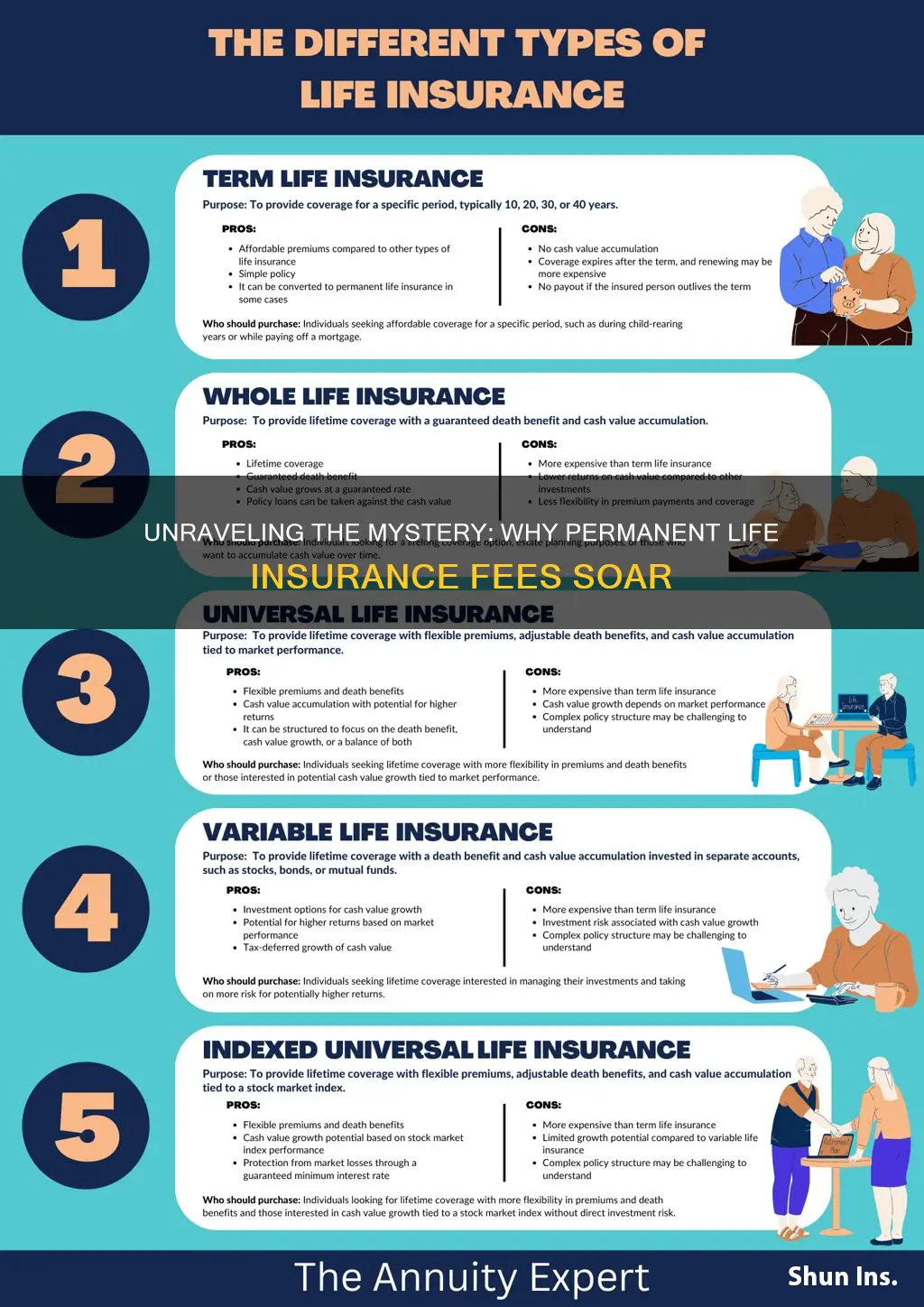
The cost of permanent life insurance can be a significant concern for many consumers, and understanding why these fees can be so high is essential for making informed financial decisions. Permanent life insurance, which provides coverage for the entire life of the insured, often comes with various fees that contribute to its overall cost. These fees may include initial premiums, policy administration charges, mortality and expense charges, and investment management fees. The high fees associated with permanent life insurance can be attributed to the comprehensive nature of the policy, which offers lifelong coverage, a cash value component, and various riders and benefits. While these features provide long-term security and flexibility, they also increase the complexity and cost of the policy, making it a more expensive option compared to term life insurance.
