Understanding the nuances between universal and variable life insurance is crucial for anyone seeking long-term financial security. Universal life insurance offers a flexible premium structure, allowing policyholders to adjust their payments over time, while variable life insurance provides an investment component, potentially offering higher returns but also carrying more risk. The key difference lies in their structure and risk factors, with universal life being more predictable and variable life offering more flexibility and potential for growth.
Universal vs Variable Life Insurance: Key Differences
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Universal life insurance is a permanent life insurance policy with a fixed death benefit. Variable life insurance combines life insurance with an investment component, allowing policyholders to invest a portion of their premium in a separate investment account. |
| Flexibility | Universal: Offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts. Policyholders can choose to pay higher premiums to increase coverage or lower them when needed. Variable: Provides more investment flexibility, allowing policyholders to adjust their investment strategy and potentially earn higher returns. |
| Death Benefit | Universal: Guarantees a fixed death benefit, which remains the same throughout the life of the policy. Variable: The death benefit fluctuates based on the performance of the underlying investments in the policy's investment account. |
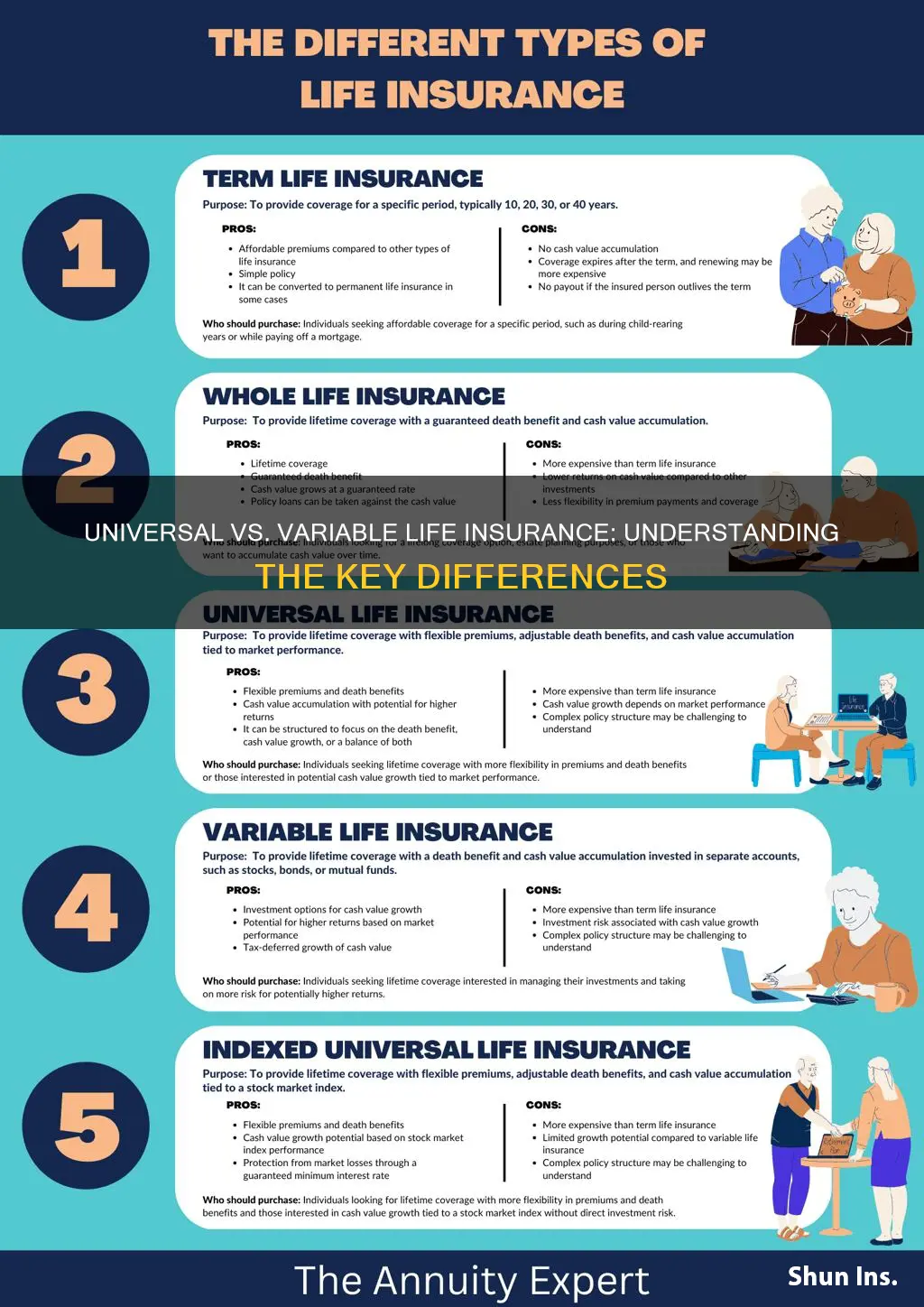
| Investment Options | Universal: Offers limited investment options, typically tied to the insurer's investment portfolio. Variable: Provides a wide range of investment options, allowing policyholders to choose from various mutual funds, stocks, bonds, and other assets. |
| Surrender Value | Universal: Accumulates cash value over time, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn. Variable: Accumulates cash value, but it is tied to the performance of the investment account. |
| Cost | Universal: Generally has higher upfront costs due to the guaranteed death benefit. Variable: May have lower upfront costs but higher ongoing fees associated with the investment management. |
| Risk | Universal: Offers more predictable risk due to the fixed death benefit. Variable: Involves investment risk, as the death benefit and cash value are dependent on investment performance. |
| Tax Advantages | Both types offer tax-deferred growth of cash value. However, the investment gains in variable life insurance are subject to market fluctuations. |
| Liquidity | Universal: Provides more liquidity as policyholders can access cash value through loans or withdrawals. Variable: Offers liquidity through the investment account, but access may be subject to penalties. |
| Longevity | Universal: Suitable for long-term financial planning due to its permanent nature. Variable: Can be suitable for those seeking both insurance and investment opportunities. |
What You'll Learn
- Definition: Universal life offers flexible premiums, while variable life's value fluctuates with market performance
- Cost: Universal life has consistent costs, whereas variable life's fees vary
- Flexibility: Universal life allows policyholders to adjust death benefits and premiums, unlike fixed variable life
