In the United States, driving without insurance is a significant concern, as it poses risks to both drivers and other road users. Despite the legal requirement for car insurance in most states, a substantial number of Americans still choose to drive without coverage. This practice can lead to severe financial consequences in the event of an accident, as the driver may be held responsible for any damages or injuries. The lack of insurance can also result in legal issues and increased insurance premiums for those who do have coverage. Understanding the reasons behind this behavior and the potential consequences is crucial to addressing this issue and ensuring road safety.
What You'll Learn
- Demographics of Uninsured Drivers: Age, gender, and income disparities in driver insurance coverage
- Financial Barriers to Insurance: Cost, affordability, and the impact of economic factors on insurance purchase
- Legal and Regulatory Context: Penalties, enforcement, and the legal framework surrounding driving without insurance
- Health and Safety Implications: Accident risks, medical costs, and public health outcomes of uninsured driving
- Policy Solutions and Initiatives: Government programs, incentives, and campaigns to increase insurance coverage

Demographics of Uninsured Drivers: Age, gender, and income disparities in driver insurance coverage
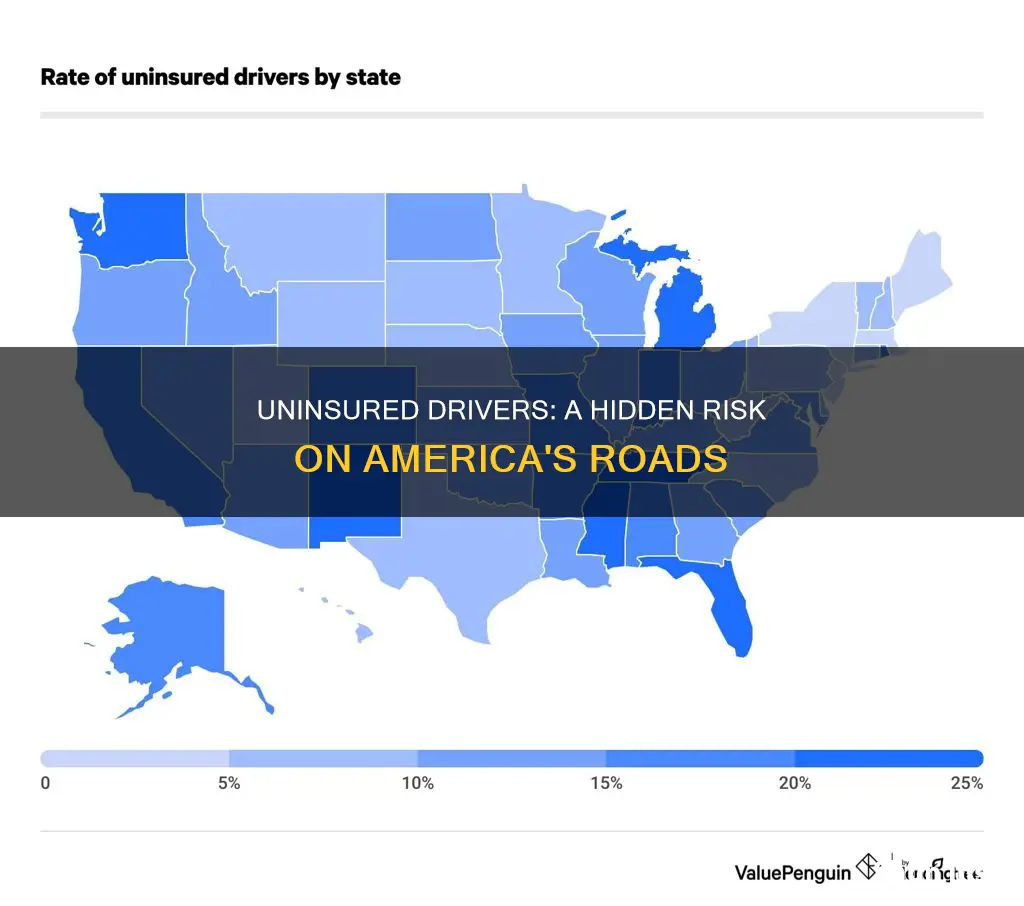
The issue of driving without insurance is a significant concern in the United States, with various demographic factors influencing the likelihood of individuals choosing to forgo insurance coverage. Research indicates that a substantial number of Americans, approximately 1 in 8, or around 12.2% of drivers, are uninsured. This percentage highlights the prevalence of this issue and underscores the need to understand the demographics associated with this behavior.
