Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and lifelong coverage. It features a savings element (cash value) that grows on a tax-deferred basis. The cash value can be used to pay premiums, as loan collateral, or surrendered for its cash value. While universal life insurance offers more flexibility than whole life insurance, it is important to closely monitor the cash value to avoid large payment requirements or policy lapse. Understanding the different types of universal life insurance, such as variable, indexed, and guaranteed universal life insurance, is crucial before purchasing a policy.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Type | Permanent life insurance |
| Coverage | Lifelong |
| Premium payments | Flexible |
| Cash value | Grows on a tax-deferred basis |
| Investment | Insurer invests a portion of the premiums |
| Interest rate | Set by the insurer, usually with a guaranteed minimum |
| Death benefit | Flexible |
| Lapse | Possible if the cash value drops to zero |
| Withdrawals | Possible, but may be taxed |
What You'll Learn

Universal life insurance offers flexibility with premium payments
Universal life insurance, also known as "flexible premium adjustable life insurance", offers a savings element (cash value) that grows on a tax-deferred basis. It provides more flexibility than whole life insurance, allowing policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits. This flexibility can be particularly useful if your income changes or becomes smaller, such as during retirement.
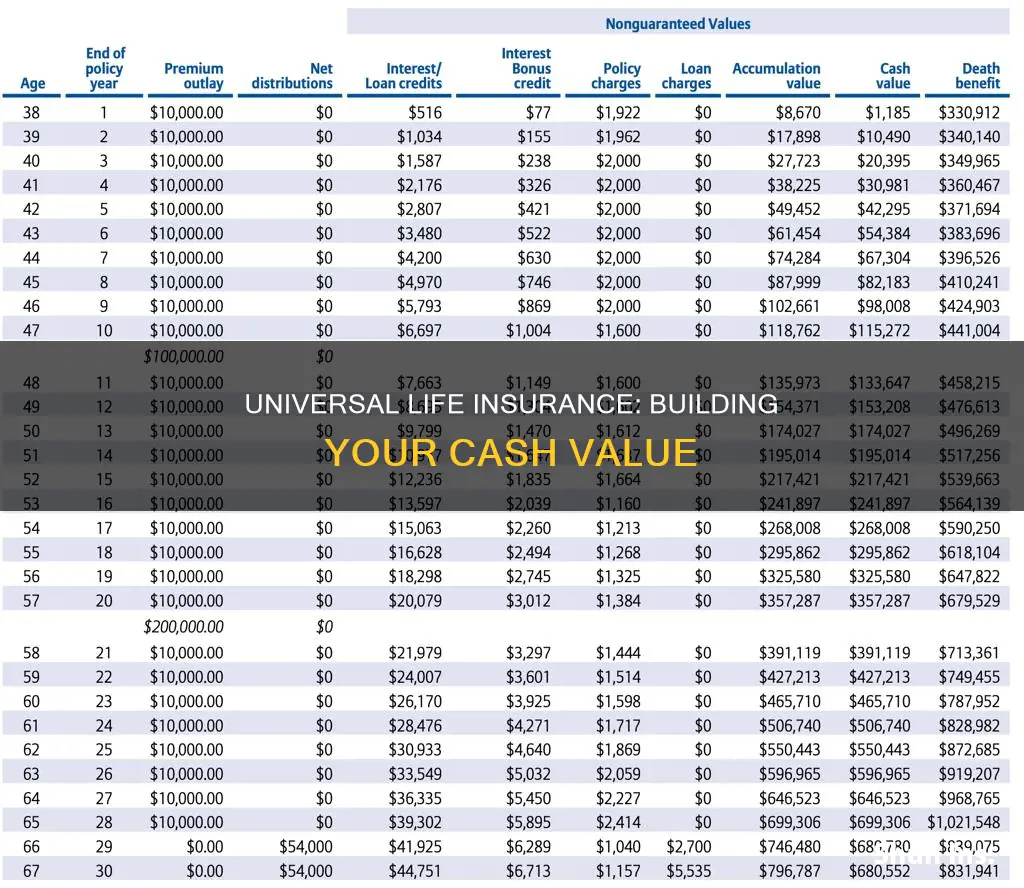
The premium payments for universal life insurance are split between the cost of coverage and the cash value. Policyholders can choose how much to pay within the minimum and maximum premium amounts. Many people opt to pay the maximum for the first several years of coverage, building a large cash value that can be used to pay premiums later on. This strategy can help ensure permanent coverage, even with a smaller income. However, it is important to closely monitor the cash value, as running out could result in higher premium costs or policy lapse.
Universal life insurance policies typically offer a guaranteed minimum interest rate, ensuring a certain minimum return on your money. The return may increase if the insurer performs well with its investments. Additionally, the cash value can be used in several ways, such as collateral for loans or to pay premiums. It is important to note that the cash value is separate from the death benefit, and your beneficiaries will only receive the latter.
Compared to whole life insurance, universal life insurance offers more flexibility in premium payments and the potential for greater cash value growth. However, it may be more complex and does not offer the same guarantees as whole life insurance. Whole life insurance premiums are fixed, whereas universal life premiums can vary, and whole life insurance guarantees a fixed interest rate, unlike universal life insurance. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on your individual needs and preferences.
Life Insurance and Stillbirth: What Coverage is Offered?
You may want to see also