What You'll Learn
- Longevity Risk: High fees due to the extended coverage period and the risk of outliving the policy
- Investment Costs: Expenses associated with investment portfolios can drive up insurance prices
- Medical Underwriting: Detailed health assessments increase costs for insurers, impacting premium rates
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to strict regulations adds complexity and expense to policy administration
- Profit Margins: Insurers need to ensure profitability, which can result in higher fees for permanent life insurance

Longevity Risk: High fees due to the extended coverage period and the risk of outliving the policy
The concept of longevity risk is a significant factor that contributes to the high fees associated with permanent life insurance. This type of insurance provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured, which means the policy is in force for an extended period compared to term life insurance. The longer the coverage duration, the higher the likelihood of the insurer incurring costs over a more extended period.
As individuals live longer, the risk of the insurer having to pay out benefits for an extended duration increases. This risk is particularly relevant for permanent life insurance, as it guarantees coverage for the entire life of the insured, regardless of when the insured person passes away. The insurer must account for the possibility of paying out benefits for several decades or even centuries, which is a substantial commitment.
The extended coverage period and the associated longevity risk lead to higher fees for several reasons. Firstly, the insurer needs to factor in the potential for long-term payouts when setting premiums. They must ensure that the policy can sustain the payments over the entire coverage period, which may include a significant number of years or even generations. This long-term financial obligation requires the insurer to set aside a substantial reserve to meet future liabilities.
Secondly, the risk of outliving the policy is a critical consideration. With permanent life insurance, the insured individual's beneficiaries are guaranteed to receive the death benefit, regardless of the insured's lifespan. This guarantee increases the insurer's risk exposure, as they must prepare for the possibility of paying out benefits for an extended period, even if the insured person outlives the expected lifespan. As a result, insurers may charge higher fees to ensure they can meet these long-term obligations.
Managing longevity risk is a complex task for insurance companies. They employ various strategies to mitigate this risk, such as adjusting premium rates, implementing investment strategies, and conducting regular policy reviews. By carefully assessing the likelihood of outliving the policy and the associated costs, insurers can set appropriate fees to ensure the sustainability of the product. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals considering permanent life insurance, as it highlights the reasons behind the higher costs and allows them to make informed decisions regarding their insurance needs.
Understanding the Opposite: Permanent Life Insurance Explained
You may want to see also

Investment Costs: Expenses associated with investment portfolios can drive up insurance prices
The high fees associated with permanent life insurance policies can often be attributed to the complex and diverse investment strategies employed by insurance companies. These strategies are designed to generate returns and ensure the long-term viability of the insurance fund, which is crucial for meeting policyholder obligations. One of the primary reasons for these investment costs is the need to maintain a robust investment portfolio that can withstand market fluctuations and provide stable returns over time.
Insurance companies invest a significant portion of their funds in various assets, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. Building and managing these investment portfolios require a dedicated team of financial experts, including investment managers, analysts, and administrative staff. These professionals are responsible for researching and selecting suitable investment opportunities, monitoring market trends, and making strategic decisions to optimize returns while minimizing risks. The costs associated with hiring and retaining such talent, along with the operational expenses of managing these diverse investments, contribute to the overall expense structure.
Additionally, insurance companies often incur expenses related to the diversification of their investment portfolios. Diversification is a critical strategy to mitigate risks and ensure the stability of the investment. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, insurance companies aim to reduce the impact of any single investment's poor performance on the entire portfolio. This process involves thorough research, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring to identify and incorporate new investment opportunities that align with the company's risk tolerance and financial goals. The costs associated with this process, including research fees, transaction costs, and the time spent on due diligence, are significant and contribute to the overall expense structure.
Furthermore, the complexity of permanent life insurance policies and the associated investment strategies can lead to higher operational costs. These policies often involve various riders, benefits, and customization options, which require intricate administrative processes. Insurance companies need to allocate resources to manage these complex policies, ensuring that all contractual obligations are met and that policyholders receive the benefits they are entitled to. The additional administrative workload and the need for specialized staff to handle these complexities contribute to the overall expense, which is ultimately reflected in the policy premiums.