- Risk: Variable life involves market risk, while universal life is more stable
- Taxation: Universal life may be taxed differently than variable life, depending on the policy type

Definition: Universal life offers flexible premiums, while variable life's value fluctuates with market performance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a unique feature: flexibility in premium payments. Unlike traditional term life insurance, where premiums are fixed for the duration of the policy, universal life insurance allows policyholders to adjust their premium payments over time. This flexibility is particularly appealing to those who may experience changes in income or financial goals. With universal life, policyholders can choose to pay higher premiums when they can afford to, potentially building up a larger cash value, and lower premiums when their financial situation demands it. This adaptability is a significant advantage, as it allows individuals to tailor their insurance coverage to their evolving needs.
In contrast, variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance with a twist. The value of a variable life insurance policy is directly linked to the performance of the financial markets. This means that the cash value of the policy, which grows over time, can fluctuate based on the investment options chosen by the insurance company. Policyholders can select from a range of investment accounts, similar to those in a mutual fund, which can offer potential for higher returns but also come with the risk of market volatility. The value of the policy can increase or decrease based on the performance of these investments, providing a dynamic and potentially rewarding aspect to the insurance product.
The key difference lies in the treatment of premiums and the underlying investment strategy. Universal life insurance provides a consistent and predictable approach to premium payments, allowing policyholders to manage their insurance needs without the added complexity of market-linked investments. On the other hand, variable life insurance introduces an element of uncertainty and potential reward, making it an attractive option for those who are comfortable with market-related risks and seek to maximize their insurance benefits through investment opportunities.
When considering these options, it's essential to understand the trade-offs. Universal life insurance offers stability and control, ensuring that premiums remain consistent and providing a reliable insurance coverage. In contrast, variable life insurance introduces a level of complexity and risk, where the policy's value can change with market conditions. Policyholders should carefully evaluate their financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term plans to determine which type of life insurance aligns best with their needs.
In summary, the choice between universal and variable life insurance depends on an individual's financial preferences and risk appetite. Universal life insurance provides a straightforward and flexible approach to insurance coverage, while variable life insurance offers a dynamic and potentially rewarding experience through market-linked investments. Understanding these definitions and characteristics is crucial for making an informed decision regarding life insurance coverage.
