Health insurance is mandatory for all residents in Germany, with two types available: statutory health insurance (SHI) and private health insurance (PHI). In 2023, SHI covered around 89% of the population, while PHI covered approximately 11%. Those who earn above a certain income threshold, are self-employed, or fall into specific occupational categories can opt for PHI.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Percentage of population covered by private insurance | 11% |
| Number of insurance companies providing private insurance | 44 |
| Number of sickness funds | 96 |
| Percentage of population covered by sickness funds | 89% |
| Minimum income threshold to be eligible for private insurance | €66,600 per year |
| Maximum income threshold to be eligible for public insurance | €66,600 per year |
| Average monthly premium for public insurance | €770 |
| Monthly income above which no increase in insurance premium | €4,987.50 |
What You'll Learn

Eligibility for private insurance
Germany's healthcare system is made up of two main components: public and private health insurance. While most of the population is covered by public insurance, some people are also eligible for private insurance. Eligibility for private insurance is based on specific criteria, and it's important to understand these requirements before making a decision. Here are the key factors that determine eligibility for private insurance in Germany:
Income Level
One of the primary factors determining eligibility for private insurance is income level. As of 2024, individuals who earn an annual income above €69,300 are eligible to opt for private health insurance. This threshold is set by the statutory health insurance system (Gesetzliche Krankenversicherung or GKV). It's important to note that this criterion applies to employed individuals, and the income threshold may vary annually.
Self-Employment
Self-employed individuals, including freelancers and business owners, can choose private health insurance regardless of their income level. However, there are exceptions to this rule for specific professions, such as artists, publicists, and farmers. If you are self-employed, you have the flexibility to select a private insurance plan that suits your needs and budget.
Civil Servants
Specific public servants, known as "Beamter," are eligible for private insurance. This group of civil servants is covered by a special health plan called "the Beihilfe," which covers 50% of most healthcare expenses. To meet the remaining 50% of their healthcare costs, civil servants often complement their coverage with private insurance.
Students
Students in certain situations may also be eligible for private insurance. For instance, students over 30 years old or those enrolled in preparatory or language courses in Germany typically cannot sign up for public insurance and, therefore, need private coverage. Additionally, international students may only be permitted to take out private insurance, depending on their circumstances.
Other Factors
There are a few other factors that may influence eligibility for private insurance in Germany. For example, specific professional groups may have access to private insurance. It's important to check with your employer or relevant authorities to understand your specific situation. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing medical conditions should be aware that private insurance companies cannot exclude them due to their health status. However, premiums may be higher to account for covering pre-existing conditions.
In conclusion, eligibility for private insurance in Germany is determined by a combination of factors, including income level, employment status, and specific circumstances such as being a student or civil servant. It's important to carefully consider your options, compare providers, and ensure you meet the eligibility criteria before making a decision about your healthcare coverage.
AARP Private Insurance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Cost of private insurance
Cost of Private Health Insurance in Germany
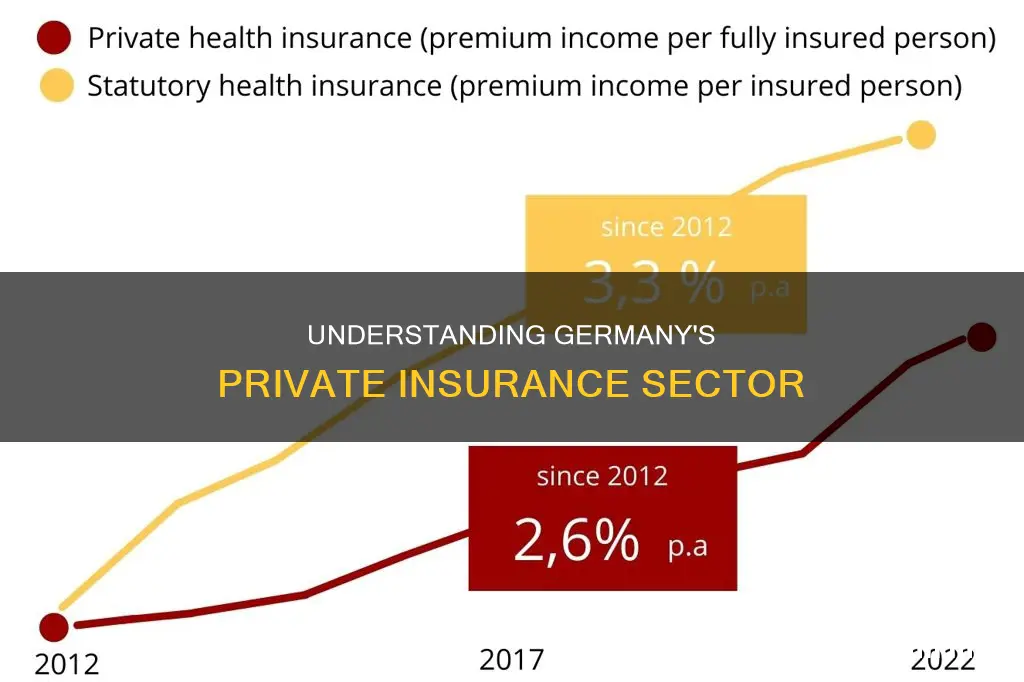
The cost of private health insurance in Germany is calculated differently from public health insurance. Private health insurance premiums are based on the level of benefits an individual wishes to include in their coverage and their current age and state of health. Private health insurance premiums are risk-based, meaning that individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or a higher likelihood of needing medical treatment will face higher premiums. The average monthly premium for men ranges from €500 to €600, while women typically pay between €600 and €700 for their private health insurance plans. Private health insurance premiums can vary from €200 to over €500 per month.