It has a savings element that grows on a tax-deferred basis
Universal life insurance, also known as flexible premium adjustable life insurance, has a savings element that grows on a tax-deferred basis. This means that the cash value of the policy increases over time, and the policyholder can access this cash value during their lifetime.
The insurer invests a portion of the premiums paid, and the return on this investment is credited to the policy, with any growth in value accumulating tax-free. This allows the cash value of the policy to grow faster than it would if it were subject to tax.
Universal life insurance policies offer a guaranteed minimum interest rate, meaning that the insurer guarantees a certain minimum return on the policyholder's money. This rate is usually set by the insurer and can change, but it ensures that the cash value of the policy will grow, even if the insurer's investments perform poorly.
The ability to build cash value is a key feature of universal life insurance and sets it apart from term life insurance, which does not have a cash value component. The cash value in a universal life insurance policy can be used in several ways, such as borrowing against it or using it to pay premiums, and it can provide financial flexibility during the policyholder's lifetime.
Spiderman's Life Insurance: An Uncertain Hero's Fate
You may want to see also

The cash value can be used as loan collateral
Universal life insurance is a form of permanent life insurance that offers lifetime coverage as long as you pay your premiums. It features a savings element (cash value) that grows on a tax-deferred basis. The cash value can be used as loan collateral in several ways.
Firstly, you can use the cash value of your universal life insurance policy as collateral on a bank loan or other types of loans. This is known as a secured loan, and lenders accept this type of insurance policy as collateral because of its guaranteed cash value and death benefit. The lender will usually lend you between 50% to 90% of your policy's cash value. It's important to note that if you default on the loan, the lender can cash in the insurance policy or deduct the loan amount from your death benefit.
Secondly, you can take out a loan directly from your insurance company, known as a policy loan. This allows you to borrow money from the cash value of your life insurance policy. The interest rates on these loans are often lower than personal loans, and they don't require a credit check. However, unpaid loans will reduce the death benefit by the outstanding amount.
Thirdly, you have the option to withdraw your policy's cash value, either partially or in full. This can be useful if you need to make a large purchase but keep in mind that there are usually penalties and surrender fees associated with early withdrawals. Withdrawals will also reduce your death benefit.
When using your universal life insurance cash value as collateral, it's important to consider the benefits and risks. One advantage is that your personal property and assets are protected even if you're unable to repay the loan. Additionally, loan proceeds are typically tax-free, and you may be able to secure more affordable interest rates due to the secured nature of the loan. However, there are also risks involved, such as outliving your projected death date or changes in interest and return rates, which may impact your ability to repay the loan.
Credit Checks: A Factor in Life Insurance Premiums?
You may want to see also

Policyholders can adjust their death benefits
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers lifetime coverage as long as you pay your premiums. It has a cash value element, and it is often referred to as "flexible premium adjustable life insurance". This flexibility means that policyholders can adjust their death benefits in several ways.
Firstly, universal life insurance policies can have either a level death benefit or an increasing death benefit. The level death benefit, also known as Option 1, maintains the same coverage throughout the life of the policy. On the other hand, the increasing death benefit, or Option 2, allows the death benefit to rise as the cash value of the policy increases over time. Most universal life insurance policies allow owners to switch between these two options with minimal restrictions.
Secondly, policyholders can increase the size of their death benefit, although this may require a medical exam. This is a good option for those who want to ensure their heirs receive a larger payout. However, increasing the death benefit will also result in higher premiums.
Thirdly, policyholders can decrease their death benefit, which will result in lower premiums. This option provides flexibility for those who may no longer need as much coverage or wish to reduce their expenses.
Finally, some life insurance policies allow policyholders to increase the death benefit as they build their cash value. This means that as the policyholder contributes more to the cash value, the death benefit will also increase.
Life Insurance and Food Stamps: Is There a Link?
You may want to see also

Universal life insurance is more complex than whole life insurance
Universal life insurance and whole life insurance are both types of permanent life insurance that offer lifelong coverage and a cash value component. However, they differ in terms of complexity, flexibility, guarantees, and cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision about which policy best suits one's financial goals and needs.
On the other hand, whole life insurance provides consistency and predictability. It offers fixed premiums, a guaranteed death benefit, and guaranteed cash value accumulation. The cash value in a whole life policy grows at a fixed interest rate, making it more stable and predictable. Whole life insurance is generally considered easier to navigate due to its fixed and guaranteed nature.
The complexity of universal life insurance also lies in the different types available, such as guaranteed universal life, indexed universal life, and variable universal life. Each type has distinct features, risks, and growth potential. For example, with indexed universal life, the cash value growth is tied to a specific stock market index, adding another layer of complexity.
In summary, universal life insurance is more complex than whole life insurance due to its flexible nature, variable interest rates, the risk of underfunding, and the need for careful management. Whole life insurance, with its fixed premiums, guaranteed benefits, and predictable cash value growth, offers a simpler and more stable option. The choice between the two ultimately depends on one's financial situation, risk tolerance, and preference for flexibility or stability.
Life Insurance: NRMA's Offerings and Your Options
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and lifelong coverage. It has a savings element (cash value) that grows on a tax-deferred basis.
Universal life insurance policies have a cash value component that is separate from the death benefit. Each time a premium payment is made, a portion is put toward the cost of insurance (e.g. administrative fees and the death benefit) and the rest becomes part of the cash value. The cash value can be used for several purposes, such as paying premiums, taking out loans, or surrendering the policy.
Universal life insurance offers flexibility in terms of premium payments and death benefits, which can be adjusted within certain limits. It also provides the potential for cash value growth and is often cheaper than whole life insurance.
Universal life insurance can be complex and difficult to understand due to the different types and features available. It may not guarantee gains on cash value, and withdrawals or loans against the cash value may deplete it or cause the policy to lapse.







