Vehicle insurance is a necessity for all car owners. It provides financial protection in the event of accidents, theft, or other incidents, and is required by law in almost every state and country. The process of obtaining vehicle insurance begins with understanding the coverage you need, including liability, comprehensive, and collision insurance. You can then obtain quotes from different insurance companies, comparing the coverages offered and their associated costs. When deciding on a policy, it is important to consider factors such as your driving history, age, and location, as these can impact your premium. Once you have selected a policy, you can purchase it directly from the insurer, ensuring you meet your state's legal requirements and have the protection you need while on the road.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Financial protection in case of car accidents, theft, or other incidents. |
| Coverage | Vehicle repairs, medical expenses, damages/injuries to others, rental cars, roadside assistance, etc. |
| Requirements | Valid driver's license, vehicle information, driving history, personal details, etc. |
| Cost Factors | Driving history, age, location, vehicle type, safety features, etc. |
| Discounts | Student, federal employee, military, safe driving, multiple policies, etc. |
| Comparison | Select same coverages, policy limits, and deductible amounts across insurers. |
| Minimum Coverage | Varies by state/country but typically includes liability coverage for injuries/damages to others. |
What You'll Learn

Understanding the different types of vehicle insurance coverage
Liability Coverage
Liability coverage is a legal requirement in most US states and is necessary to drive a car. It covers damages for injuries and property damage to others resulting from an accident for which you are legally responsible. Liability insurance will pay for other people's medical bills and property damage after accidents that you cause. It is required in nearly every state and covers expenses like medical bills and property damage but does not cover any expenses for the policyholder or their passengers.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays to repair or replace the policyholder's car after an accident, regardless of fault. It covers damage to your vehicle if you collide with another object or vehicle. Collision insurance is not required by state laws but is mandatory for leased or financed cars. It helps cover the costs of repairing or replacing your car if it's damaged in an accident, regardless of who is at fault.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive coverage provides protection for damage to your vehicle caused by something other than an accident. It typically covers incidents like vandalism, certain weather events, and accidents with animals. Comprehensive insurance is not required by state laws but is usually needed for leased or financed cars. It helps protect your vehicle from unforeseen events and covers the costs of repairs.
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage
This type of coverage protects you in the event of an accident with an uninsured or underinsured driver. It covers vehicle damage and medical expenses. Uninsured motorist coverage includes uninsured motorist bodily injury coverage, which pays for bodily injury costs for you and your passengers if involved in an accident with an uninsured driver or a hit-and-run driver. It also includes uninsured motorist property damage coverage, which pays for damage to your car in such situations. Underinsured motorist coverage, on the other hand, helps cover bodily injury costs if the other driver doesn't have sufficient insurance.
Medical Payments Coverage
Medical payments coverage helps pay for the policyholder's direct medical expenses after an accident. It covers medical and funeral expenses for the policyholder, their family members, or passengers. This type of coverage is mandatory in some states and can provide valuable financial protection in the event of an accident.
Personal Injury Protection (PIP)
Personal injury protection (PIP) covers medical expenses and, in some cases, lost income resulting from a covered accident. It may cover up to 80% of medical and other related expenses. PIP is required in certain states and offers additional benefits beyond standard medical payments coverage.
Additional Coverages
Other types of vehicle insurance coverages include gap insurance, rental reimbursement insurance, roadside assistance, and classic car insurance. Gap insurance covers the difference between your car's value and the amount you owe on your loan or lease if your vehicle is totaled or stolen. Rental reimbursement insurance helps cover the cost of a rental car if your vehicle is being repaired or is undrivable after an accident. Roadside assistance provides services like towing, jump-starts, and flat tire changes. Classic car insurance offers specialized coverage for vintage and classic vehicles, tailored to the unique needs of collectors.
Choosing Vehicle Insurance: What to Consider
You may want to see also

