Life assurance and life insurance are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Life assurance, also known as whole life insurance, is a long-term financial product that provides coverage for the entire life of the policyholder. It offers a guaranteed death benefit and a cash value component that grows over time. This type of insurance is typically more expensive but provides lifelong coverage and potential investment opportunities. On the other hand, life insurance is a more general term that refers to any insurance policy that pays out a death benefit upon the insured individual's death. It can be term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specific period, or permanent life insurance, which offers lifelong coverage. Understanding these nuances is essential for individuals to choose the right coverage based on their financial goals and needs.
What You'll Learn
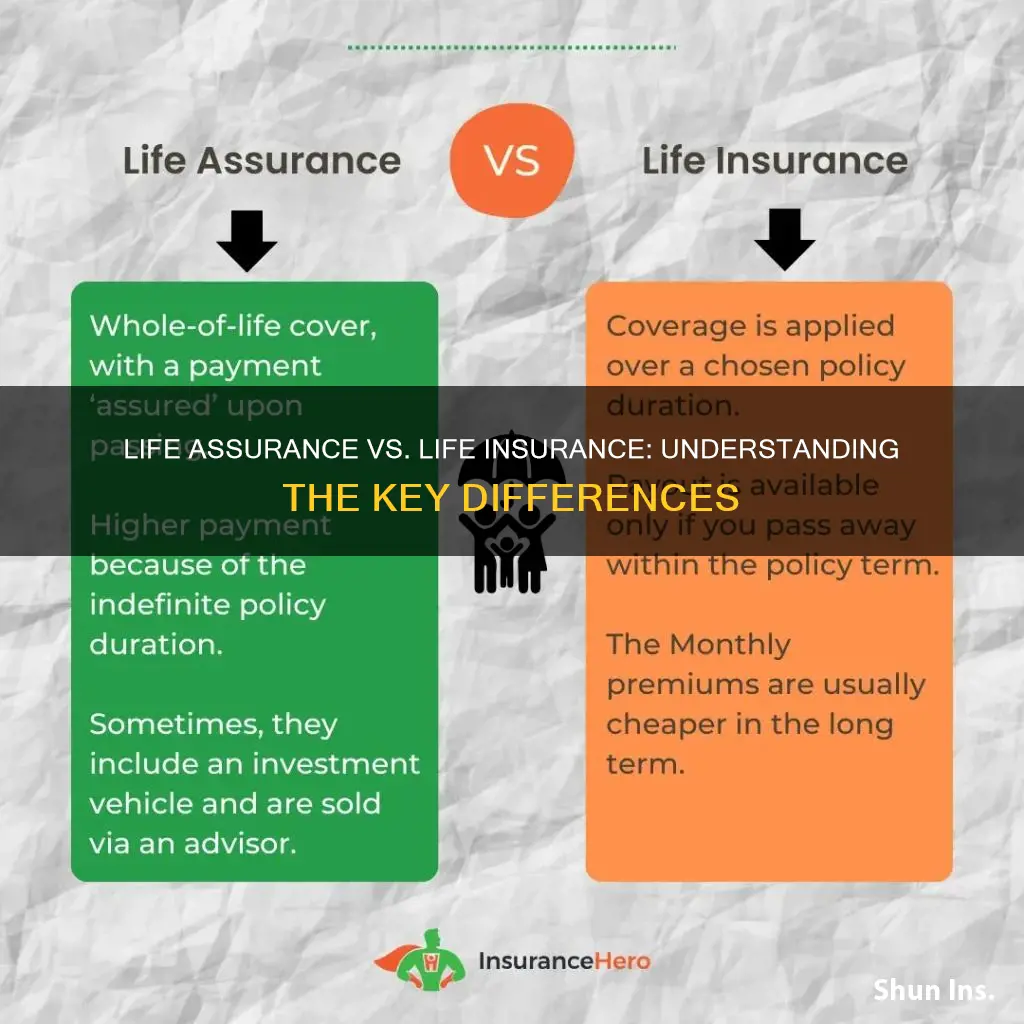
- Definition: Life assurance is a UK term for life insurance, offering financial protection against death
- Coverage: Both provide financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the insured person's death
- Regulation: UK life assurance is regulated by the FCA, while US life insurance is regulated by state insurance departments
- Taxation: In the UK, life assurance policies are often exempt from inheritance tax
- Benefits: Both offer financial security, but life insurance may have additional features like critical illness coverage

Definition: Life assurance is a UK term for life insurance, offering financial protection against death
Life assurance and life insurance are essentially the same product, but they are referred to by different names in different regions. In the United Kingdom, the term "life assurance" is commonly used to describe a financial protection policy that provides a payout to the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of their death. This payout, often referred to as a death benefit, is designed to offer financial security and peace of mind to the policyholder's family or designated recipients.