In summary, the high fees associated with permanent life insurance are driven by the investment costs incurred by insurance companies to maintain and grow their investment portfolios. These costs include talent acquisition and retention, operational expenses, diversification strategies, and the administrative burden of managing complex policies. Understanding these factors is essential for policyholders to make informed decisions when choosing life insurance providers and to appreciate the financial considerations that contribute to the overall cost of these policies.
Unraveling the Mystery: Employee Optional Life Insurance Explained
You may want to see also

Medical Underwriting: Detailed health assessments increase costs for insurers, impacting premium rates
The process of medical underwriting is a critical aspect of the insurance industry, especially when it comes to permanent life insurance policies. This process involves a thorough evaluation of an individual's health and medical history to determine their risk profile as an insurance candidate. While it is an essential step to ensure the financial security of both the insurer and the policyholder, it also contributes significantly to the high costs associated with permanent life insurance.
Detailed health assessments are a key component of medical underwriting. These assessments may include a comprehensive review of medical records, laboratory tests, physical examinations, and even interviews with healthcare professionals. The goal is to identify any pre-existing health conditions, lifestyle factors, or genetic predispositions that could potentially lead to future health issues. This level of scrutiny is necessary for insurers to assess the risk they are taking on by offering a life insurance policy to a particular individual.
The increased costs for insurers arise from several factors. Firstly, the more comprehensive and detailed the health assessment, the higher the administrative expenses. Insurers often employ medical professionals and underwriters who specialize in reviewing complex medical information, which requires significant time and expertise. These professionals need to carefully analyze medical records, interpret test results, and make informed decisions, all of which contribute to the overall cost.
Secondly, the identification of pre-existing health conditions or high-risk factors can lead to higher claims and payouts in the future. Insurers must consider the potential long-term impact of these factors on the insured individual's health. For example, a history of chronic diseases or a family predisposition to certain illnesses may result in more frequent or severe health events, increasing the likelihood of insurance claims. As a result, insurers may charge higher premiums to account for these potential risks.
Furthermore, the impact of detailed health assessments on premium rates is direct and significant. When an insurer conducts a thorough medical underwriting process, they can more accurately assess the risk associated with a particular policyholder. This assessment allows them to set premium rates that reflect the individual's health status and potential risks. Consequently, individuals with healthier profiles and lower risk factors may benefit from lower premium rates, while those with identified health concerns may face higher costs. This dynamic further contributes to the overall higher fees associated with permanent life insurance.
Life Insurance and THC: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to strict regulations adds complexity and expense to policy administration
The high fees associated with permanent life insurance policies can be attributed, in part, to the intricate web of regulatory compliance that surrounds this type of insurance. Insurance companies, especially those offering permanent life insurance, must navigate a complex landscape of legal and regulatory requirements to ensure they meet the standards set by financial authorities. These regulations are designed to protect policyholders and maintain the stability of the insurance market. However, they also contribute to the overall cost structure of the policies.
Regulatory compliance involves a multitude of tasks, including thorough risk assessment, detailed policy documentation, and ongoing reporting to regulatory bodies. For permanent life insurance, which provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured, the regulatory scrutiny is particularly stringent. Insurance companies must demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the policyholder's financial situation, health, and potential risks to ensure the policy's validity and the protection it offers. This process is resource-intensive and often requires a significant amount of time and expertise from the insurer's staff.
The complexity arises from the need to adhere to various regulations, such as those related to solvency, capital requirements, and consumer protection. Insurance regulators mandate that companies maintain specific levels of financial resources to meet their obligations, especially in the case of permanent life insurance, where long-term commitments are made. These capital requirements add to the operational costs, as insurance providers must invest in assets or maintain reserves to meet these standards. Moreover, the documentation and reporting processes are rigorous, requiring detailed records and frequent updates to ensure compliance.
The expense of regulatory compliance is further exacerbated by the need for ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Insurance policies, especially those with long-term commitments like permanent life insurance, are subject to changes in market conditions, interest rates, and economic trends. Regulators require insurers to regularly review and update their policies, ensuring they remain compliant and provide adequate coverage. This dynamic nature of regulation adds an extra layer of complexity and cost to policy administration.
