-related issues
Travel insurance is a form of financial protection that can be purchased when booking a trip. It is designed to protect travellers from financial losses resulting from travel-related issues. The specific risks covered by travel insurance vary depending on the provider and the plan chosen. However, it is important to note that travel insurance does not cover every possible scenario and typically excludes losses arising from expected or reasonably foreseeable events.
When purchasing travel insurance, it is essential to carefully review the covered reasons outlined in the plan. These covered reasons may include:
- Terrorist events at the destination within a specified timeframe before the traveller's scheduled arrival.
- Serious illness, injury, or death of the insured traveller, travelling companion, or family member.
- Job termination or layoff of the insured traveller or travelling companion, provided certain conditions are met.
- Cessation of services by the airline, cruise line, or other carrier due to specific circumstances, such as a strike, natural disaster, or bad weather.
- Attendance of the birth of a family member's child.
- Natural disasters, fires, floods, burglaries, or vandalism that render the destination or the traveller's home uninhabitable.
- Traffic accidents involving the insured traveller or travelling companion en route to the point of departure, requiring medical attention or vehicle repairs.
- Legal separation or divorce of the insured traveller or travelling companion after the insurance effective date but before the scheduled departure.
It is worth noting that travel insurance typically does not cover losses related to known, foreseeable, or expected events, epidemics, government prohibitions, warnings, or travel advisories. However, some travel insurance plans may include specific covered reasons related to COVID-19.
To fully understand the financial protection offered by a travel insurance plan, it is crucial to carefully read the plan documents and ask questions to clarify any uncertainties.
Understanding the Tax Implications of Term Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
People buy insurance to protect themselves and their families from financial losses in the event of an accident, illness, or death. It provides peace of mind and helps them achieve their financial goals.
The main reasons people buy insurance are to:
- Protect valuable purchases, property, and possessions
- Provide financial protection if sued
- Support their family in the event of their death
- Help with illness and health maintenance costs
- Achieve financial goals, such as saving for retirement or a child's education
Insurance provides peace of mind by offering financial protection against risks and uncertainties. It allows people to shift their risks to the insurer and focus on their goals without worrying about potential losses.
Insurance is crucial for businesses as it helps keep commerce moving, enables them to obtain loans, and ensures stability. It also helps businesses recover from disasters, protects small businesses from becoming risk-averse, and prevents monopolies from forming.
There are various types of insurance available, including:
- Life insurance
- Health insurance
- Home insurance
- Auto insurance
- Travel insurance







