The concept of life insurance is a crucial aspect of financial planning, providing a safety net for individuals and their families. When considering life insurance, it's essential to understand the average life insurance coverage, which varies depending on several factors. These factors include age, health, lifestyle, and the amount of coverage desired. The average life insurance policy typically ranges from $100,000 to $500,000, but this can significantly increase or decrease based on individual circumstances. This paragraph aims to explore the average life insurance coverage and its implications for different demographics.
What You'll Learn
- Life Insurance Basics: Understanding coverage types, benefits, and policy structures
- Average Premiums: Exploring factors affecting rates and typical costs
- Term vs. Permanent: Comparing duration and long-term financial implications
- Age and Health: How age and health status impact insurance affordability
- Coverage Amounts: Determining suitable death benefit amounts for individuals

Life Insurance Basics: Understanding coverage types, benefits, and policy structures
Life insurance is a financial tool that provides a safety net for individuals and their families, offering financial protection and peace of mind. It is a contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the policyholder's death. This fundamental concept of life insurance is crucial for ensuring financial security and covering various expenses that may arise after the policyholder's passing.
There are primarily two types of life insurance coverage: Term Life and Permanent Life. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, often 10, 20, or 30 years. It is a cost-effective way to secure financial protection during a specific period, such as when a family is dependent on the policyholder's income. During this term, the insurer guarantees to pay out a predetermined death benefit if the policyholder passes away. Once the term ends, the policy may be renewed, but the cost could increase. On the other hand, permanent life insurance, including whole life and universal life, offers lifelong coverage. It provides a death benefit and also includes an investment component, allowing the policy to accumulate cash value over time. This type of insurance is more expensive but offers long-term financial security.
The benefits of life insurance are extensive. Firstly, it ensures financial stability for the family, covering essential expenses like mortgage payments, children's education, and daily living costs. It also provides funds for funeral and burial expenses, which can be a significant financial burden without insurance. Additionally, life insurance can be a valuable asset for estate planning, allowing beneficiaries to inherit a tax-free sum, which can be invested or used to achieve their financial goals. Moreover, some policies offer an additional feature of long-term care benefits, providing financial assistance for nursing home or assisted living costs.
When considering life insurance, it's essential to understand the various policy structures. A whole life policy guarantees a death benefit and has a fixed premium, ensuring consistent costs over time. It also builds cash value, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn. Universal life insurance, on the other hand, offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts. Policyholders can adjust these parameters to manage costs and ensure adequate coverage. Additionally, some policies provide an option for conversion, allowing a term life policy to become permanent coverage if desired.
In summary, life insurance is a vital tool for managing financial risks and providing long-term security. Understanding the different coverage types, such as term and permanent life, is essential for choosing the right policy. The benefits of life insurance extend beyond financial protection, offering peace of mind and the ability to plan for the future. By exploring the various policy structures and their features, individuals can make informed decisions to secure their loved ones' financial well-being.
Credit Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Average Premiums: Exploring factors affecting rates and typical costs
Before we delve into the specifics of average life insurance premiums, it's essential to understand what life insurance is and why it's crucial. Life insurance is a financial protection tool that provides a monetary benefit to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon their death. It offers financial security to the insured's family, covering expenses like funeral costs, mortgage payments, or daily living expenses. The average life insurance premium is the amount an individual pays regularly to maintain their policy.
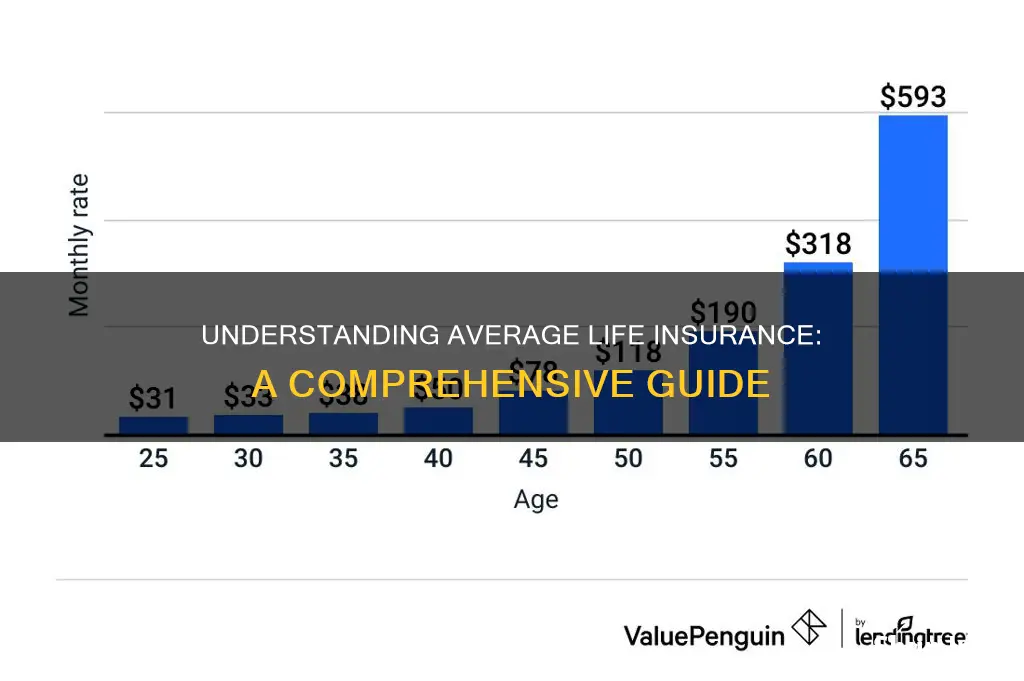
Several factors influence the average life insurance premium, and understanding these factors is crucial for anyone considering purchasing a policy. Age is a significant determinant; younger individuals typically pay lower premiums as they have a longer life expectancy, reducing the risk for insurers. As individuals age, premiums increase due to the higher likelihood of claiming the policy. Additionally, health status plays a vital role. Insurers may request medical history and conduct health assessments to determine the risk of insuring an individual. A healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can lead to lower premiums.