The primary purpose of life assurance is to ensure that the financial obligations and commitments of the policyholder are met, even if they are no longer around. This can include various expenses, such as mortgage payments, children's education fees, outstanding debts, or simply providing for the family's daily living expenses. By having a life assurance policy, individuals can create a safety net for their loved ones, ensuring that they are financially protected in the worst-case scenario.
When purchasing life assurance, policyholders typically select a premium amount, which is the regular payment made to the insurance company. This premium is calculated based on various factors, including the policyholder's age, health, lifestyle, and the desired death benefit amount. The insurance company then uses these premiums to fund the policy and provide the promised financial protection.
It is important to note that life assurance policies can vary in terms of coverage and flexibility. Some policies may offer a fixed death benefit, while others might provide an adjustable amount based on the policyholder's needs. Additionally, certain policies may include additional features, such as critical illness coverage or income protection, which can enhance the overall protection offered.
In summary, life assurance, as a UK term for life insurance, is a vital financial tool that provides individuals with peace of mind and financial security for their loved ones. It ensures that the policyholder's beneficiaries receive a death benefit, helping to cover essential expenses and maintain their standard of living in the event of the policyholder's passing. Understanding the concept of life assurance is crucial for anyone seeking to protect their family's financial well-being.
The Cost of Mortgage Life Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Coverage: Both provide financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the insured person's death
The primary purpose of both life assurance and life insurance is to provide financial security and support to the beneficiaries in the unfortunate event of the insured person's death. This coverage ensures that the designated individuals or entities receive a financial payout, which can help cover various expenses and provide for their future needs. Whether it's life assurance or life insurance, the core function remains the same: to offer a safety net for the loved ones left behind.
When it comes to coverage, both products are designed to pay out a lump sum or regular income to the beneficiaries upon the insured individual's passing. This financial support can be crucial for covering funeral expenses, outstanding debts, mortgage payments, or simply providing for the family's daily living costs. The amount of coverage provided can vary depending on the policyholder's preferences and needs, allowing them to choose the level of financial protection that suits their situation.
Life insurance and life assurance policies typically offer flexibility in terms of coverage options. Policyholders can select different types of policies, such as term life insurance, which provides coverage for a specified period, or permanent life insurance, which offers lifelong coverage. Additionally, riders or add-ons can be included to enhance the policy's benefits, such as critical illness coverage or accidental death benefits, further customizing the policy to meet specific requirements.
The process of obtaining coverage is generally straightforward. Policyholders work with insurance providers to determine the appropriate coverage amount, choose beneficiaries, and select the policy type that best fits their financial goals. Once the policy is in place, the insured individual pays regular premiums, and in return, the insurance company promises to provide the specified financial support to the beneficiaries when the time comes.
In summary, both life assurance and life insurance are financial products that offer coverage to provide financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the insured person's death. They offer flexibility in policy options and coverage amounts, ensuring that individuals can tailor their insurance plans to their unique needs and provide peace of mind for their loved ones.
Globe Life Insurance: Whole Life or Term?
You may want to see also

Regulation: UK life assurance is regulated by the FCA, while US life insurance is regulated by state insurance departments
The regulatory frameworks for life assurance and life insurance differ significantly between the UK and the United States, primarily due to the distinct nature of these financial products and the varying approaches to consumer protection in each country. In the UK, life assurance, often referred to as term life insurance, is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). The FCA is an independent regulatory body that oversees the financial services industry, ensuring that firms provide fair, clear, and transparent services to consumers. When it comes to life assurance, the FCA's role is to protect policyholders by setting standards for product design, marketing, and distribution. This includes ensuring that the terms and conditions of life assurance policies are clear and understandable, and that the products are suitable for the intended market.
In contrast, in the United States, life insurance is regulated by state insurance departments rather than a single federal agency. Each state has its own insurance department, which is responsible for overseeing and regulating insurance companies operating within its jurisdiction. These state departments set and enforce rules and standards for life insurance products, including underwriting guidelines, policy requirements, and consumer protection laws. This decentralized regulatory approach in the US means that the regulation of life insurance can vary from state to state, with each state having its own set of rules and guidelines.
The UK's reliance on the FCA for regulating life assurance is a result of the comprehensive and standardized approach to financial regulation. The FCA's oversight ensures that life assurance products are consistent and meet specific criteria, providing consumers with a level of protection and transparency. This regulation includes setting rules for product design, ensuring fair pricing, and maintaining the integrity of the market. In the US, the state-by-state regulation allows for more flexibility and customization in life insurance products, but it also means that consumers may encounter varying levels of protection and regulation depending on their state of residence.
Understanding these regulatory differences is crucial for consumers, especially when considering international life assurance or life insurance products. It highlights the importance of researching and comparing policies from different providers, ensuring that the chosen product complies with the relevant regulatory standards in both the UK and the US. Additionally, it underscores the need for consumers to be aware of their rights and protections under the respective regulatory bodies to make informed decisions regarding their life assurance or insurance needs.