Private health insurance is designed for individuals who meet specific criteria, such as income thresholds and occupational status. Higher-income earners and self-employed individuals often opt for private health insurance as it provides greater control over their healthcare. Private health insurance offers tailored plans, granting more extensive coverage and quicker access to healthcare services.
When choosing a private health insurance provider, it is crucial to evaluate health insurance options and consider extras like nursing care coverage. It is also important to compare the cost of private health insurance by assessing factors like deductibles and co-payments. Private insurance premiums vary, typically ranging from €80 to €1,500 per month.
Private health insurance premiums are generally lower than statutory health insurance contributions for individuals who earn above the compulsory insurance threshold. However, since each insured person requires a separate contract in the private sector, private health insurance may be more expensive for families. Private health insurance is not available to everyone and is generally reserved for individuals with higher incomes or specific professions, potentially excluding some individuals from comprehensive coverage.
Hiring a Private Insurance Adjuster: When and Why You Should
You may want to see also

Pros and cons of private insurance
Pros of Private Insurance
- Better service: Private patients generally receive better service as doctors and clinics can earn more from private insurance. This means quicker appointments, treatment from the most qualified doctors, and private rooms in hospitals.
- Individual choice: You can choose additional treatment forms such as acupuncture, homeopathy, osteopathy, and Chinese medicine.
- More coverage: Many types of special treatments and services are often covered by private insurance.
- Lower costs for high-income earners: Private insurance offers a fixed monthly fee, so for those with high incomes, the costs can be lower than with public insurance.
- Lower insurance premiums: Private insurance can be cheaper, allowing you to save a lot of money (up to €3,000 per year).
- More benefits: Private insurance covers more costs than public insurance for many treatments, including non-medical practitioners.
- Individual deductible: You can select a deductible for treatment costs to reduce the premium amount.
- Sustainable contribution: The contribution is independent of your income and is not affected by demographic changes.
- Control over benefits: You can adjust your benefits and premium according to your needs.
- Guaranteed coverage: Private insurance coverage is guaranteed by contractual agreement and cannot be curtailed or changed.
Cons of Private Insurance
- Difficulty returning to public insurance: It is difficult to switch back to public insurance after choosing private insurance, and it may become impossible as you age.
- Higher costs for families: Unlike public insurance, private insurance does not automatically cover family members, and you must pay individually for your spouse and children.
- Impact on cash flow: With private insurance, you will need to pay your medical bills in advance and then wait for reimbursement from the insurance company.
- Higher costs for older people: Private insurance premiums are calculated based on age and existing illnesses, so they tend to increase as you get older.
- Limited eligibility: Only those who earn above a certain income threshold (69,300 € as of 2024), are self-employed, or are students can opt for private insurance.
Barmer Insurance: Public or Private?
You may want to see also

Public vs private insurance
Overview
In Germany, health insurance is mandatory for all residents, including foreign researchers and scientists. There are two types of health insurance: public and private. Public health insurance is known as statutory health insurance (Gesetzliche Krankenversicherung, or GKV), and private health insurance is known as private Krankenversicherung (PKV).
As of 2023, around 90% of Germany's residents are covered by public health insurance. This is partly because residents must meet certain criteria to be eligible for private insurance.
Eligibility
To be eligible for private insurance, you must meet at least one of the following criteria:
- Earn more than a predetermined amount (e.g., €66,600 or €69,300 per year, depending on the source)
- Be self-employed
- Be a university student
However, even if you meet one or more of these criteria, you are not obligated to choose private insurance. You can still opt for statutory health coverage.