How to compare vehicle insurance quotes
Comparing vehicle insurance quotes can be a confusing process, but it's important to do your research to ensure you're getting the best deal. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to compare vehicle insurance quotes:
Decide on the coverage you need:
It's important to understand the different types of vehicle insurance coverage available. Most states require drivers to have a minimum amount of liability coverage. If your vehicle is new or leased, you may also need comprehensive and collision coverage. Consider your needs and decide on the coverage types and amounts that best suit your situation.
Gather your information:
Before comparing quotes, gather all the necessary information. This includes personal information such as your age, gender, marital status, driving history, and vehicle information such as the make, model, and vehicle identification number (VIN). You'll also need information about your current insurance policy, if applicable.
Use comparison tools:
Utilize online comparison tools or websites to get quotes from multiple insurance companies. Websites like Insurify, Compare.com, and Policygenius are recommended for their ease of use and accurate, real-time quotes. Input your information and compare the quotes offered by different insurers.
Evaluate important factors:
When comparing quotes, consider factors such as price, coverage options, customer reviews, and the insurer's reputation. Ensure that you are comparing similar coverage levels and deductibles across different insurers to make an accurate evaluation.
Choose a reputable insurer:
Select an insurance company that offers competitive rates, has positive customer reviews, and provides reliable customer service. Check for financial strength and customer complaint records to ensure the insurer is reputable and capable of handling your claims.
Look for discounts:
Many insurance companies offer discounts that can help lower your premium. Look for insurers that offer discounts for safe driving, bundling policies, paying your premium in full, or other factors that apply to your situation.
Compare at least three quotes:
The Insurance Information Institute (III) recommends comparing at least three quotes to find the best policy for your needs. By comparing multiple quotes, you can be confident that you're getting a competitive rate and finding the right balance between coverage and cost.
Remember, the goal is to find an insurance policy that offers the coverage you need at a price that fits your budget. Take your time, do your research, and don't be afraid to ask questions or reach out to insurance agents for clarification.
Vehicle Adjuster: How to Start
You may want to see also

Factors that affect vehicle insurance rates
When it comes to vehicle insurance rates, there are a number of factors that can affect the price you pay. Here are some of the key factors:
Driving History
Your driving record is one of the biggest factors in determining your insurance rates. A history of moving traffic violations, at-fault accidents, or a DUI/DWI conviction will result in higher insurance rates. The longer you drive without any incidents, the better your insurance rates will be.
Age and Driving Experience
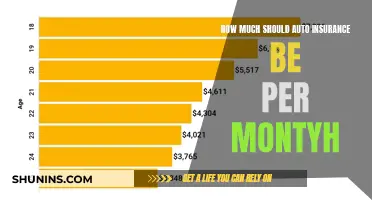
Young and inexperienced drivers will pay higher insurance rates as they are more likely to be involved in accidents. Insurance rates typically decrease when a driver turns 25, and senior drivers may see an increase in rates after the age of 65 due to an increased likelihood of being injured in a collision.
Location
Your location can impact insurance rates due to factors such as weather claims, accidents, car theft, cost of medical care, car repair costs, and frequency of auto accident lawsuits. Drivers in metropolitan areas tend to pay more for coverage than those in suburban or rural areas.
Type of Car
The type of car you drive also affects insurance rates. Insurance companies will consider past claims, repair costs, theft rates, and comprehensive claim payments for similar models. Brand-new sports cars or vehicles with high repair costs and poor safety records will typically have higher premiums.
Coverage Selections
The coverage you choose will impact your insurance rates. While you should ensure you have the coverage you need, don't skimp on coverage just to save money. Liability insurance is required in most states, and other types of coverage such as collision and comprehensive insurance may also be necessary.
Credit Score
Your credit score can affect your insurance rates in most states. A low credit score may result in higher premiums, while a good credit score can indicate financial stability and responsibility, leading to lower rates.
Vehicle Insurance: Am I Covered?
You may want to see also