Age is a critical factor in determining insurance coverage. Younger drivers, particularly those in their teens and early twenties, are more likely to be uninsured. This demographic is often associated with higher-risk profiles, and the lack of insurance can be attributed to several reasons. Firstly, younger individuals may have limited financial resources, making it challenging to afford insurance premiums. Additionally, they might perceive a lower risk of accidents or legal consequences, leading to a reluctance to purchase coverage. As individuals age, they tend to become more financially stable, and the need for insurance becomes more apparent, especially as they accumulate assets and face potential liabilities.
Gender also plays a role in insurance coverage decisions. Studies suggest that men are slightly more likely to be uninsured compared to women. This disparity can be attributed to various factors, including differences in risk-taking behaviors and financial priorities. Historically, men have been more inclined to engage in risky driving practices, and this behavior may contribute to a higher likelihood of accidents, making insurance less appealing. On the other hand, women often prioritize financial stability and long-term planning, which can lead to a greater emphasis on insurance coverage.
Income level is a significant determinant of insurance coverage. Uninsured drivers are disproportionately represented among low-income households. Financial constraints are a primary reason for not purchasing insurance. Lower-income individuals often struggle to afford the premiums, especially when they lack comprehensive financial resources. Additionally, they may work in jobs that offer limited or no benefits, including health and auto insurance. The lack of employer-provided coverage can further exacerbate the issue. As income increases, the likelihood of having insurance coverage tends to rise, indicating a direct correlation between financial stability and insurance acquisition.
Understanding these demographics is crucial for policymakers, insurance providers, and road safety advocates. By recognizing the age, gender, and income disparities among uninsured drivers, targeted interventions can be developed. For instance, educational campaigns aimed at younger drivers can emphasize the importance of insurance and provide information on affordable options. Financial incentives or subsidies for low-income individuals could also be explored to encourage insurance coverage. Addressing these disparities is essential to improving road safety, reducing financial risks, and ensuring that all drivers are adequately protected by insurance.
Smart Ways to Lower Home and Auto Insurance Costs
You may want to see also

Financial Barriers to Insurance: Cost, affordability, and the impact of economic factors on insurance purchase
The high cost of insurance is a significant financial barrier that prevents many Americans from obtaining coverage, especially in the context of driving. The idea that 'how many Americans drive with no insurance' is a critical issue, as it directly relates to the economic challenges faced by a large portion of the population. The primary reason for this phenomenon is the sheer expense of insurance premiums, which can be prohibitively high for individuals and families with limited financial resources.
In many states, the minimum liability coverage required by law is often insufficient to cover the damages in the event of an accident. This leaves drivers with two options: either purchase additional comprehensive and collision coverage, which significantly increases the cost, or drive without adequate insurance. The latter choice is made more appealing by the immediate financial relief it provides, but it also exposes them to legal consequences and potential financial ruin in the event of an accident.
Economic factors play a crucial role in this scenario. For instance, the rising cost of living and increasing expenses associated with healthcare, education, and basic necessities have left many Americans struggling to make ends meet. As a result, they may view insurance as a non-essential expense, especially if they believe they are unlikely to be involved in an accident. This mindset, coupled with the lack of financial literacy and understanding of the long-term benefits of insurance, contributes to the problem.
Furthermore, the affordability of insurance is further complicated by the presence of multiple insurance providers, each with its own pricing structure and policies. This can make it challenging for consumers to compare prices and find the best deals, often leading to a sense of being overwhelmed and, consequently, a decision to forgo insurance. Additionally, the lack of financial incentives or subsidies for low-income individuals can exacerbate the issue, making it even more difficult for them to access affordable insurance options.
Addressing these financial barriers requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, insurance companies could offer more flexible payment plans and discounts to make coverage more accessible. Governments and non-profit organizations can also play a role by providing financial assistance or subsidies to low-income individuals, ensuring that insurance remains a viable option for all. Moreover, educating the public about the importance of insurance and the potential consequences of driving without it can help shift perceptions and encourage responsible behavior.