In summary, the high fees associated with permanent life insurance are, to a significant extent, a result of the stringent regulatory environment. Adhering to these regulations is essential for maintaining the integrity of the insurance industry and protecting policyholders. However, the process is resource-intensive, requiring detailed documentation, risk assessment, and ongoing compliance measures, all of which contribute to the overall cost of providing permanent life insurance policies. Understanding and managing these regulatory requirements are critical aspects of the insurance business, influencing the pricing and administration of such policies.
Health Insurance: A Key to Longevity?
You may want to see also

Profit Margins: Insurers need to ensure profitability, which can result in higher fees for permanent life insurance
The high fees associated with permanent life insurance can often be attributed to the insurance companies' need to maintain and grow their profit margins. Insurers, like any other business, operate with the primary goal of generating a profit, and this is especially crucial for long-term, permanent life insurance policies. These policies offer a range of benefits, including lifelong coverage, cash value accumulation, and potential investment returns, which can be attractive to policyholders. However, providing such comprehensive coverage and features comes at a cost, and insurers need to ensure that these costs are covered and that they can generate a return on their investments.
Profit margins are a critical aspect of the insurance industry's financial health. Insurers must balance the premiums they charge with the expected payouts and administrative expenses. For permanent life insurance, the fees are structured to account for the extended coverage period, which can last for decades. During this time, the insurer needs to cover various expenses, including mortality costs (the cost of paying out death benefits), administrative fees, and the potential for investment returns to fund policyholder benefits. The longer the policy term, the more complex and costly it becomes for the insurer to manage, especially when considering the potential for market fluctuations and economic changes over an extended period.
Insurers often invest a portion of the premiums collected in various financial instruments to generate returns and ensure they can meet their financial obligations. This investment strategy is essential for permanent life insurance as it provides the funds needed to pay out death benefits and accumulate cash value. However, investing in financial markets carries risks, and insurers must carefully manage these risks while also ensuring they can provide stable returns to policyholders. The higher fees associated with permanent life insurance can, therefore, be seen as a reflection of the insurer's efforts to navigate these financial complexities and maintain a healthy profit margin.
Additionally, the fees may also include administrative costs related to policy management, customer service, and regulatory compliance. Permanent life insurance policies are typically more complex than term life insurance, requiring more frequent policy reviews, adjustments, and updates. These administrative tasks demand resources and expertise, contributing to the overall cost structure. Insurers need to allocate funds to maintain a robust infrastructure to support the long-term nature of these policies, which can result in higher fees for consumers.
In summary, the high fees associated with permanent life insurance are a direct result of insurers' focus on profitability and the need to manage complex financial obligations over extended periods. By ensuring healthy profit margins, insurers can sustain their operations, provide the promised benefits, and navigate the financial markets to offer competitive products. While this may lead to higher costs for policyholders, it is essential for the stability and longevity of the permanent life insurance industry.
Corporate Life Insurance: Are Proceeds Taxable?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Permanent life insurance, such as whole life or universal life, offers a range of benefits, including lifelong coverage, cash value accumulation, and investment components. However, these features come at a cost. The fees in permanent life insurance policies are primarily attributed to the comprehensive nature of the coverage and the various expenses involved in providing these benefits. These expenses include the cost of death benefits, administrative fees, investment management charges, and the profit margin for the insurance company. Additionally, the long-term commitment of permanent policies requires higher upfront costs to ensure the policyholder's needs are met throughout their lifetime.
While the fees in permanent life insurance might seem high, there are strategies to potentially reduce the overall cost. One approach is to choose a simpler policy with fewer riders or additional benefits, as these add-ons can increase the premium. Another strategy is to increase the initial premium payment, as this can sometimes result in a lower overall cost over time. Additionally, shopping around and comparing quotes from different insurance providers can help identify policies with competitive rates and better fee structures.
Yes, the fees in permanent life insurance can be viewed as an investment component, especially when considering the cash value accumulation feature. The cash value grows over time and can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing financial flexibility. While the investment aspect may not yield high returns, it offers a guaranteed growth potential and a safety net for the policyholder. The fees contribute to building this cash value, which can be a valuable asset and a source of financial security for the policyholder's beneficiaries.