What vehicle insurance does and doesn't cover
Vehicle insurance is a financial safeguard in case of car accidents, theft, or other auto incidents. It covers damage to your vehicle and protects you financially if you're liable for someone else's injuries or damages. Auto insurance can also pay for medical bills for you and your passengers if you're injured in an accident or if you're hit by an uninsured or underinsured driver.
What Vehicle Insurance Covers:
- Damage to other people's property and injuries caused by an accident that you're found at fault for.
- Bodily injury coverage.
- Property damage coverage.
- Uninsured motorist coverage.
- Medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of fault.
- Damage to your vehicle caused by events beyond your control, including theft, vandalism, natural disasters, and falling objects.
- Damage to your vehicle caused by collisions with objects or other vehicles, including guardrails, fences, and trees.
- Rental car reimbursement while your vehicle is being repaired or replaced after an accident.
- Roadside assistance, including labor to change a flat tire, towing, and more.
- Protection from uninsured or underinsured motorists.
What Vehicle Insurance Doesn't Cover:
- Basic car insurance doesn't cover maintenance or general wear and tear, including electrical wear and tear.
- People who regularly drive your car but aren't listed on your policy.
- Personal items that are damaged or stolen from your vehicle. These may be covered by homeowners or renters insurance.
- Damage from previous owners.
- Intentional damage caused by the policyholder.
Remove Vehicles from USAA Insurance Coverage
You may want to see also

How to get vehicle insurance
Getting vehicle insurance is a simple process, but it's important to do your research to ensure you get the best deal. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to get vehicle insurance:
Step 1: Gather Information
First, you'll need to collect all the relevant information about yourself and your vehicle. This includes personal details such as your name, date of birth, driver's license number, and address. For your vehicle, you'll need to know the make, model, and year, vehicle identification number (VIN), mileage, and any safety features or anti-theft devices.
Step 2: Choose Your Coverage Options
There are different types of vehicle insurance coverage options available, and it's important to understand what each one offers. The most common types of coverage include:
- Fully comprehensive insurance: This covers damage to your vehicle, as well as injuries to yourself and others, and damage to other people's property.
- Third-party, fire, and theft: This covers repair costs for other people's vehicles and property, as well as your own vehicle if it's stolen or damaged by fire.
- Third-party only: This covers injury or damage caused to other people and their property. It does not cover any costs for damage to your own vehicle.
Step 3: Shop Around
It's important to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best deal. You can do this by reaching out to insurance agents or brokers, or by using online comparison tools. Make sure to compare like-for-like when reviewing quotes, including coverages, policy limits, and deductibles.
Step 4: Compare Quotes
When comparing quotes, look at the coverages, policy limits, and deductibles offered by each provider. Also, consider any discounts that may be available, as these can vary between insurers. By comparing these factors, you can ensure you're getting the best value for your money.
Step 5: Purchase Your Policy
Once you've found the right policy at the right price, it's time to purchase your vehicle insurance policy. You can often do this directly online or through an agent. Make sure to review the terms and conditions carefully before finalizing your purchase.
Insurance Write-Offs: What Happens When Your Car Is Totaled
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Vehicle insurance provides financial protection in the event of car accidents, theft, or other incidents beyond your control. It covers damage to your vehicle and protects you financially if you're liable for someone else's injuries or damages.
The standard coverages on most auto insurance policies include liability coverage, auto comprehensive coverage, auto collision coverage, medical payments/personal injury protection, and uninsured/underinsured motorist bodily injury and property damage.
Vehicle insurance typically does not cover maintenance or general wear and tear, mechanical failure, people who regularly drive your car but aren't listed on your policy, or driving for a ridesharing platform.
You will need at least the minimum amount of vehicle insurance required by your state or country. This typically includes a minimum amount of liability coverage. Your state or lender may also require additional coverages, such as UM/UIM, PIP, or medical payments coverage, and comprehensive and collision coverage.
To get vehicle insurance, you will need to provide some personal and vehicle information, along with a brief driving history. This information will help determine your coverage needs, deductible, and policy cost. You can then compare quotes from different insurance companies to find the best option for you.