Life Insurance: Global Coverage and Death Benefits
You may want to see also

Cost: Universal life has consistent costs, whereas variable life's fees vary
Universal life insurance offers a unique advantage in terms of cost structure compared to its counterpart, variable life insurance. One of the key differences lies in the predictability and consistency of expenses associated with each type of policy. Universal life insurance policies typically come with fixed premiums, which means that the cost of coverage remains the same over the policy's duration. This predictability is a significant advantage for policyholders, as they can plan their finances more effectively, knowing that their insurance premiums will not fluctuate significantly. With universal life, individuals can budget for their long-term insurance needs without the uncertainty that comes with variable costs.
In contrast, variable life insurance policies introduce an element of variability in their pricing structure. The fees and expenses associated with variable life insurance can change over time, often depending on the performance of underlying investments. These policies may include investment fees, management charges, and other variable costs that can fluctuate based on market conditions. As a result, policyholders may experience varying insurance costs, which can be a concern for those seeking stability in their financial planning.
The consistent cost structure of universal life insurance provides a sense of security and control. Policyholders can accurately estimate their future insurance expenses, making it easier to manage their finances and plan for retirement or other financial goals. This predictability is particularly valuable for individuals who prefer a more stable and controlled approach to insurance. On the other hand, variable life insurance may appeal to those who are comfortable with the potential for lower costs during market downturns but are also willing to accept the risk of higher fees when markets perform well.
When considering the cost aspect, it is essential to understand the long-term implications. Universal life insurance's consistent costs can result in lower overall expenses over the policy's lifetime, especially if the policy remains in force for an extended period. Variable life insurance, while offering potential cost savings during favorable market conditions, may also come with higher fees when markets are performing well, which could impact the overall cost structure.
In summary, the cost structure is a critical factor in differentiating universal and variable life insurance. Universal life insurance provides the advantage of consistent and predictable costs, making it an attractive option for those seeking financial stability. In contrast, variable life insurance introduces an element of variability, which may be suitable for some but could also lead to uncertainty in long-term financial planning. Understanding these cost differences is essential for individuals to make informed decisions when choosing between universal and variable life insurance policies.
Cancer Testing and Life Insurance: What's the Link?
You may want to see also

Flexibility: Universal life allows policyholders to adjust death benefits and premiums, unlike fixed variable life
Universal life insurance offers a unique level of flexibility that sets it apart from other types of life insurance, particularly when compared to fixed variable life insurance. One of the key advantages of universal life is the ability to customize and adjust various aspects of the policy to suit the policyholder's needs and financial situation.
In contrast to fixed variable life insurance, where the death benefit and premiums are predetermined and cannot be changed, universal life provides policyholders with the freedom to make adjustments. This flexibility allows individuals to tailor their insurance coverage according to their evolving circumstances. For instance, policyholders can choose to increase or decrease the death benefit, which represents the amount paid to the beneficiary upon the insured's death, based on their changing financial goals and risk tolerance. This adaptability is especially beneficial for those who want to ensure their loved ones are adequately protected without being locked into a rigid structure.
Furthermore, universal life policies often offer the option to adjust premiums, which are the regular payments made by the policyholder. These premiums can be customized to fit the policyholder's budget and financial capabilities. Unlike fixed variable life, where premiums are set for the entire term of the policy, universal life allows for premium adjustments, providing a more dynamic and personalized insurance experience. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for individuals who may experience fluctuations in their income or financial obligations over time.
The ability to adjust death benefits and premiums in universal life insurance empowers policyholders to make informed decisions based on their current financial status and future plans. This level of control ensures that the insurance coverage remains relevant and effective throughout the policyholder's life, providing peace of mind and financial security. In summary, the flexibility offered by universal life insurance, in contrast to the rigid nature of fixed variable life, allows individuals to create a customized insurance plan that aligns with their unique needs and preferences.
Life Insurance Dividends: Taxable or Not?
You may want to see also

Risk: Variable life involves market risk, while universal life is more stable
Variable life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a flexible investment component. It provides a way for policyholders to potentially earn higher returns compared to traditional whole life insurance. The investment aspect of variable life insurance is what sets it apart, as it allows the policyholder to allocate a portion of their premium payments into various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This investment element introduces market risk, meaning the performance of the policy's investment portfolio can fluctuate over time, impacting the overall value of the policy. Policyholders have the freedom to choose different investment strategies, which can lead to varying levels of risk and potential returns.
On the other hand, universal life insurance offers a more stable and predictable approach. It provides a guaranteed death benefit and a fixed premium structure, ensuring that the policyholder's monthly payments remain consistent over the long term. The primary focus of universal life insurance is to provide lifelong coverage, and the premiums are typically higher than those of term life insurance. While universal life insurance does not offer the same level of investment flexibility as variable life, it provides a more secure and predictable financial plan. The stability of universal life insurance makes it an attractive option for those seeking long-term financial security without the added complexity of market-related risks.