Cost
The cost of health insurance in Germany can vary between €100 to €500 per month or more, depending on eligibility for private or public insurance.
For public insurance, the contribution rate is typically around 14.6% of the resident's income, with a cap on contributions for higher incomes. Private insurance premiums are risk-based and calculated based on individual circumstances, such as age, health condition, and desired coverage.
Coverage
The scope of coverage differs between public and private insurance. Public insurance covers a basic, universal standard of healthcare for all residents. Private insurance providers have greater flexibility to tailor their coverage and offer premium treatments and services.
Public insurance covers:
- In-patient (hospital) care as a ward patient
- Out-patient care from a general practitioner or medical specialist
- Statutory sick pay when the employer's duty to pay is over
- Dependents (non-working spouse, civil partner, and children up to a specified age) living at the same address as the policyholder
Private insurance often covers additional treatments and services, such as:
- Dental implants
- Glasses or contact lenses
- Private rooms in hospitals
- Acupuncture
- Homeopathy
- Osteopathy
- Chinese medicine
Other Considerations
There are several other factors to consider when choosing between public and private insurance in Germany:
- Ease of use: With public insurance, you rarely have to worry about your coverage once you're signed up. All pre-existing conditions are covered, whereas private insurance may have a price surcharge for pre-existing conditions.
- Dependents: Public insurance covers dependents for free, whereas private insurance requires separate coverage for each family member, which can be more costly.
- Cost for high-income earners: While private insurance premiums are generally cheaper for young and healthy individuals, they can be more expensive for high-income earners. Public insurance contributions are based on income and have a cap, ensuring that costs remain reasonable for high-income individuals.
- Service and treatment: Private insurance often provides better service and treatment, as doctors and clinics can earn more from private patients. This may result in immediate appointments, treatment by the most qualified doctors, and single rooms in hospitals.
- Flexibility: Private insurance allows you to adjust your benefits and premiums to meet your specific needs. You can choose a higher deductible to reduce your monthly premiums.
- Switching between systems: It is difficult to switch from private to public insurance in Germany, so it is important to carefully consider your decision.
- Paperwork and reimbursement: With private insurance, you will need to pay your medical bills in advance and then get reimbursed by your insurance company. Public insurance typically involves less paperwork and direct payment to the doctor or healthcare provider.
- Supplementary coverage: If you have public insurance but want additional coverage, you can opt for supplementary private insurance to cover treatments not included in your public plan, such as dental care or treatment in a private hospital.
Quartz Private Insurance: Is It Worth the Cost?
You may want to see also

How to obtain private insurance
Private health insurance in Germany is an option for those who are self-employed, high-income earners, or belong to specific professional groups. It offers more flexibility and access to a broader network of healthcare providers. Here are the steps to obtain private insurance:
- Check eligibility: Ensure that you meet the criteria for private health insurance, such as being self-employed, a high-income earner, or a member of specific professional groups.
- Research and compare providers: Research and compare different private health insurance providers in Germany, including well-known ones like Dr. Walter or Feather Insurance. Compare their coverage options, benefits, premiums, and additional services to find the best fit.
- Request quotes: Contact selected insurance providers to request personalized quotes. Provide information such as age, health history, desired coverage level, and other relevant details.
- Complete the application: Choose a provider and complete their application form. Submit the required documentation, such as identification and proof of income.
- Undergo a health assessment: Private insurers may require a health assessment, which can involve a medical questionnaire or examination, to assess any pre-existing conditions and risks.
- Policy approval and commencement: If your application is approved, carefully review the issued policy, which will detail your coverage, premium, and additional terms and conditions.
- Cancel previous insurance (if applicable): If you had statutory health insurance, inform your previous provider and comply with any cancellation requirements.
It is important to note that private health insurance premiums are generally higher than statutory health insurance contributions, and coverage for pre-existing conditions may vary. Therefore, it is crucial to explore different providers and compare their offerings to make an informed decision.
Haven's Private Hire Insurance: Stratford-specific Coverage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Around 11% of the German population is covered by private health insurance.
Private health insurance is available to those who earn above a certain income threshold, are self-employed, or are students.
Private health insurance premiums vary depending on age, health condition, and desired coverage. They can range from €200 to over €500 per month.
Private health insurance offers more choice and flexibility than public health insurance. It covers alternative/natural remedies, provides higher reimbursements for dental work, and reimburses vision products. It also allows for a choice of doctors and hospitals worldwide.
Yes, private health insurance premiums must be paid even if you are ill or not working. There may also be limits on dental reimbursements in the first years, and co-insurance payments may be required. Switching between public and private health insurance should be carefully considered as it is not a decision that can be made lightly.