Credit life insurance is a type of insurance policy that pays off your outstanding debts in the event of your death. It is typically used for large loans, such as mortgages or car loans, and can be purchased when taking out a line of credit. The policy pays off the loan if the borrower dies, ensuring that any co-signers or heirs are not burdened with the debt. While credit life insurance is not always built into a loan, lenders may offer it as an option for borrowers. It is important to note that credit life insurance is not the same as term life insurance or whole life insurance, which offer more flexibility and control over the payout.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is it? | A type of life insurance policy designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding debts if the policyholder dies. |
| Who is it for? | People who want to ensure they can pay down a large loan like a mortgage or car loan. |
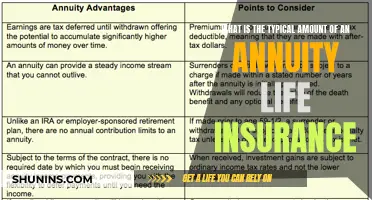
| Who benefits? | The lender. The payout goes to the lender, not the policyholder's heirs. |
| Who offers it? | Banks, credit unions, car dealers, and finance companies. |
| Who underwrites it? | The Canada Life Assurance Company (Canada Life), among others. |
| Who regulates it? | Federal law in the US; similar entities in Canada. |
| Who doesn't need it? | People who can qualify for traditional life insurance that covers the amount of debt they require. |
| Who might need it? | People who can't qualify for traditional life insurance due to medical reasons. |
| What are the alternatives? | Traditional term life insurance; existing life insurance; savings or investment accounts. |
| What are the different types? | Credit life insurance; term life insurance; mortgage protection insurance. |
What You'll Learn

What is credit life insurance?
Credit life insurance is a type of life insurance policy that pays off a borrower's outstanding debts if they die. It is typically used to ensure that large loans, such as mortgages or car loans, can be paid off. The value of a credit life insurance policy decreases over time as the loan is paid off, and the debt decreases.
Credit life insurance is often offered when someone borrows a significant amount of money, such as for a mortgage, car loan, or large line of credit. The policy then pays off the loan in the event that the borrower dies. This type of insurance can be useful if someone has a co-signer on the loan or dependents who rely on the underlying asset, such as a home. In most cases, heirs who are not co-signers on loans are not obligated to pay off the loans of the deceased. However, in some states that recognize community property, a spouse may be liable for the deceased's debts.
Credit life insurance is different from permanent life insurance, which remains in effect for the policyholder's lifetime. Credit life insurance is specific to a particular loan and only pays out to satisfy that loan. Once the loan is paid in full, the credit life insurance contract ends and does not apply to any other loans or expenses.
Credit life insurance is typically more expensive than traditional life insurance and the payout goes to the lender, not the policyholder's heirs. However, it often has less stringent health screening requirements and does not require a medical exam. Credit life insurance is always voluntary and lenders may not require it or base their lending decisions on whether the borrower accepts it.
Term Life Insurance: Maximum Coverage Duration Explained
You may want to see also

How does credit life insurance work?
Credit life insurance is a type of life insurance policy designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding debts if the policyholder dies. It is typically offered when someone borrows a significant amount of money, such as for a mortgage, car loan, or large line of credit. The policy pays off the loan in the event that the borrower dies.
Credit life insurance is a specialized type of policy intended to pay off specific outstanding debts in case the borrower dies before the debt is fully repaid. The face value of a credit life insurance policy decreases as the loan amount is paid off over time until there is no remaining balance. The death benefit of a credit life insurance policy also decreases as the policyholder's debt decreases.
Credit life insurance is typically offered by banks, credit unions, car dealers, and finance companies when someone applies for a loan or credit line. It is not required by law, and it is illegal for lenders to make it a requirement for a loan. However, it may be built into a loan, which would increase the borrower's monthly payments.
There are two main ways that credit life insurance premiums can be paid:
- Single premium: The cost of the policy is added to the loan principal, and the borrower pays interest on the total borrowed amount.
- Monthly outstanding balance: Premiums are paid monthly, either in fixed installments or payments that change depending on the borrower's balance.
Credit life insurance can be a good option for those who want to protect their co-signers or dependents in the event of their death. However, it is important to note that the payout from a credit life insurance policy goes directly to the lender, not to the policyholder's heirs. If the goal is to provide financial protection for beneficiaries, a traditional term life insurance policy may be a better option. Term life insurance is also usually more affordable than credit life insurance for the same coverage amount.
Life Insurance: Natural Disaster Coverage Explained
You may want to see also