Smoking is a critical factor affecting life insurance rates. Smokers are considered high-risk individuals, and insurers may charge significantly higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of health complications. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption or drug use can also impact premium costs. Another essential factor is lifestyle choices, such as occupation and hobbies. High-risk occupations, like construction or mining, may result in higher premiums due to the increased risk of accidents or injuries. Additionally, dangerous hobbies, such as skydiving or racing, can also lead to increased insurance costs.
The type of life insurance policy chosen also affects premium rates. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers a straightforward and cost-effective solution for those seeking temporary coverage. On the other hand, whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage and includes an investment component, resulting in higher premiums. The amount of coverage required is another critical factor. Higher coverage amounts mean higher premiums, as the insurer takes on more risk by paying out a substantial sum upon the insured's death.
In conclusion, understanding the factors that influence average life insurance premiums is essential for making informed decisions. Age, health, lifestyle choices, and the type of policy all play a role in determining the cost of coverage. By considering these factors, individuals can choose the most suitable life insurance policy that provides the necessary financial protection for themselves and their loved ones. It is always advisable to consult with insurance professionals to tailor a policy that meets specific needs and budget requirements.
Life Insurance Options for Terminally Ill Patients
You may want to see also

Term vs. Permanent: Comparing duration and long-term financial implications
The concept of life insurance is a crucial financial tool, providing a safety net for individuals and their families. When considering life insurance, one of the fundamental decisions is choosing between term life insurance and permanent (or whole life) insurance. Both options offer unique advantages and considerations, especially when it comes to duration and long-term financial implications. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed choice.
Term Life Insurance:
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, often ranging from 10 to 30 years. It is a more affordable and straightforward option, offering a temporary safety net for your loved ones. During the term, the policy provides a death benefit if the insured individual passes away. The key advantage of term life is its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for those seeking short-term coverage. For example, if you have a mortgage or young children, a 20-year term policy can ensure financial stability during these critical years. As the term ends, you may choose to renew the policy or opt for a different type of insurance.
Permanent (Whole Life) Insurance:
In contrast, permanent life insurance offers lifelong coverage, providing a sense of security that extends far beyond the initial term. This type of policy accumulates cash value over time, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn. The long-term financial implications of permanent life insurance are significant. Firstly, it ensures that your beneficiaries receive a death benefit regardless of when you pass away, providing a more comprehensive safety net. Additionally, the cash value can be a valuable asset, allowing policyholders to access funds for various financial needs, such as education expenses or business ventures. However, permanent life insurance is generally more expensive and complex, requiring a long-term commitment.
Comparing Duration:
The primary distinction between term and permanent life insurance is the duration of coverage. Term life is designed for a specific period, providing a focused safety net during critical life stages. On the other hand, permanent life insurance offers lifelong coverage, ensuring financial protection throughout your entire life. This long-term aspect of permanent insurance can be particularly beneficial for those seeking a more comprehensive and permanent solution.
Long-Term Financial Implications:
When considering the long-term financial implications, term life insurance is often more affordable and suitable for those with temporary financial needs. It provides a clear-cut solution for a defined period. In contrast, permanent life insurance offers a more substantial financial commitment, with potential long-term benefits. The cash value accumulation in permanent policies can be a valuable financial asset, providing flexibility and security. However, the higher costs and complexity of permanent insurance should be carefully evaluated to ensure it aligns with your financial goals and long-term plans.
In summary, the choice between term and permanent life insurance depends on your specific needs and financial objectives. Term life is ideal for short-term coverage and cost-effective solutions, while permanent life insurance provides lifelong security and potential long-term financial benefits. Understanding the duration and financial implications of each option is crucial in making an informed decision regarding your life insurance needs.