Lyft Driving: Impact on Insurance Rates and Coverage
You may want to see also

Legal and Regulatory Context: Penalties, enforcement, and the legal framework surrounding driving without insurance
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding driving without insurance in the United States is complex and varies by state. Each state has its own set of laws and penalties for driving without insurance, and these laws are designed to protect both drivers and other road users. The primary legal framework is typically found in state insurance codes and motor vehicle laws, which mandate that drivers carry a certain level of insurance coverage.
Penalties for driving without insurance can be severe and are often designed to deter individuals from operating a vehicle without the required coverage. These penalties may include fines, license suspension or revocation, and even imprisonment in some cases. For instance, in California, driving without insurance can result in a fine of up to $1,000 for the first offense, and subsequent offenses can lead to higher fines and potential jail time. Similarly, in New York, the penalties range from a $300 fine for the first offense to a $1,000 fine and up to 15 days in jail for subsequent violations. These penalties are often structured to increase in severity with each subsequent offense, reflecting the state's commitment to ensuring road safety and financial responsibility.
Enforcement of these laws is typically carried out by state motor vehicle departments and insurance regulators. Law enforcement officers are authorized to pull over and cite drivers who are found to be driving without insurance. In some states, insurance companies also play a role in enforcement by reporting policyholders who do not maintain the required coverage. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the legal framework is effectively enforced and that drivers are held accountable for their actions.
The legal framework also includes provisions for the protection of innocent victims. When an uninsured driver causes an accident, they may be held personally liable for any damages or injuries sustained by other parties. This can result in civil lawsuits and financial penalties, in addition to the criminal penalties for driving without insurance. As a result, the consequences of driving without insurance extend beyond the immediate legal penalties, impacting an individual's financial and personal well-being.
Understanding the specific legal and regulatory context in one's state is crucial for drivers. This includes knowing the insurance requirements, the potential penalties for non-compliance, and the enforcement mechanisms in place. By adhering to these laws, drivers can avoid the serious consequences of driving without insurance, ensuring a safer and more responsible driving environment for everyone.
Auto Insurance: Wisconsin's Minimum Requirements and You
You may want to see also

Health and Safety Implications: Accident risks, medical costs, and public health outcomes of uninsured driving
The issue of driving without insurance is a significant concern in the United States, with far-reaching implications for public health and safety. According to recent studies, a substantial number of Americans choose to drive without the necessary coverage, often due to financial constraints or a lack of understanding of the importance of insurance. This practice carries severe consequences, affecting not only the individuals involved in accidents but also the broader community.
One of the primary health and safety implications is the increased risk of accidents and their potential severity. When drivers operate vehicles without insurance, they often lack the financial protection that insurance provides. In the event of an accident, the uninsured driver may be financially responsible for all damages and medical expenses, which can be devastating. This situation can lead to a higher likelihood of accidents going unreported or unresolved, as the financial burden may discourage victims from seeking legal action or medical treatment. Moreover, without insurance, the injured parties may struggle to afford necessary medical care, potentially resulting in long-term health complications or even death.
The financial burden of medical costs is a critical aspect of this issue. Uninsured drivers and their passengers are at risk of incurring substantial medical bills, especially in cases of severe injuries or accidents involving multiple vehicles. The lack of insurance coverage means that individuals must pay for medical treatment out of pocket, which can lead to financial ruin. This is particularly concerning as medical expenses in the US are already high, and the absence of insurance can exacerbate the problem, making it difficult for accident victims to access timely and affordable healthcare.
Public health outcomes are also significantly impacted by uninsured driving. The consequences extend beyond individual accidents, affecting the overall well-being of communities. When a large portion of the population lacks insurance, the healthcare system may experience increased strain, especially during emergencies. This can lead to longer wait times for medical services and potentially compromise the quality of care. Additionally, the financial burden on accident victims can contribute to long-term health issues, as individuals may delay or forgo necessary treatments due to cost, resulting in a decline in overall public health.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Public awareness campaigns can educate drivers about the importance of insurance and the potential risks of driving without coverage. Policy interventions, such as mandatory insurance requirements and subsidies for low-income individuals, can also help reduce the number of uninsured drivers. By implementing these measures, the health and safety implications of uninsured driving can be mitigated, ensuring that Americans have access to the necessary financial protection and medical care in the event of an accident.