The key difference in terms of risk lies in the investment nature of the policies. Variable life insurance allows policyholders to take on market risks, where the value of their investment portfolio can rise and fall with market conditions. This can be advantageous if the investments perform well, but it also means that the policy's cash value and death benefit may fluctuate. In contrast, universal life insurance provides a more conservative approach, ensuring that the policy's value and death benefit remain relatively stable over time, regardless of market performance.
When considering the risk factor, it's essential to understand that variable life insurance is more suitable for those who are comfortable with market volatility and are willing to accept the potential for higher returns. It is a more complex product that requires careful consideration of the investment options and their associated risks. In contrast, universal life insurance is often preferred by individuals seeking a simpler, more stable financial plan, especially those who prioritize long-term financial security and predictability.
In summary, the choice between variable and universal life insurance depends on an individual's risk tolerance, financial goals, and preference for stability. Variable life insurance offers the potential for higher returns but involves market risk, while universal life insurance provides a more secure and predictable financial plan, making it a popular choice for those seeking long-term coverage without the added complexity of variable investments. Understanding these risk differences is crucial in making an informed decision regarding life insurance coverage.
Cocaine Use: Insurance Test Detection Times
You may want to see also

Taxation: Universal life may be taxed differently than variable life, depending on the policy type
Universal life insurance offers a unique tax advantage compared to variable life insurance, primarily due to its policy structure. When you purchase a universal life policy, you typically pay a fixed premium, and a portion of this premium goes towards building cash value, which grows tax-deferred. This means that the cash value in the policy grows without being subject to annual income tax, similar to a tax-deferred savings account. This tax-deferred growth can be a significant benefit, especially for long-term financial planning.
The key difference in taxation arises when it comes to withdrawals or surrenders from the policy. When you take a withdrawal or surrender a universal life policy, the amount you receive is generally not taxable as income. This is because the cash value has been growing tax-deferred, and the initial premium payments have already been taxed. As long as the policy is in force, any withdrawals or surrenders are treated as a return of your own money, not as taxable income.
In contrast, variable life insurance policies have a more complex structure. With a variable life policy, a portion of your premium goes towards funding an investment account, which can be invested in various assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. The performance of these investments directly impacts the cash value of the policy. When you make withdrawals or surrenders from a variable life policy, the tax treatment can vary. If the policy has been in force for more than a year, any withdrawals or surrenders may be subject to income tax, as the cash value has grown due to the investment performance, which is generally taxable.
Additionally, the tax implications of variable life insurance can be more nuanced. If the policy's investment performance results in a gain, this gain is typically taxable as ordinary income when withdrawn. However, if the policy has been in force for more than a year, a portion of the withdrawal may be tax-free, allowing you to withdraw a combination of the initial premium payments and the investment gains. This flexibility in tax treatment can be advantageous for those who want to access their funds while minimizing tax consequences.
Understanding the tax implications of both universal and variable life insurance is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Universal life insurance's tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals can provide long-term savings benefits. On the other hand, variable life insurance's tax treatment of withdrawals and investment gains requires careful consideration, especially when planning for tax efficiency in the long term. Consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional can help individuals navigate these complexities and choose the life insurance policy that best aligns with their financial goals and tax strategies.
Aviva Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Universal life insurance offers flexible premiums and a permanent policy, allowing policyholders to adjust their coverage and invest a portion of the premium in an investment account. Variable life insurance, on the other hand, provides a combination of insurance and investment features, with the investment value varying based on market performance.
In universal life insurance, the investment component is typically fixed and linked to an interest rate, ensuring a guaranteed return. Variable life insurance, however, invests in a separate account that mirrors a specific market index or other investment options, allowing for potential higher returns but also carrying more risk.
Absolutely. Universal life insurance policies often allow policyholders to pay premiums at any time, in any amount, as long as the minimum requirements are met. This flexibility enables individuals to adjust their payments based on their financial situation, making it suitable for those who prefer a more adaptable insurance plan.
Variable life insurance policies offer tax-deferred growth on the investment portion. This means that any earnings or gains within the policy's investment account are not subject to immediate taxation. Additionally, policyholders can make tax-deductible premium payments, providing a potential tax benefit over time.