Life Insurance Policy Loans: Understanding Collateral and Risks
You may want to see also

Taxation: In the UK, life assurance policies are often exempt from inheritance tax
In the UK, the taxation of life assurance policies is an important consideration for individuals and their estates. When it comes to inheritance tax, life assurance policies often play a significant role in estate planning. Unlike life insurance, which is designed to provide financial protection and pay out a lump sum or regular income to beneficiaries upon the insured individual's death, life assurance policies have a specific tax treatment.
Life assurance policies are typically considered an asset of the policyholder's estate. However, there are certain tax advantages associated with these policies. One key benefit is that life assurance policies are often exempt from inheritance tax (IHT) in the UK. This means that the proceeds of the policy, upon the death of the policyholder, are not subject to IHT, provided certain conditions are met. The policy must be held for at least two years, and the proceeds must be paid out to the beneficiaries. This exemption can be a valuable tool for individuals looking to pass on wealth to their loved ones without incurring significant tax liabilities.
The tax treatment of life assurance policies is distinct from that of life insurance. While life insurance is generally not exempt from IHT, life assurance policies can offer a tax-efficient way to provide financial security. This is particularly useful for those who want to ensure that their beneficiaries receive a tax-free payout, allowing them to use the funds for various purposes, such as covering funeral expenses, paying off debts, or providing financial support to family members.
It is essential for individuals to understand the implications of these tax rules when structuring their estate and making decisions about life assurance policies. By taking advantage of the IHT exemption, policyholders can ensure that their loved ones receive a tax-efficient inheritance, potentially reducing the overall tax burden on the estate. This aspect of taxation highlights the importance of careful financial planning and the potential benefits of utilizing life assurance policies as part of a comprehensive estate strategy.
Aviva Life Insurance: Adding a Beneficiary Simplified
You may want to see also

Benefits: Both offer financial security, but life insurance may have additional features like critical illness coverage
Life assurance and life insurance are two terms often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts in the financial and insurance sectors. While both provide financial protection and peace of mind, understanding the nuances between the two is essential for individuals seeking appropriate coverage.
Life assurance, also known as term life insurance, is a straightforward financial product designed to provide a lump sum payment (known as a death benefit) to the policyholder's beneficiaries upon the insured individual's death. This type of insurance is typically chosen for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for individuals who want basic financial security for their loved ones during a specific period. For instance, a 30-year term life insurance policy ensures that the beneficiaries receive the death benefit if the insured person passes away within those 30 years.
On the other hand, life insurance encompasses a broader category of financial products that offer more comprehensive coverage. It includes various types of policies, such as whole life, universal life, and variable life insurance. Life insurance policies often provide a death benefit, but they may also offer additional benefits and features. For example, whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage and accumulates cash value over time, which can be borrowed against or withdrawn. Universal life insurance offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts, allowing policyholders to adjust their coverage as their needs change.
One of the key advantages of life insurance is the potential for additional coverage. For instance, many life insurance policies include critical illness coverage, which provides a lump sum payment if the insured individual is diagnosed with a specified critical illness. This feature can be invaluable, as it offers financial protection beyond the standard death benefit, ensuring that the insured person and their family are supported during a challenging time. Critical illness coverage can help cover medical expenses, debt payments, and daily living costs, providing a safety net when health issues arise.
In summary, while both life assurance and life insurance offer financial security, life insurance often provides more comprehensive coverage and additional benefits. Understanding the differences between these two types of insurance is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions about their financial protection and ensure that their loved ones are adequately supported in the event of their passing or in the face of critical health issues.
Finding Life Insurance After a Loved One's Death
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The term "life assurance" is commonly used in the United Kingdom and some Commonwealth countries, while "life insurance" is the term used in the United States and Canada. Both terms essentially refer to the same financial product, which is a contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company. The key difference is in the terminology and the specific regulations governing these products in different regions.
Life assurance/life insurance policies offer financial protection to the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of the insured person's death. The policyholder pays regular premiums to the insurance company, and in return, the insurer promises to pay a lump sum or regular income to the designated beneficiaries when the insured individual passes away. This financial safety net can help cover various expenses, such as mortgage payments, children's education, or outstanding debts, providing peace of mind and financial security to the policyholder's loved ones.
Yes, there can be subtle differences in the way these products are regulated and sold. In some countries, "life assurance" may imply a more comprehensive approach, covering not only death but also critical illness or disability. On the other hand, "life insurance" might be used to describe policies that focus primarily on death coverage. However, these variations are often more about marketing and regional preferences rather than significant differences in the product itself.
In most cases, the term "life assurance" and "life insurance" are interchangeable, and you can typically use one to describe the other without any legal or regulatory issues. However, if you are considering purchasing a policy, it's essential to understand the specific terms and conditions offered by the insurance company in your region to ensure you are getting the coverage that best suits your needs.