What does credit life insurance cover?
Credit life insurance is a type of life insurance policy designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding debts if the policyholder dies. It is typically offered when a borrower takes out a large loan, such as a mortgage or car loan, and it is used to ensure that the loan can be paid off in the event of the borrower's death.
The face value of a credit life insurance policy decreases as the loan amount is paid off over time, and the policy term corresponds with the loan maturity. This means that if the borrower dies before the loan is fully repaid, the credit life insurance policy will pay off the remaining debt. The payout from the policy goes directly to the lender, not to the borrower's heirs, and the beneficiary of the policy is the lender that provided the funds for the debt being insured.
Credit life insurance is often offered with auto loans and home loans, and it can cover the remaining debt on a mortgage if the borrower dies before paying off the loan. It can also be offered to cover other types of loans, such as open lines of credit and credit cards.
In addition to providing financial protection for the lender, credit life insurance can also protect a co-signer on the loan from having to repay the debt in the event of the borrower's death. It is important to note that credit life insurance is optional and is not required by lenders. While it can provide peace of mind and financial protection, it may cost more than traditional life insurance and primarily benefits the lender rather than the borrower's heirs.
Life Insurance: New Jersey Manufacturers' Comprehensive Coverage Options
You may want to see also

Is credit life insurance worth it?
Credit life insurance is a type of insurance policy designed to pay off a borrower's outstanding debts in the event of their death. It is typically used to ensure that large loans, such as mortgages or car loans, can be paid off. The face value of a credit life insurance policy decreases as the loan amount is paid off over time. This type of insurance is usually offered when a borrower takes out a significant amount of money, and the policy pays off the loan if the borrower dies.
Credit life insurance is often a guaranteed issue policy, meaning that eligibility is based solely on the borrower's status, and no medical exam is required. This can be beneficial for individuals who are in poor health or who may struggle to qualify for traditional life insurance. Additionally, credit life insurance can protect co-signers on loans from having to repay the debt in the event of the borrower's death.
However, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. Credit life insurance typically costs more than traditional life insurance, and the payout goes directly to the lender, not the borrower's heirs. The value of credit life insurance policies may also decrease over time as the outstanding loan balance is reduced.
When deciding if credit life insurance is worth it, individuals should consider their health status, the cost of the insurance, and their desire to protect co-signers or heirs from debt burden. If the main goal is to protect beneficiaries, traditional term life insurance may be a more affordable option that provides more coverage for the same price. Term life insurance also allows the beneficiary to use the payout as they see fit, rather than it going directly to the lender.
In conclusion, while credit life insurance can provide peace of mind and protect loved ones from debt burden, it is important to weigh the costs and benefits against alternative options like term life insurance to make an informed decision. Consulting a financial professional can help individuals determine if credit life insurance is the right choice for their specific situation.
Life Insurance and UTMA: A Child's Future Security
You may want to see also

How much does credit life insurance cost?
The cost of credit life insurance depends on several factors, including the type of credit, the type of policy, and the loan amount. Credit life insurance is typically more expensive than traditional life insurance because it is perceived as a higher-risk product. The eligibility criteria for credit life insurance are less stringent, as it is a guaranteed issue product that does not require a medical exam or health disclosures. The applicant's health status is irrelevant because what is being insured is the loan balance, not the life of the borrower.
The cost of credit life insurance can be structured in two ways: as a single premium or as monthly outstanding balance payments. In the former, the cost of the policy is added to the loan principal, and the borrower pays interest on the total borrowed amount, including the premium. In the latter, premiums are paid monthly, either as fixed installments or as payments that vary according to the outstanding balance.
The State of Wisconsin Department of Financial Institutions provides an example of credit life insurance costing $370 annually for a coverage amount of $50,000. In contrast, a healthy, non-smoking 40-year-old man could pay an average of $28.42 per month ($341 per year) for a $500,000, 20-year term life insurance policy.
When considering the cost of credit life insurance, it is important to remember that it primarily benefits the lender, and there may be more affordable alternatives, such as term life insurance, that offer more flexibility and control over the payout.
Business Benefits of Collateral Life Insurance Assignments
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Credit life insurance is a type of insurance policy that pays off a borrower's outstanding debts if the policyholder dies. It is typically used to ensure that the borrower can pay off a large loan, such as a mortgage or car loan.
Credit life insurance is offered when a borrower takes out a significant amount of money, such as for a mortgage, car loan, or large line of credit. The policy pays off the loan in the event that the borrower dies.
Credit life insurance can provide peace of mind by ensuring that any co-signers on the loan will not be responsible for making loan payments after the borrower's death. It can also protect heirs from being saddled with outstanding loan payments and ensure that they receive the borrower's assets. Additionally, credit life insurance does not require a medical exam, making it a viable option for individuals who may not qualify for traditional life insurance due to health conditions.
Credit life insurance policies can be more expensive compared to other types of life insurance policies. The premiums may be added to the loan balance and charged interest, increasing the overall cost. Additionally, the payout of a credit life insurance policy decreases as the loan is paid off, while the premiums typically remain the same.
No, credit life insurance is not required for a house line of credit or any other type of loan. It is optional and can be purchased by the borrower if they wish to ensure that their debts will be covered in the event of their death.