Virginia Vehicle Insurance Lookup: Quick Guide
You may want to see also

Policy Solutions and Initiatives: Government programs, incentives, and campaigns to increase insurance coverage
The issue of Americans driving without insurance is a significant public health and safety concern, as it can lead to severe financial consequences and legal issues for both drivers and other road users. To address this problem, policymakers and government agencies have implemented various initiatives and programs aimed at increasing insurance coverage among drivers. Here are some policy solutions and initiatives that have been proposed and implemented:
Government Programs and Subsidies: One of the most effective ways to encourage insurance coverage is through government-funded programs and subsidies. The federal government, in collaboration with state governments, can design and implement low-cost or free insurance schemes for low-income individuals and families. For example, the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK offers a comprehensive health insurance program called NHS Insurance, which provides coverage for medical expenses and is available to all UK residents. Similarly, the US government could explore the idea of a universal healthcare system or a state-based public option for auto insurance, making coverage more affordable and accessible. Subsidies and tax incentives can be provided to insurance companies to offer discounted rates for drivers who purchase insurance, especially those with lower incomes.
Incentivizing Insurance Purchase: Governments can introduce incentives to motivate drivers to obtain insurance. For instance, a 'No-Fault Insurance' system, where drivers' own insurance companies cover their damages regardless of fault, can encourage more people to purchase insurance. This system reduces the financial burden on individuals and promotes a safer driving environment. Additionally, offering tax credits or deductions for insurance premiums paid by individuals can make insurance more affordable. Another approach is to implement a point-based system where drivers earn points for safe driving behavior, which can lead to lower insurance premiums. This approach rewards responsible driving and encourages drivers to maintain a clean driving record.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Launching public awareness campaigns is crucial to educating drivers about the importance of insurance and the legal and financial implications of driving without coverage. These campaigns can utilize various media platforms, including social media, television, and radio, to reach a wide audience. The campaigns can highlight the risks associated with driving uninsured, such as financial liabilities, legal consequences, and potential accidents. By sharing real-life stories and case studies, the government can create a sense of urgency and encourage drivers to obtain insurance. For instance, a campaign titled "Drive Safe, Stay Insured" could emphasize the long-term benefits of insurance and the potential savings compared to the costs of an accident.
Mandatory Insurance Laws: Enforcing mandatory insurance laws is a direct approach to ensuring that all drivers have the necessary coverage. States can introduce and enforce strict regulations that require drivers to purchase auto insurance before registering their vehicles. This approach has been successful in some countries, such as the UK, where the Motor Insurance Database (MID) ensures that all vehicles are insured. Penalties for non-compliance can include fines, license suspension, or even vehicle impoundment. By making insurance a legal requirement, the government can significantly reduce the number of uninsured drivers on the road.
Community-Based Initiatives: Local governments and community organizations can collaborate to implement initiatives that promote insurance coverage. For example, community centers or local businesses can offer insurance information sessions or workshops to educate residents about the importance of insurance and available options. These initiatives can also provide assistance with insurance applications and help individuals navigate the process of obtaining coverage. Additionally, community-led campaigns can focus on specific demographics, such as young drivers or immigrants, who may face unique challenges in accessing insurance.
Ohio Stop Gap Insurance: Must-Have or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
It's difficult to determine an exact number, but according to various studies and surveys, the percentage of uninsured drivers in the United States varies. As of 2022, the Insurance Research Council (IRC) estimated that around 13% of drivers in the U.S. were uninsured. This translates to approximately 1 in 8 drivers.
There are several reasons why some Americans choose to drive without insurance. Common factors include affordability, lack of understanding of the importance of insurance, and a false sense of security that they might not get into an accident. Some individuals may also intentionally avoid insurance due to previous claims or a history of accidents, which can lead to higher premiums.
Yes, driving without car insurance can result in legal consequences. Each state has its own laws regarding insurance requirements for drivers. Failure to comply with these laws can lead to fines, license suspension, or even arrest. Additionally, if an uninsured driver is involved in an accident, they may face increased liability and potential legal issues. It is essential for drivers to understand and adhere to their state's insurance regulations to avoid these penalties.