Canceling Life Insurance with AIG American General: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Age and Health: How age and health status impact insurance affordability
The concept of life insurance is a crucial financial tool, providing a safety net for individuals and their families. When considering life insurance, it's essential to understand how age and health status significantly influence the cost and availability of coverage. These factors are critical in determining the average life insurance premium and the overall affordability of the policy.
Age is a primary determinant of insurance rates. As individuals age, the risk of developing health issues increases, and this is reflected in insurance premiums. Younger people generally enjoy lower insurance rates because they are considered healthier and have a longer life expectancy. Insurance companies often use age-based tiers to categorize policyholders, with younger individuals falling into lower-risk categories and thus benefiting from more affordable premiums. For instance, a 25-year-old might pay significantly less for life insurance than a 55-year-old, all else being equal.
Health status plays an equally important role in insurance affordability. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those who engage in high-risk activities may face higher insurance premiums or even be deemed uninsurable by some companies. Chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer, can significantly impact insurance costs. Additionally, lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive drinking, or an inactive lifestyle can also affect insurance rates. Insurance providers often request medical history and may conduct health assessments to gauge the risk associated with insuring an individual.
The impact of age and health on insurance affordability is further emphasized by the concept of risk-based pricing. Insurance companies use statistical models to predict the likelihood of various health issues and calculate premiums accordingly. Younger and healthier individuals are generally considered lower-risk, resulting in more competitive rates. Conversely, older individuals with health concerns may be classified as higher-risk, leading to higher premiums or even difficulty in obtaining coverage.
In summary, age and health status are critical factors in determining the average life insurance premium. Younger individuals with good health often benefit from lower rates, while older individuals or those with health issues may face higher costs or challenges in securing insurance. Understanding these influences is essential for individuals seeking to protect themselves and their loved ones through life insurance. It highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regularly reviewing insurance policies to ensure they remain affordable and adequate over time.
CSV in Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Coverage Amounts: Determining suitable death benefit amounts for individuals
When considering life insurance, one of the most crucial aspects is determining the appropriate coverage amount, often referred to as the death benefit. This amount represents the financial payout that your beneficiaries will receive in the event of your passing. Choosing the right coverage amount is essential to ensure that your loved ones are financially secure and can maintain their standard of living during a challenging time.
The process of determining the suitable death benefit involves a careful evaluation of various factors. Firstly, consider your current financial obligations and future expenses. This includes mortgage payments, children's education costs, ongoing living expenses, and any other debts or financial commitments. By calculating the total value of these obligations, you can estimate the amount needed to cover these expenses in your absence. For instance, if you have a substantial mortgage, student loans, or a large family with significant educational costs ahead, you might opt for a higher coverage amount to ensure these financial responsibilities are met.
Another critical factor is your income and the financial role you play in your family's household. If you are the primary breadwinner, providing the majority of the family's income, a larger death benefit would be more appropriate to ensure your family's financial stability. Additionally, consider the number of dependents you have, as the coverage amount should adequately support their needs, including education, healthcare, and daily living expenses.
It's important to strike a balance between providing sufficient financial security and ensuring that the insurance premium remains affordable. A common approach is to aim for a coverage amount that is 10 to 15 times your annual income. This guideline can serve as a starting point, but it's essential to customize it based on individual circumstances. For example, if you have a stable and high-income job, you might consider a higher multiple, while those with lower incomes might opt for a lower multiple to ensure the policy remains financially viable.
Furthermore, it's beneficial to review and adjust your coverage amount periodically. Life events such as marriage, the birth of a child, or significant financial milestones can trigger a need for increased coverage. For instance, starting a family might require a higher death benefit to cover the costs of raising children, while purchasing a home could necessitate a larger payout to settle the mortgage. Regularly assessing your life's circumstances will help you maintain appropriate coverage.
Latent TB: Getting Life Insurance?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The average life insurance policy typically covers a significant portion of an individual's estimated future expenses, such as mortgage payments, education costs, or living expenses for beneficiaries. The coverage amount varies widely depending on factors like age, health, lifestyle, and the type of policy chosen. On average, a life insurance policy might provide coverage equivalent to 5-10 times the insured's annual income.
The duration of a life insurance policy can vary. Term life insurance is designed to provide coverage for a specific period, often 10, 20, or 30 years. After the term ends, the policy may lapse unless renewed. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for the insured's entire lifetime, as long as premiums are paid.
Several factors determine the cost of life insurance. Age is a significant factor, as younger individuals generally pay lower premiums. Health status, including any pre-existing medical conditions, plays a crucial role. Lifestyle choices like smoking, excessive drinking, or engaging in extreme sports can also impact premium rates. Additionally, the type of policy, coverage amount, and the insured's occupation may affect the cost.
Yes, it is possible to obtain life insurance with pre-existing health conditions, but it may be more challenging and expensive. Insurers often consider health factors when evaluating risk. Individuals with pre-existing conditions might be classified as 'high-risk' and may require a medical examination or additional health questions on the application. Some companies offer specialized policies for those with health concerns, but the coverage and rates can vary.